C++11中头文件thread的使用
C++11中加入了<thread>头文件,此头文件主要声明了std::thread线程类。C++11的标准类std::thread对线程进行了封装。std::thread代表了一个线程对象。应用C++11中的std::thread便于多线程程序的移值。
<thread>是C++标准程序库中的一个头文件,定义了C++11标准中的一些表示线程的类、用于互斥访问的类与方法等。
类std::thread表示一个线程。初始化时给出该线程的执行函数(或是可以调用的对象)。线程对象构造后即开始运行。默认情况下,C++11的子线程必须与主线程会合,即在主线程中调用thread::join()函数,这避免了子线程还在执行,主线程已经执行结束而撤销的情况。
如果子线程的执行函数需要参数,可把实参列表写在std::thread对象构造函数的参数列表中。如果把可调用对象(callable object)作为参数传给子线程的构造函数,则把该可调用对象复制一份给子线程。如果需要传递可调用对象的左值引用给子线程,则采用std::ref()来产生对象的引用、然后把引用值再传进去给子线程。
C++11所定义的线程是和操作系统的线程一一对应的,也就是说我们生成的线程都是直接接受操作系统的调度的,一个进程所能创建的线程数目以及一个操作系统所能创建的总的线程数据等都由运行时操作系统限定。
std::thread中主要声明三类函数:(1)、构造函数、拷贝构造函数(拷贝构造函数被禁用,意味着thread不可被拷贝构造,但能被转移(move)或者互换(swap))及析构函数;(2)、成员函数;(3)、静态成员函数(hardware_concurrency,检测硬件并发特性, Returns the number of hardware thread contexts)。
std::thread类成员函数:
(1)、get_id:获取线程ID,返回一个类型为std::thread::id的对象。
(2)、joinable:检查线程是否可被join。检查thread对象是否标识一个活动(active)的可行性线程。缺省构造的thread对象、已经完成join的thread对象、已经detach的thread对象都不是joinable。
(3)、join:调用该函数会阻塞当前线程。阻塞调用者(caller)所在的线程直至被join的std::thread对象标识的线程执行结束。
(4)、detach:将当前线程对象所代表的执行实例与该线程对象分离,使得线程的执行可以单独进行。一旦线程执行完毕,它所分配的资源将会被释放。
(5)、native_handle:该函数返回与std::thread具体实现相关的线程句柄。native_handle_type是连接thread类和操作系统SDK API之间的桥梁,如在Linux g++(libstdc++)里,native_handle_type其实就是pthread里面的pthread_t类型,当thread类的功能不能满足我们的要求的时候(比如改变某个线程的优先级),可以通过thread类实例的native_handle()返回值作为参数来调用相关的pthread函数达到目录。This member function is only present in class thread if the library implementation supports it. If present, it returns a value used to access implementation-specific information associated to the thread.
(6)、swap:交换两个线程对象所代表的底层句柄。
(7)、operator=:moves the thread object
(8)、hardware_concurrency:静态成员函数,返回当前计算机最大的硬件并发线程数目。基本上可以视为处理器的核心数目。
另外,std::thread::id表示线程ID,定义了在运行时操作系统内唯一能够标识该线程的标识符,同时其值还能指示所标识的线程的状态。Values of this type are returned by thread::get_id and this_thread::get_id to identify threads.
有时候我们需要在线程执行代码里面对当前调用者线程进行操作,针对这种情况,C++11里面专门定义了一个命名空间this_thread,此命名空间也声明在<thread>头文件中,其中包括get_id()函数用来获取当前调用者线程的ID;yield()函数可以用来将调用者线程跳出运行状态,重新交给操作系统进行调度,即当前线程放弃执行,操作系统调度另一线程继续执行;sleep_until()函数是将线程休眠至某个指定的时刻(time point),该线程才被重新唤醒;sleep_for()函数是将线程休眠某个指定的时间片(time span),该线程才被重新唤醒,不过由于线程调度等原因,实际休眠实际可能比sleep_duration所表示的时间片更长。
std::thread:Class to represent individual threads of execution. A thread of execution is a sequence of instructions that can be executed concurrently with other such sequences in multithreading environments, while sharing a same address space.
std::this_thread:This namespace groups a set of functions that access the current thread.
