C++11中头文件atomic的使用
原子库为细粒度的原子操作提供组件,允许无锁并发编程。涉及同一对象的每个原子操作,相对于任何其他原子操作是不可分的。原子对象不具有数据竞争(data race)。原子类型对象的主要特点就是从不同线程访问不会导致数据竞争。因此从不同线程访问某个原子对象是良性(well-defined)行为,而通常对于非原子类型而言,并发访问某个对象(如果不做任何同步操作)会导致未定义(undifined)行为发生。
atomic是C++标准程序库中的一个头文件,定义了C++11标准中的一些表示线程、并发控制时原子操作的类与方法等。此头文件主要声明了两大类原子对象:std::atomic和std::atomic_flag,另外还声明了一套C风格的原子类型和与C兼容的原子操作的函数。在多线程并发执行时,原子操作是线程不会被打断的执行片段。一些程序设计更为注重性能和效率,需要开发lock-free的算法和数据结构,这就需要更为底层的原子操作与原子类型。原子类型对象的主要特点就是从不同线程并发访问是良性(well-defined)行为,不会导致竞争危害。与之相反,不做适当控制就并发访问非原子对象则会导致未定义(undifined)行为。
atomic_flag类:是一种简单的原子布尔类型,只支持两种操作:test_and_set(flag=true)和clear(flag=false)。跟std::atomic的其它所有特化类不同,它是锁无关的。结合std::atomic_flag::test_and_set()和std::atomic_flag::clear(),std::atomic_flag对象可以当作一个简单的自旋锁(spin lock)使用。atomic_flag只有默认构造函数,禁用拷贝构造函数,移动构造函数实际上也禁用。如果在初始化时没有明确使用宏ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT初始化,那么新创建的std::atomic_flag对象的状态是未指定的(unspecified),既没有被set也没有被clear;如果使用该宏初始化,该std::atomic_flag对象在创建时处于clear状态。
(1)、test_and_set:返回该std::atomic_flag对象当前状态,检查flag是否被设置,若被设置直接返回true,若没有设置则设置flag为true后再返回false。该函数是原子的。
(2)、clear:清除std::atomic_flag对象的标志位,即设置atomic_flag的值为false。
std::atomic类模板:std::atomic比std::atomic_flag功能更加完善。C++11标准库std::atomic提供了针对bool类型、整形(integral)和指针类型的特化实现。每个std::atomic模板的实例化和完全特化定义一个原子类型。若一个线程写入原子对象,同时另一个线程从它读取,则行为良好定义。而且,对原子对象的访问可以按std::memory_order所指定建立线程间同步,并排序非原子的内存访问。std::atomic可以以任何可平凡复制(Trivially Copyable)的类型T实例化。std::atomic既不可复制亦不可移动。
除了std::atomic和std::atomic_flag外,<atomic>还包括了基于std::atomic_flag类的C风格API和基于std::atomic类模板的C风格API。
与原子对象初始化相关的两个宏:
(1)、ATOMIC_VAR_INIT(val):初始化std::atomic对象。This macro expands to a token sequence suitable to initialize an atomic object (of static storage duration) with a value of val. This macro exists for compatibility with C implementations, in which it is used as a constructor-like function for(default-constructed) atomic objects; In C++, this initialization may be performed directly by the initialization constructor.
(2)、ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT:初始化std::atomic_flag对象。This macro is defined in such a way that it can be used to initialize an object of type atomic_flag to the clear state.
std::atomic:Objects of atomic types contain a value of a particular type (T). The main characteristic of atomic objects is that access to this contained value from different threads cannot cause data races (i.e., doing that is well-defined behavior, with accesses properly sequenced). Generally, for all other objects, the possibility of causing a data race for accessing the same object concurrently qualifies the operation as undefined behavior. Additionally, atomic objects have the ability to synchronize access to other non-atomic objects in their threads by specifying different memory orders.
std::atomic_flag:Atomic flags are boolean atomic objects that support two operations:test-and-set and clear.
下面是从其他文章中copy的<atomic>测试代码,详细内容介绍可以参考对应的reference:
#include "atomic.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <atomic>
#include <vector>
#include <thread>
#include <sstream>namespace atomic {
/
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/atomic/atomic/atomic/
std::atomic<bool> ready(false);
// atomic_flag::atomic_flag: Constructs an atomic_flag object
// The atomic_flag is in an unspecified state on construction (either set or clear),
// unless it is explicitly initialized to ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT.
std::atomic_flag winner = ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT;void count1m(int id)
{while (!ready) { std::this_thread::yield(); } // wait for the ready signalfor (volatile int i = 0; i < 1000000; ++i) {} // go!, count to 1 millionif (!winner.test_and_set()) { std::cout << "thread #" << id << " won!\n"; }
};int test_atomic_atomic()
{// atomic::atomic: Constructs an atomic objectstd::vector<std::thread> threads;std::cout << "spawning 10 threads that count to 1 million...\n";for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i) threads.push_back(std::thread(count1m, i));ready = true;for (auto& th : threads) th.join();return 0;
}/
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/atomic/atomic/compare_exchange_weak/
// a simple global linked list:
struct Node { int value; Node* next; };
std::atomic<Node*> list_head(nullptr);void append(int val)
