C++11中头文件chrono的使用
在C++11中,<chrono>是标准模板库中与时间有关的头文件。该头文件中所有函数与类模板均定义在std::chrono命名空间中。
std::chrono是在C++11中引入的,是一个模板库,用来处理时间和日期的Time library。要使用chrono库,需要include<chrono>,其所有实现均在chrono命名空间下。
std::chrono::duration:记录时间长度的,表示一段时间,如1分钟、2小时、10毫秒等。表示为类模板duration的对象,用一个count representation与一个period precision表示。例如,10毫秒的10为count representation,毫秒为period precision。
template<class Rep, class Period = ratio<1> > class duration;第一个模板参数为表示时间计数的数据类型。成员函数count返回该计数。第二个模板参数表示计数的一个周期,一般是std::ratio类型,表示一个周期(即一个时间嘀嗒tick)是秒钟的倍数或分数,在编译时应为一个有理数常量。
std::chrono::time_point:记录时间点的,表示一个具体时间。例如某人的生日、今天的日出时间等。表示为类模板time_point的对象。用相对于一个固定时间点epoch的duration来表示。
std::chrono::clocks:时间点相对于真实物理时间的框架。至少提供了3个clock:
(1)、system_clock:当前系统范围(即对各进程都一致)的一个实时的日历时钟(wallclock)。
(2)、steady_clock:当前系统实现的一个维定时钟,该时钟的每个时间嘀嗒单位是均匀的(即长度相等)。
(3)、high_resolution_clock:当前系统实现的一个高分辨率时钟。
chrono is the name of a header, but also of a sub-namespace: All the elements in this header(except for the common_type specializations) are not defined directly under the std namespace (like most of the standard library) but under the std::chrono namespace.
The elements in this header deal with time. This is done mainly by means of three concepts:
(1)、Durations: They measure time spans, like: one minute, two hours, or ten milliseconds. In this library, they are represented with objects of the duration class template, that couples a count representation and a period precision (e.g., ten milliseconds has ten as count representation and milliseconds as period precision).
(2)、Time points:A reference to a specific point in time, like one's birthday, today's dawn, or when the next train passes. In this library, objects of the time_point class template express this by using a duration relative to an epoch (which is a fixed point in time common to all time_point objects using the same clock).
(3)、Clocks: A framework that relates a time point to real physical time. The library provides at least three clocks that provide means to express the current time as a time_point: system_clock, steady_clock and high_resolution_clock.
std::chrono::duration:A duration object expresses a time span by means of a count and a period.
std::chrono::duration_values:This is a traits class to provide the limits and zero value of the type used to represent the count in a duration object.
std::chrono::high_resolution_clock:The members of clock classes provide access to the current time_point.high_resolution_clock is the clock with the shortest tick period. It may be a synonym for system_clock or steady_clock.
std::chrono::steady_clock/std::chrono::system_clock:Clock classes provide access to the current time_point. system_clock is a system-wide realtime clock. steady_clock is specifically designed to calculate time intervals.
std::chrono::time_point:A time_point object expresses a point in time relative to a clock's epoch.
下面是从其他文章中copy的<chrono>测试代码,详细内容介绍可以参考对应的reference:
#include "chrono.hpp"
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <ratio>
#include <ctime>
#include <iomanip>///
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/chrono/duration/
int test_chrono_duration()
{
{ // duration::duration: Constructs a duration object// chrono::duration_cast: Converts the value of dtn into some other duration type,// taking into account differences in their periodstypedef std::chrono::duration<int> seconds_type;typedef std::chrono::duration<int, std::milli> milliseconds_type;typedef std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<60 * 60>> hours_type;hours_type h_oneday(24); // 24hseconds_type s_oneday(60 * 60 * 24); // 86400smilliseconds_type ms_oneday(s_oneday); // 86400000msseconds_type s_onehour(60 * 60); // 3600s//hours_type h_onehour (s_onehour); // NOT VALID (type truncates), use:hours_type h_onehour(std::chrono::duration_cast<hours_type>(s_onehour));milliseconds_type ms_onehour(s_onehour); // 3600000ms (ok, no type truncation)std::cout << ms_onehour.count() << "ms in 1h" << std::endl;
}{ // duration operators: +、-、*、/、>、<、!=、and so onstd::chrono::duration<int> foo;std::chrono::duration<int> bar(10);// counts: foo bar// --- ---foo = bar; // 10 10foo = foo + bar; // 20 10++foo; // 21 10--bar; // 21 9foo *= 2; // 42 9foo /= 3; // 14 9//bar += (foo % bar); // 14 14std::cout << std::boolalpha;std::cout << "foo==bar: " << (foo == bar) << std::endl;std::cout << "foo: " << foo.count() << std::endl;std::cout << "bar: " << bar.count() << std::endl;