下面是从其他文章中copy的<thread>测试代码,详细内容介绍可以参考对应的reference:
#include "thread2.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
#include <memory>
#include <list>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <iomanip>
#include <ctime>
#include <algorithm>namespace thread_ {std::atomic<int> global_counter(0);#ifdef _MSC_VER///
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/thread/thread/thread/static void increase_global(int n) { for (int i = 0; i<n; ++i) ++global_counter; }static void increase_reference(std::atomic<int>& variable, int n) { for (int i = 0; i<n; ++i) ++variable; }struct C : std::atomic<int> {C() : std::atomic<int>(0) {}void increase_member(int n) { for (int i = 0; i<n; ++i) fetch_add(1); }
};int test_thread_thread()
{// thread::thread: Constructs a thread objectstd::vector<std::thread> threads;std::cout << "increase global counter with 10 threads...\n";for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i)threads.push_back(std::thread(increase_global, 1000));std::cout << "increase counter (foo) with 10 threads using reference...\n";std::atomic<int> foo(0);for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i)threads.push_back(std::thread(increase_reference, std::ref(foo), 1000));std::cout << "increase counter (bar) with 10 threads using member...\n";C bar;for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i)threads.push_back(std::thread(&C::increase_member, std::ref(bar), 1000));std::cout << "synchronizing all threads...\n";for (auto& th : threads) th.join();std::cout << "global_counter: " << global_counter << '\n';std::cout << "foo: " << foo << '\n';std::cout << "bar: " << bar << '\n';return 0;
}// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/thread/thread/detach/
static void pause_thread(int n)
{std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(n));std::cout << "pause of " << n << " seconds ended\n";
}int test_thread_detach()
{// thread::detach: Detaches the thread represented by the object from the calling thread,// allowing them to execute independently from each other.std::cout << "Spawning and detaching 3 threads...\n";std::thread(pause_thread, 1).detach();std::thread(pause_thread, 2).detach();std::thread(pause_thread, 3).detach();std::cout << "Done spawning threads.\n";std::cout << "(the main thread will now pause for 5 seconds)\n";// give the detached threads time to finish (but not guaranteed!):pause_thread(5);return 0;
}//
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/thread/thread/get_id/
std::thread::id main_thread_id = std::this_thread::get_id();static void is_main_thread()
{// this_thread::get_id: Returns the thread id of the calling thread.// This value uniquely identifies the thread.if (main_thread_id == std::this_thread::get_id())std::cout << "This is the main thread.\n";elsestd::cout << "This is not the main thread.\n";
}int test_thread_get_id()
{// thread::get_id: Returns the thread id// If the thread object is joinable, the function returns a value that uniquely identifies the thread.// If the thread object is not joinable, the function returns a default - constructed object of member type thread::id.is_main_thread();std::thread th(is_main_thread);th.join();return 0;
}/
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/thread/thread/join/
int test_thread_join()
{// thread::join: The function returns when the thread execution has completed.std::cout << "Spawning 3 threads...\n";std::thread t1(pause_thread, 1);std::thread t2(pause_thread, 2);std::thread t3(pause_thread, 3);std::cout << "Done spawning threads. Now waiting for them to join:\n";t1.join();t2.join();t3.join();std::cout << "All threads joined!\n";return 0;
}///
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/thread/thread/joinable/
static void mythread()
{// do stuff...