{ // append an element to the listNode* oldHead = list_head;Node* newNode = new Node{ val, oldHead };// what follows is equivalent to: list_head = newNode, but in a thread-safe way:while (!list_head.compare_exchange_weak(oldHead, newNode))newNode->next = oldHead;
}int test_atomic_compare_exchange_weak()
{// atomic::compare_exchange_weak: Compares the contents of the atomic object's contained value with expected:// -if true, it replaces the contained value with val(like store).// - if false, it replaces expected with the contained value// spawn 10 threads to fill the linked list:std::vector<std::thread> threads;for (int i = 0; i<10; ++i) threads.push_back(std::thread(append, i));for (auto& th : threads) th.join();// print contents:for (Node* it = list_head; it != nullptr; it = it->next)std::cout << ' ' << it->value;std::cout << '\n';// cleanup:Node* it; while (it = list_head) { list_head = it->next; delete it; }return 0;
}///
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/atomic/atomic/exchange/
std::atomic<bool> winner_(false);void count1m_(int id)
{while (!ready) {} // wait for the ready signalfor (int i = 0; i<1000000; ++i) {} // go!, count to 1 millionif (!winner_.exchange(true)) { std::cout << "thread #" << id << " won!\n"; }
};int test_atomic_exchange()
{// atomic::exchange: Replaces the contained value by val and returns the value it had immediately beforestd::vector<std::thread> threads;std::cout << "spawning 10 threads that count to 1 million...\n";for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i) threads.push_back(std::thread(count1m_, i));ready = true;for (auto& th : threads) th.join();return 0;
}/
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/atomic/atomic/load/
std::atomic<int> foo(0);void set_foo(int x)
{foo.store(x, std::memory_order_relaxed); // set value atomically
}void print_foo()
{int x;do {x = foo.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); // get value atomically} while (x == 0);std::cout << "foo: " << x << '\n';
}int test_atomic_load()
{// atomic::load: Returns the contained value.// The operation is atomic and follows the memory ordering specified by sync.std::thread first(print_foo);std::thread second(set_foo, 10);first.join();second.join();return 0;
}// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/atomic/atomic/operator=/
std::atomic<int> foo_ = 0;void set_foo_(int x)
{foo_ = x;
}void print_foo_()
{while (foo_ == 0) { // wait while foo_=0std::this_thread::yield();}std::cout << "foo_: " << foo_ << '\n';
}int test_atomic_operator()
{// atomic::operator=: Replaces the stored value by val.// This operation is atomic and uses sequential consistency (memory_order_seq_cst).// To modify the value with a different memory orderingstd::thread first(print_foo_);std::thread second(set_foo_, 10);first.join();second.join();return 0;
}///
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/atomic/atomic/store/
int test_atomic_store()
{// atomic::store: Replaces the contained value with val.// The operation is atomic and follows the memory ordering specified by sync.std::thread first(print_foo);std::thread second(set_foo, 10);first.join();second.join();return 0;
}/
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/atomic/atomic_flag/clear/
std::atomic_flag lock_stream = ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT;
std::stringstream stream;void append_number(int x)
{while (lock_stream.test_and_set()) {}stream << "thread #" << x << '\n';lock_stream.clear();
}int test_atomic_flag_atomic_clear()
{// atomic_flag::clear: Clears the atomic_flag (i.e., sets it to false)//Clearing the atomic_flag makes the next call to member atomic_flag::test_and_set on this object return false.// The operation is atomic and follows the memory ordering specified by sync.// atomic_flag::test_and_set: Sets the atomic_flag and returns whether it was already set immediately before the call// The entire operation is atomic (an atomic read-modify-write operation): the value is not affected by other threads// between the instant its value is read (to be returned) and the moment it is modified by this function.std::vector<std::thread> threads;for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i) threads.push_back(std::thread(append_number, i));for (auto& th : threads) th.join();std::cout << stream.str();return 0;
}} // namespace atomic
GitHub:https://github.com/fengbingchun/Messy_Test
相关文章:

Oracle回收站
回收站是删除对象使用的存储空间。可以使用实例参数recyclebin禁用回收站,默认是on,可以为某个会话或系统设置为off或on。所有模式都有一个回收站。 当表空间不足时可以自动重用回收站对象占用的表空间(此后不可能恢复对象)&#…
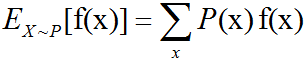
协方差矩阵介绍及C++/OpenCV/Eigen的三种实现
函数f(x)关于某分布P(x)的期望(expectation)或者期望值(expected value)是指,当x由P产生,f作用于x时,f(x)的平均值。对于离散型随机变量,这可以通过求和得到:对于连续型随机变量可以通过求积分得到:当概率分…
10分钟搭建你的第一个图像识别模型 | 附完整代码
(图片由AI科技大本营付费下载自视觉中国)作者 | Pulkit Sharma译者 | 王威力来源 | 数据派THU(ID:DatapiTHU)【导读】本文介绍了图像识别的深度学习模型的建立过程,通过陈述实际比赛的问题、介绍模型框架和…

Rancher 2.2.2 发布,优化 Kubernetes 集群运维
开发四年只会写业务代码,分布式高并发都不会还做程序员? >>> Rancher 2.2.2 发布了。Rancher 是一个开源的企业级 Kubernetes 平台,可以管理所有云上、所有发行版、所有 Kubernetes集群,解决了生产环境中企业用户可能面…

EXP/EXPDP, IMP/IMPDP应用
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> EXP/EXPDP, IMP/IMPDP应用 exp name/pwddbname filefilename.dmp tablestablename rowsy indexesn triggersn grantsn $ sqlplus username/passwordhostname:port/SERVICENAME OR $ sqlplus username Enter password:…

微软语音AI技术与微软听听文档小程序实践 | AI ProCon 2019
演讲嘉宾 | 赵晟、张鹏整理 | 伍杏玲来源 | CSDN(ID:CSDNnews)【导语】9 月 7 日,在CSDN主办的「AI ProCon 2019」上,微软(亚洲)互联网工程院人工智能语音团队首席研发总监赵晟、微软࿰…

C++11中std::condition_variable的使用
<condition_variable>是C标准程序库中的一个头文件,定义了C11标准中的一些用于并发编程时表示条件变量的类与方法等。条件变量是并发程序设计中的一种控制结构。多个线程访问一个共享资源(或称临界区)时,不但需要用互斥锁实现独享访问以避免并发错…

docker基础文档(链接,下载,安装)
一、docker相关链接1.docker中国区官网(包含部分中文文档,下载安装包,镜像加速器):https://www.docker-cn.com/2.docker官方镜像仓库:https://cloud.docker.com/3.docker下载:https://www.docker-cn.com/community-edi…

一个JS对话框,可以显示其它页面,
还不能自适应大小 garyBox.js // JavaScript Document// gary 2014-3-27// 加了 px 在google浏览器没加这个发现设置width 和height没有用 //gary 2014-3-27 //实在不会用那些JS框架,自己弄个,我只是想要个可以加载其它页面的对话框而以,这里用了别人的…

只需4秒,这个算法就能鉴别你的LV是真是假
(图片付费下载自视觉中国)导语:假冒奢侈品制造这个屡禁不止的灰色产业,每年给正品商家和消费者造成上千亿的损失,对企业和消费者造成伤害。作为全球奢侈品巨头,LVMH 对假冒奢侈品的打击十分重视。LVMH 其旗…
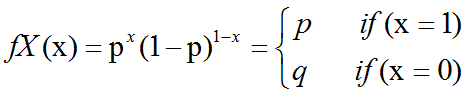
概率论中伯努利分布(bernoulli distribution)介绍及C++11中std::bernoulli_distribution的使用
Bernoulli分布(Bernoulli distribution):是单个二值随机变量的分布。它由单个参数∈[0,1],给出了随机变量等于1的概率。它具有如下的一些性质:P(x1) P(x0)1-P(xx) x(1-)1-xEx[x] Varx(x) (1-)伯努力分布(Bernoulli distribution,又…