}{ // duration::count: Returns the internal count (i.e., the representation value) of the duration object.using namespace std::chrono;// std::chrono::milliseconds is an instatiation of std::chrono::duration:milliseconds foo(1000); // 1 secondfoo *= 60;std::cout << "duration (in periods): ";std::cout << foo.count() << " milliseconds.\n";std::cout << "duration (in seconds): ";std::cout << foo.count() * milliseconds::period::num / milliseconds::period::den;std::cout << " seconds.\n";
}{ // duration::max: Returns the maximum value of duration// duration::min: Returns the minimum value of durationstd::cout << "system_clock durations can represent:\n";std::cout << "min: " << std::chrono::system_clock::duration::min().count() << "\n";std::cout << "max: " << std::chrono::system_clock::duration::max().count() << "\n";
}{ // duration::zero: Returns a duration value of zerousing std::chrono::steady_clock;steady_clock::time_point t1 = steady_clock::now();std::cout << "Printing out something...\n";steady_clock::time_point t2 = steady_clock::now();steady_clock::duration d = t2 - t1;if (d == steady_clock::duration::zero())std::cout << "The internal clock did not tick.\n";elsestd::cout << "The internal clock advanced " << d.count() << " periods.\n";
}{ // chrono::time_point_cast: Converts the value of tp into a time_point type with a different duration internal object,// taking into account differences in their durations's periods.using namespace std::chrono;typedef duration<int, std::ratio<60 * 60 * 24>> days_type;time_point<system_clock, days_type> today = time_point_cast<days_type>(system_clock::now());std::cout << today.time_since_epoch().count() << " days since epoch" << std::endl;
}return 0;
}//
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/chrono/high_resolution_clock/
int test_chrono_high_resolution_clock()
{// high_resolution_clock::now: Returns the current time_point in the frame of the high_resolution_clockusing namespace std::chrono;high_resolution_clock::time_point t1 = high_resolution_clock::now();std::cout << "printing out 1000 stars...\n";for (int i = 0; i<1000; ++i) std::cout << "*";std::cout << std::endl;high_resolution_clock::time_point t2 = high_resolution_clock::now();duration<double> time_span = duration_cast<duration<double>>(t2 - t1);std::cout << "It took me " << time_span.count() << " seconds.";std::cout << std::endl;return 0;
}///
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/chrono/steady_clock/
int test_chrono_steady_clock()
{// steady_clock is specifically designed to calculate time intervals.// steady_clock::now: Returns the current time_point in the frame of the steady_clock.using namespace std::chrono;steady_clock::time_point t1 = steady_clock::now();std::cout << "printing out 1000 stars...\n";for (int i = 0; i<1000; ++i) std::cout << "*";std::cout << std::endl;steady_clock::time_point t2 = steady_clock::now();duration<double> time_span = duration_cast<duration<double>>(t2 - t1);std::cout << "It took me " << time_span.count() << " seconds.";std::cout << std::endl;return 0;
}//
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/chrono/system_clock/
int test_chrono_system_clock()
{// system_clock is a system-wide realtime clock.{ // system_clock::from_time_t: Converts t into its equivalent of member type time_point.using namespace std::chrono;// create tm with 1/1/2000:std::tm timeinfo = std::tm();timeinfo.tm_year = 100; // year: 2000timeinfo.tm_mon = 0; // month: januarytimeinfo.tm_mday = 1; // day: 1ststd::time_t tt = std::mktime(&timeinfo);system_clock::time_point tp = system_clock::from_time_t(tt);system_clock::duration d = system_clock::now() - tp;// convert to number of days:typedef duration<int, std::ratio<60 * 60 * 24>> days_type;days_type ndays = duration_cast<days_type> (d);// display result:std::cout << ndays.count() << " days have passed since 1/1/2000";std::cout << std::endl;
}{ // system_clock::now: Returns the current time_point in the frame of the system_clockusing namespace std::chrono;duration<int, std::ratio<60 * 60 * 24> > one_day(1);system_clock::time_point today = system_clock::now();system_clock::time_point tomorrow = today + one_day;time_t tt;tt = system_clock::to_time_t(today);std::cout << "today is: " << ctime(&tt);tt = system_clock::to_time_t(tomorrow);std::cout << "tomorrow will be: " << ctime(&tt);
}{ // system_clock::to_time_t: Converts tp into its equivalent of type time_t.using namespace std::chrono;duration<int, std::ratio<60 * 60 * 24> > one_day(1);system_clock::time_point today = system_clock::now();system_clock::time_point tomorrow = today + one_day;time_t tt;tt = system_clock::to_time_t(today);std::cout << "today is: " << ctime(&tt);tt = system_clock::to_time_t(tomorrow);std::cout << "tomorrow will be: " << ctime(&tt);
}return 0;
}//
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/chrono/time_point/
int test_chrono_time_point()
{
{ // time_point operators: +、-、==、!=using namespace std::chrono;system_clock::time_point tp, tp2; // epoch valuesystem_clock::duration dtn(duration<int>(1)); // 1 second// tp tp2 dtn// --- --- ---tp += dtn; // e+1s e 1stp2 -= dtn; // e+1s e-1s 1stp2 = tp + dtn; // e+1s e+2s 1stp = dtn + tp2; // e+3s e+2s 1stp2 = tp2 - dtn; // e+3s e+1s 1sdtn = tp - tp2; // e+3s e+1s 2sstd::cout << std::boolalpha;std::cout << "tp == tp2: " << (tp == tp2) << std::endl;std::cout << "tp > tp2: " << (tp>tp2) << std::endl;std::cout << "dtn: " << dtn.count() << std::endl;
}{ // time_point::time_point: Constructs a time_point objectusing namespace std::chrono;system_clock::time_point tp_epoch; // epoch valuetime_point <system_clock, duration<int>> tp_seconds(duration<int>(1));system_clock::time_point tp(tp_seconds);std::cout << "1 second since system_clock epoch = ";std::cout << tp.time_since_epoch().count();std::cout << " system_clock periods." << std::endl;// display time_point:std::time_t tt = system_clock::to_time_t(tp);std::cout << "time_point tp is: " << ctime(&tt);
}{ // time_point::time_since_epoch: Returns a duration object with the time span value between the epoch and the time pointusing namespace std::chrono;system_clock::time_point tp = system_clock::now();system_clock::duration dtn = tp.time_since_epoch();std::cout << "current time since epoch, expressed in:" << std::endl;std::cout << "periods: " << dtn.count() << std::endl;std::cout << "seconds: " << dtn.count() * system_clock::period::num / system_clock::period::den;std::cout << std::endl;
}return 0;
}///
// reference: https://zh.wikibooks.org/wiki/C%2B%2B/STL/Chrono
static long fibonacci(unsigned n)
{if (n < 2) return n;return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
}int test_chrono_1()
{
{ // std::chrono::time_pointstd::chrono::system_clock::time_point now = std::chrono::system_clock::now();std::time_t now_c = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(now - std::chrono::hours(24));std::cout << "24 hours ago, the time was " << now_c << '\n';std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point start = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();std::cout << "Hello World\n";std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point end = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();std::cout << "Printing took "<< std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(end - start).count() << "us.\n";
}{ // std::chrono::durationusing shakes = std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<1, 100000000>>;using jiffies = std::chrono::duration<int, std::centi>;using microfortnights = std::chrono::duration<float, std::ratio<12096, 10000>>;using nanocenturies = std::chrono::duration<float, std::ratio<3155, 1000>>;std::chrono::seconds sec(1);std::cout << "1 second is:\n";std::cout << std::chrono::duration_cast<shakes>(sec).count() << " shakes\n";std::cout << std::chrono::duration_cast<jiffies>(sec).count() << " jiffies\n";std::cout << microfortnights(sec).count() << " microfortnights\n";std::cout << nanocenturies(sec).count() << " nanocenturies\n";
}{ // std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock> start, end;start = std::chrono::system_clock::now();std::cout << "f(42) = " << fibonacci(42) << '\n';end = std::chrono::system_clock::now();std::chrono::duration<double> elapsed_seconds = end - start;std::time_t end_time = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(end);std::cout << "finished computation at " << std::ctime(&end_time)<< "elapsed time: " << elapsed_seconds.count() << "s\n";
}return 0;
}
GitHub:https://github.com/fengbingchun/Messy_Test
相关文章:
为什么平头哥做芯片如此迅猛?
作者 | 胡巍巍 发自杭州云栖大会责编 | 唐小引来源 | CSDN(ID:CSDNnews)2018年10月31日,阿里旗下的平头哥半导体有限公司成立。如今,平头哥成立不到一年,就已成绩斐然。2019年9月25日,阿里巴巴旗…