关于View测量中的onMeasure函数
在自定义View中我们通常会重写onMeasure,下面来说说这个onMeasure有什么作用 onMeasure主要用于对于View绘制时进行测量 Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);…

zabbix二次开发之从mysql取值在运维平台js图表展现
前沿:集群控制平台已经要慢慢的灰度上线了,出问题的时候,才找点bug,时间有点空闲。正好看了下zabbix的数据库,产生了自己想做一套能更好的展现zabbix的页面。更多内容请到我的个人的博客站点,blog.xiaorui.…
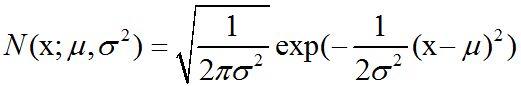
概率论中高斯分布(正态分布)介绍及C++11中std::normal_distribution的使用
高斯分布:最常用的分布是正态分布(normal distribution),也称为高斯分布(Gaussian distribution):正态分布N(x;μ,σ2)呈现经典的”钟形曲线”的形状,其中中心峰的x坐标由μ给出,峰的宽度受σ控制。正态分布由两个参数…

AI落地遭“卡脖子”困境:为什么说联邦学习是解决良方?
作者 | Just出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)毋庸置疑,在业界对人工智能(AI)应用落地备受期待的时期,数据这一重要支点却越来越成为一个“卡脖子”的难题。AI落地需要数据来优化模型效果,但大…

Linux下截取指定时间段日志并输出到指定文件
sed -n /2019-04-22 16:10:/,/2019-04-22 16:20:/p log.log > bbb.txt 转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/mrwuzs/p/10752037.html

nginx+keepalive主从双机热备+自动切换解决方案
环境采集cenots 6.3 64位迷你安装,因为安装前,你需要做一些工作yum install -y make wget如果你愿意可以更新下系统,更换下yum源.1.安装keepalive官方最新版 keepalived-1.2.7tar zxvf keepalived-1.2.7.tar.gzcd keepalived-1.2.7在此之前。…
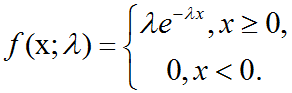
概率论中指数分布介绍及C++11中std::exponential_distribution的使用
指数分布:在深度学习中,我们经常会需要一个在x0点处取得边界点(sharp point)的分布。为了实现这一目的,我们可以使用指数分布(exponential distribution): p(x;λ) λlx≥0exp(-λx)指数分布使用指示函数(indicator function) lx≥…
肖仰华:知识图谱构建的三要素、三原则和九大策略 | AI ProCon 2019
演讲嘉宾 | 肖仰华(复旦大学教授、博士生导师,知识工场实验室负责人) 编辑 | Jane 出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100) 近两年,知识图谱技术得到了各行各业的关注,无论是企业公司还…

Docker mongo副本集环境搭建
1、MongoDB Docker 镜像安装 docker pull mongo 2、Docker容器创建 MongoDB Docker 容器创建有以下几个问题: 1- MongoDB 容器基本创建方法和数据目录挂载 2- MongoDB 容器的数据迁移 3- MongoDB 设置登录权限问题docker run -p 27017:27017 -v <LocalDirectoryP…

菜鸟学习HTML5+CSS3(一)
主要内容: 1.新的文档类型声明(DTD) 2.新增的HTML5标签 3.删除的HTML标签 4.重新定义的HTML标签 一、新的文档类型声明(DTD) HTML 5的DTD声明为:<!doctype html>、<!DOCTYPE html>、<!DOCTY…
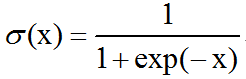
激活函数之logistic sigmoid函数介绍及C++实现
logistic sigmoid函数:logistic sigmoid函数通常用来产生Bernoulli分布中的参数,因为它的范围是(0,1),处在的有效取值范围内。logisitic sigmoid函数在变量取绝对值非常大的正值或负值时会出现饱和(saturate)现象,意味着函数会变得…