Vue 组件库 heyui@1.18.0 发布,新增地址选择、图片预览组件
开发四年只会写业务代码,分布式高并发都不会还做程序员? 新增 CategoryPicker 新增组件 CategoryPicker,地址级联组件的最佳方案。 <CategoryPicker :option"option" v-model"value"/> 相关文档 ImagePreview 新…

HTML5 Dashboard – 那些让你激动的 Web 技术
HTML5 Dashboard 是一个 Mozilla 推出的项目,里面展示了最前沿的 HTML5,CSS3,JavaScript 技术。每一项技术都有简洁,在线演示以及详细的文档链接。这些技术将成为未来一段时间 Web 开发的顶尖技术,如果不想落伍的话就赶…

计算机解决问题没有奇技淫巧,但动态规划还是有点套路
作者 | labuladong来源 | labuladong(ID:labuladong) 【导读】动态规划算法似乎是一种很高深莫测的算法,你会在一些面试或算法书籍的高级技巧部分看到相关内容,什么状态转移方程,重叠子问题,最优子结构等高…

idea下,Jetty采用main方法启动web项目
为什么80%的码农都做不了架构师?>>> 对于maven多模块的spring web项目,本地开发时,启动的方式一般有如下几种: 使用容器(tomcat/jetty/resin等),该方式需要ide支持,而社…
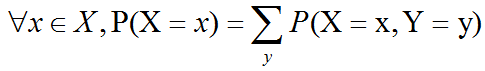
概率论中均值、方差、标准差介绍及C++/OpenCV/Eigen的三种实现
概率论是用于表示不确定性声明(statement)的数学框架。它不仅提供了量化不确定性的方法,也提供了用于导出新的不确定性声明的公理。在人工智能领域,概率论主要有两种用途。首先,概率法则告诉我们AI系统如何推理,据此我们设计一些算…

[转]CentOS 5.5下FTP安装及配置
一、FTP的安装 1、检测是否安装了FTP : [rootlocalhost ~]# rpm -q vsftpd vsftpd-2.0.5-16.el5_5.1 否则显示:[rootlocalhost ~]# package vsftpd is not installed 查看ftp运行状态 service vsftpd status 2、如果没安装FTP,运行yum install vsftpd命令进行安装 如…

C++11中头文件thread的使用
C11中加入了<thread>头文件,此头文件主要声明了std::thread线程类。C11的标准类std::thread对线程进行了封装。std::thread代表了一个线程对象。应用C11中的std::thread便于多线程程序的移值。 <thread>是C标准程序库中的一个头文件,定义了…

python3 urllib 类
urllib模块中的方法 1.urllib.urlopen(url[,data[,proxies]]) 打开一个url的方法,返回一个文件对象,然后可以进行类似文件对象的操作。本例试着打开google >>> import urllib >>> f urllib.urlopen(http://www.google.com.hk/) >&…
阿里飞天大数据飞天AI平台“双生”系统正式发布,9大全新数据产品集中亮相
作者 | 夕颜 责编 | 唐小引 出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100) 如今,大数据和 AI 已经成为两个分不开的词汇,没有大数据,AI 就失去了根基;没有 AI,数据不会呈现爆发式的增长。如何将 AI 与大…