NLP重要模型详解,换个方式学(内附资源)
(图片有AI科技大本营付费下载自视觉中国)作者 | Jaime Zornoza,马德里技术大学译者 | 陈之炎校对 | 王威力编辑 | 黄继彦来源 | 数据派THU(ID:DatapiTHU)【导语】本文带你以前所未有的方式了解深度学习神经…
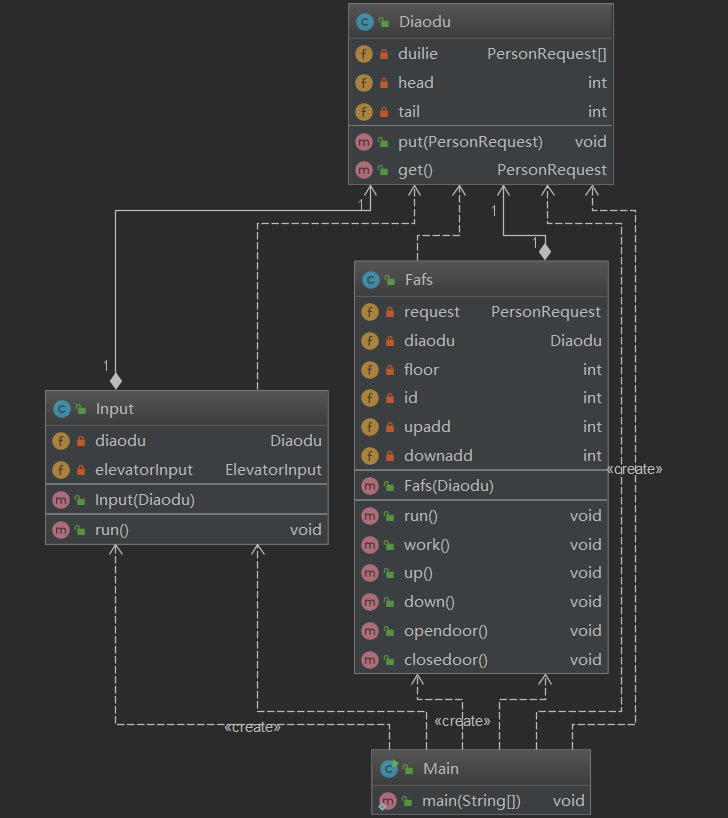
大闸蟹的OO第二单元总结
OO的第二单元是讲多线程的协作与控制,三次作业分别为FAFS电梯,ALS电梯和三部需要协作的电梯。三次作业由浅入深,让我们逐渐理解多线程的工作原理和运行状况。 第一次作业: 第一次作业是傻瓜电梯,也就是完全不需要考虑捎…

构建ASP.NET MVC4+EF5+EasyUI+Unity2.x注入的后台管理系统(31)-MVC使用RDL报表
原文:构建ASP.NET MVC4EF5EasyUIUnity2.x注入的后台管理系统(31)-MVC使用RDL报表这次我们来演示MVC3怎么显示RDL报表,坑爹的微软把MVC升级到5都木有良好的支持报表,让MVC在某些领域趋于短板 我们只能通过一些方式来使用rdl报表。 Razor视图不支持asp.net…

18段代码带你玩转18个机器学习必备交互工具
(图片有AI科技大本营付费下载自视觉中国)作者 | 曼纽尔阿米纳特吉(Manuel Amunategui)、迈赫迪洛佩伊(Mehdi Roopaei)来源 | 大数据(ID:hzdashuju)【导读】本文简要介绍将…
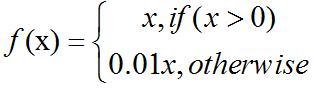
激活函数之ReLU/softplus介绍及C++实现
softplus函数(softplus function):ζ(x)ln(1exp(x)).softplus函数可以用来产生正态分布的β和σ参数,因为它的范围是(0,∞)。当处理包含sigmoid函数的表达式时它也经常出现。softplus函数名字来源于它是另外一个函数的平滑(或”软化”)形式,这…

windows server 2012 用sysdba登录报错 ORA-01031
报错显示:C:\Users\Administrator>sqlplus / as sysdba SQL*Plus: Release 11.2.0.1.0 Production on 星期三 4月 24 09:09:33 2019 Copyright (c) 1982, 2010, Oracle. All rights reserved. ERROR:ORA-01031: 权限不足 请输入用户名: 1、查看本地用户和组确认权…

[SignalR]初步认识以及安装
原文:[SignalR]初步认识以及安装1.什么是ASP.NET SignalR? ASP .NET SignalR是一个 ASP .NET 下的类库,可以在ASP .NET 的Web项目中实现实时通信。什么是实时通信的Web呢?就是让客户端(Web页面)和服务器端可以互相通知…
CUDA Samples:Vector Add
以下CUDA sample是分别用C和CUDA实现的两向量相加操作,参考CUDA 8.0中的sample:C:\ProgramData\NVIDIA Corporation\CUDA Samples\v8.0\0_Simple,并对其中使用到的CUDA函数进行了解说,各个文件内容如下:common.hpp:#ifndef FBC_CU…