关于JavaScript的闭包(closure)
(转载自阮一峰博客) 闭包(closure)是Javascript语言的一个难点,也是它的特色,更是函数式编程的重要思想之一,很多高级应用都要依靠闭包实现。 下面就是我的学习笔记,对于Javascript初…
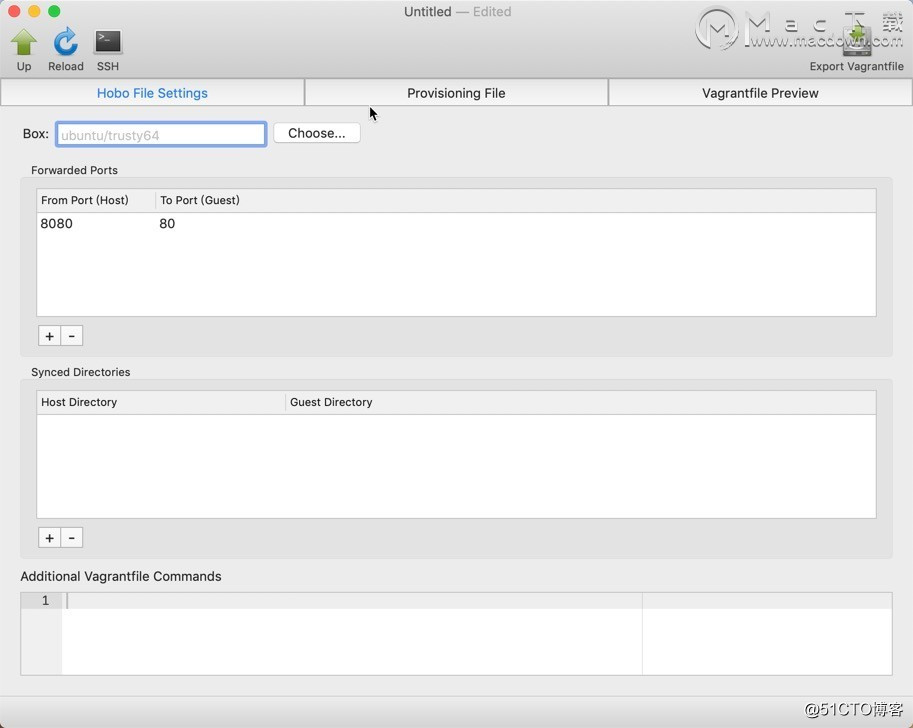
Vagrant控制管理器——“Hobo”
Hobo是控制Vagrant盒子和在Mac上编辑Vagrantfiles的最佳和最简单的方法。您可以快速启动,停止和重新加载您的Vagrant机器。您可以从头开始轻松创建新的Vagrantfile。点击进入,尽享Hobo for Mac全部功能! Hobo做什么? 启动…

微众银行AI团队开源联邦学习框架,并发布《联邦学习白皮书1.0》
(图片由AI科技大本营付费下载自视觉中国)编辑 | Jane来源 | 《联邦学习白皮书1.0》出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)【导语】2019年,联邦学习成为业界技术研究与应用的焦点。近日,微众银行 AI 项目组编制…

C++11中头文件atomic的使用
原子库为细粒度的原子操作提供组件,允许无锁并发编程。涉及同一对象的每个原子操作,相对于任何其他原子操作是不可分的。原子对象不具有数据竞争(data race)。原子类型对象的主要特点就是从不同线程访问不会导致数据竞争。因此从不同线程访问某个原子对象…

Oracle回收站
回收站是删除对象使用的存储空间。可以使用实例参数recyclebin禁用回收站,默认是on,可以为某个会话或系统设置为off或on。所有模式都有一个回收站。 当表空间不足时可以自动重用回收站对象占用的表空间(此后不可能恢复对象)&#…
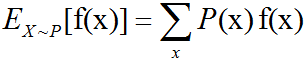
协方差矩阵介绍及C++/OpenCV/Eigen的三种实现
函数f(x)关于某分布P(x)的期望(expectation)或者期望值(expected value)是指,当x由P产生,f作用于x时,f(x)的平均值。对于离散型随机变量,这可以通过求和得到:对于连续型随机变量可以通过求积分得到:当概率分…
10分钟搭建你的第一个图像识别模型 | 附完整代码
(图片由AI科技大本营付费下载自视觉中国)作者 | Pulkit Sharma译者 | 王威力来源 | 数据派THU(ID:DatapiTHU)【导读】本文介绍了图像识别的深度学习模型的建立过程,通过陈述实际比赛的问题、介绍模型框架和…

Rancher 2.2.2 发布,优化 Kubernetes 集群运维
开发四年只会写业务代码,分布式高并发都不会还做程序员? >>> Rancher 2.2.2 发布了。Rancher 是一个开源的企业级 Kubernetes 平台,可以管理所有云上、所有发行版、所有 Kubernetes集群,解决了生产环境中企业用户可能面…

EXP/EXPDP, IMP/IMPDP应用
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> EXP/EXPDP, IMP/IMPDP应用 exp name/pwddbname filefilename.dmp tablestablename rowsy indexesn triggersn grantsn $ sqlplus username/passwordhostname:port/SERVICENAME OR $ sqlplus username Enter password:…

微软语音AI技术与微软听听文档小程序实践 | AI ProCon 2019
演讲嘉宾 | 赵晟、张鹏整理 | 伍杏玲来源 | CSDN(ID:CSDNnews)【导语】9 月 7 日,在CSDN主办的「AI ProCon 2019」上,微软(亚洲)互联网工程院人工智能语音团队首席研发总监赵晟、微软࿰…

C++11中std::condition_variable的使用
<condition_variable>是C标准程序库中的一个头文件,定义了C11标准中的一些用于并发编程时表示条件变量的类与方法等。条件变量是并发程序设计中的一种控制结构。多个线程访问一个共享资源(或称临界区)时,不但需要用互斥锁实现独享访问以避免并发错…

docker基础文档(链接,下载,安装)
一、docker相关链接1.docker中国区官网(包含部分中文文档,下载安装包,镜像加速器):https://www.docker-cn.com/2.docker官方镜像仓库:https://cloud.docker.com/3.docker下载:https://www.docker-cn.com/community-edi…

一个JS对话框,可以显示其它页面,
还不能自适应大小 garyBox.js // JavaScript Document// gary 2014-3-27// 加了 px 在google浏览器没加这个发现设置width 和height没有用 //gary 2014-3-27 //实在不会用那些JS框架,自己弄个,我只是想要个可以加载其它页面的对话框而以,这里用了别人的…

只需4秒,这个算法就能鉴别你的LV是真是假
(图片付费下载自视觉中国)导语:假冒奢侈品制造这个屡禁不止的灰色产业,每年给正品商家和消费者造成上千亿的损失,对企业和消费者造成伤害。作为全球奢侈品巨头,LVMH 对假冒奢侈品的打击十分重视。LVMH 其旗…
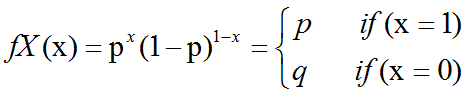
概率论中伯努利分布(bernoulli distribution)介绍及C++11中std::bernoulli_distribution的使用
Bernoulli分布(Bernoulli distribution):是单个二值随机变量的分布。它由单个参数∈[0,1],给出了随机变量等于1的概率。它具有如下的一些性质:P(x1) P(x0)1-P(xx) x(1-)1-xEx[x] Varx(x) (1-)伯努力分布(Bernoulli distribution,又…

关于View测量中的onMeasure函数
在自定义View中我们通常会重写onMeasure,下面来说说这个onMeasure有什么作用 onMeasure主要用于对于View绘制时进行测量 Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);…

zabbix二次开发之从mysql取值在运维平台js图表展现
前沿:集群控制平台已经要慢慢的灰度上线了,出问题的时候,才找点bug,时间有点空闲。正好看了下zabbix的数据库,产生了自己想做一套能更好的展现zabbix的页面。更多内容请到我的个人的博客站点,blog.xiaorui.…
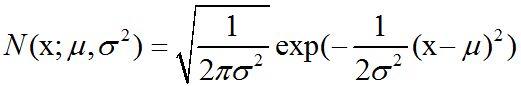
概率论中高斯分布(正态分布)介绍及C++11中std::normal_distribution的使用
高斯分布:最常用的分布是正态分布(normal distribution),也称为高斯分布(Gaussian distribution):正态分布N(x;μ,σ2)呈现经典的”钟形曲线”的形状,其中中心峰的x坐标由μ给出,峰的宽度受σ控制。正态分布由两个参数…

AI落地遭“卡脖子”困境:为什么说联邦学习是解决良方?
作者 | Just出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)毋庸置疑,在业界对人工智能(AI)应用落地备受期待的时期,数据这一重要支点却越来越成为一个“卡脖子”的难题。AI落地需要数据来优化模型效果,但大…

Linux下截取指定时间段日志并输出到指定文件
sed -n /2019-04-22 16:10:/,/2019-04-22 16:20:/p log.log > bbb.txt 转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/mrwuzs/p/10752037.html