}int test_thread_joinable()
{// thread::joinable: Returns whether the thread object is joinable.// A thread object is joinable if it represents a thread of execution.std::thread foo; // 缺省构造函数,线程不可执行std::thread bar(mythread);std::cout << "Joinable after construction:\n" << std::boolalpha;std::cout << "foo: " << foo.joinable() << '\n';std::cout << "bar: " << bar.joinable() << '\n';if (foo.joinable()) foo.join();if (bar.joinable()) bar.join();std::cout << "Joinable after joining:\n" << std::boolalpha;std::cout << "foo: " << foo.joinable() << '\n';std::cout << "bar: " << bar.joinable() << '\n';return 0;
}//
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/thread/thread/operator=/
int test_thread_operator()
{// thread::operator=: Move-assign thread// If the object is currently not joinable, it acquires the thread of execution represented by rhs(if any).// If it is joinable, terminate() is called.// After the call, rhs no longer represents any thread of execution(as if default - constructed).std::thread threads[5]; // default-constructed threadsstd::cout << "Spawning 5 threads...\n";for (int i = 0; i<5; ++i)threads[i] = std::thread(pause_thread, i + 1); // move-assign threadsstd::cout << "Done spawning threads. Now waiting for them to join:\n";for (int i = 0; i<5; ++i)threads[i].join();std::cout << "All threads joined!\n";return 0;
}//
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/thread/this_thread/sleep_for/
int test_this_thread_sleep_for()
{// this_thread::sleep_for: Blocks execution of the calling thread during the span of time specified by rel_time.// The execution of the current thread is stopped until at least rel_time has passed from now.// Other threads continue their execution.std::cout << "countdown:\n";for (int i = 10; i>0; --i) {std::cout << i << std::endl;std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));}std::cout << "Lift off!\n";return 0;
}/
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/thread/this_thread/sleep_until/
int test_this_thread_sleep_until()
{// this_thread::sleep_until: Blocks the calling thread until abs_time.// The execution of the current thread is stopped until at least abs_time, while other threads may continue to advance.using std::chrono::system_clock;std::time_t tt = system_clock::to_time_t(system_clock::now());struct std::tm * ptm = std::localtime(&tt);
#ifdef _MSC_VERstd::cout << "Current time: " << std::put_time(ptm, "%X") << '\n';
#endifstd::cout << "Waiting for the next minute to begin...\n";++ptm->tm_min; ptm->tm_sec = 0;std::this_thread::sleep_until(system_clock::from_time_t(mktime(ptm)));
#ifdef _MSC_VERstd::cout << std::put_time(ptm, "%X") << " reached!\n";
#endifreturn 0;
}/
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/thread/this_thread/yield/
std::atomic<bool> ready(false);static void count1m(int id)
{while (!ready) { // wait until main() sets ready...std::this_thread::yield();}for (volatile int i = 0; i<1000000; ++i) {}std::cout << id << std::endl;
}int test_this_thread_yield()
{// this_thread::yield: The calling thread yields, offering the implementation the opportunity to reschedule.// This function shall be called when a thread waits for other threads to advance without blocking.std::thread threads[10];std::cout << "race of 10 threads that count to 1 million:\n";for (int i = 0; i<10; ++i) threads[i] = std::thread(count1m, i);ready = true; // go!for (auto& th : threads) th.join();std::cout << '\n';return 0;
}//
// reference: https://zh.wikibooks.org/zh-hans/C%2B%2B/STL/Thread
template<typename T>
class SyncQueue {
public:SyncQueue(int maxSize) :m_maxSize(maxSize), m_needStop(false) {}void Put(const T&x) { Add(x); }void Put(T&&x) { Add(std::forward<T>(x)); }void Take(std::list<T>& list){std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);m_notEmpty.wait(locker, [this] {return m_needStop || NotEmpty(); });if (m_needStop) return;list = std::move(m_queue);m_notFull.notify_one();}void Take(T& t){std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);m_notEmpty.wait(locker, [this] {return m_needStop || NotEmpty(); });if (m_needStop) return;t = m_queue.front();m_queue.pop_front();m_notFull.notify_one();}void Stop(){{std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);m_needStop = true;}m_notFull.notify_all();m_notEmpty.notify_all();}bool Empty(){std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);return m_queue.empty();}bool Full(){std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);return m_queue.size() == m_maxSize;}size_t Size(){std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);return m_queue.size();}int Count(){return m_queue.size();}private:bool NotFull() const{bool full = m_queue.size() >= m_maxSize;if (full)std::cout << "full, waiting, thread id: " << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;return !full;}bool NotEmpty() const{bool empty = m_queue.empty();if (empty)std::cout << "empty,waiting, thread id: " << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;return !empty;}template<typename F>void Add(F&&x){std::unique_lock< std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);m_notFull.wait(locker, [this] {return m_needStop || NotFull(); });if (m_needStop) return;m_queue.push_back(std::forward<F>(x));m_notEmpty.notify_one();}private:std::list<T> m_queue; //缓冲区std::mutex m_mutex; //互斥量和条件变量结合起来使用std::condition_variable m_notEmpty;//不为空的条件变量std::condition_variable m_notFull; //没有满的条件变量int m_maxSize; //同步队列最大的sizebool m_needStop; //停止的标志
};const int MaxTaskCount = 100;
class ThreadPool {
public:using Task = std::function<void()>;ThreadPool(int numThreads = std::thread::hardware_concurrency()) : m_queue(MaxTaskCount){Start(numThreads);}~ThreadPool(void){//如果没有停止时则主动停止线程池Stop();}void Stop(){std::call_once(m_flag, [this] {StopThreadGroup(); }); //保证多线程情况下只调用一次StopThreadGroup}void AddTask(Task&&task){m_queue.Put(std::forward<Task>(task));}void AddTask(const Task& task){m_queue.Put(task);}private:void Start(int numThreads){m_running = true;//创建线程组for (int i = 0; i <numThreads; ++i) {m_threadgroup.push_back(std::make_shared<std::thread>(&ThreadPool::RunInThread, this));}}void RunInThread(){while (m_running) {//取任务分别执行std::list<Task> list;m_queue.Take(list);for (auto& task : list) {if (!m_running)return;task();}}}void StopThreadGroup(){m_queue.Stop(); //让同步队列中的线程停止m_running = false; //置为false,让内部线程跳出循环并退出for (auto thread : m_threadgroup) { //等待线程结束if (thread)thread->join();}m_threadgroup.clear();}std::list<std::shared_ptr<std::thread>> m_threadgroup; //处理任务的线程组SyncQueue<Task> m_queue; //同步队列std::atomic_bool m_running; //是否停止的标志std::once_flag m_flag;
};void TestThdPool()
{ThreadPool pool; bool runing = true;std::thread thd1([&pool, &runing] {while (runing) {std::cout << "produce " << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;pool.AddTask([] {std::cout << "consume " << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;});}});std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(10));runing = false;pool.Stop();thd1.join();getchar();
}int test_thread_pool()
{TestThdPool();return 0;
}//
int test_thread_hardware_concurrency()
{std::cout << " the number of hardware thread contexts: " << std::thread::hardware_concurrency() << std::endl;return 0;
}#endif//
// reference: https://thispointer.com/c-11-multithreading-part-1-three-different-ways-to-create-threads/// creating a thread using function objects
class DisplayThread {
public:void operator()() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)std::cout<<"Display Thread Executing"<<std::endl;}
};int test_thread_1()
{std::thread threadObj((DisplayThread()));for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)std::cout<<"Display From Main Thread "<<std::endl;std::cout<<"Waiting For Thread to complete"<<std::endl;threadObj.join();std::cout<<"Exiting from Main Thread"<<std::endl;return 0;
}// reference: https://thispointer.com/c-11-multithreading-part-1-three-different-ways-to-create-threads/// creating a thread using lambda functions
int test_thread_2()
{int x = 9;std::thread threadObj([]{for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)std::cout<<"Display Thread Executing"<<std::endl;});for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)std::cout<<"Display From Main Thread"<<std::endl;threadObj.join();std::cout<<"Exiting from Main Thread"<<std::endl;return 0;
}// reference: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/10673585/start-thread-with-member-function// start thread with member function
class bar {
public:void foo() {std::cout << "hello from member function" << std::endl;}
};int test_thread_3()
{std::thread t(&bar::foo, bar());t.join();return 0;
}bool flag1 = true, flag2 = true;void print_xxx()
{while (1) {if (!flag1) break;std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));fprintf(stdout, "print xxx\n");}
}void print_yyy()
{while (1) {if (!flag2) break;std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(2));fprintf(stdout, "print yyy\n");}
}int test_thread_4()
{std::thread th1(print_xxx);std::thread th2(print_yyy);std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::minutes(2));flag1 = false;flag2 = false;th1.join();th2.join();return 0;
}} // namespace::thread_
GitHub:https://github.com/fengbingchun/Messy_Test
相关文章:

python3 urllib 类
urllib模块中的方法 1.urllib.urlopen(url[,data[,proxies]]) 打开一个url的方法,返回一个文件对象,然后可以进行类似文件对象的操作。本例试着打开google >>> import urllib >>> f urllib.urlopen(http://www.google.com.hk/) >&…
阿里飞天大数据飞天AI平台“双生”系统正式发布,9大全新数据产品集中亮相
作者 | 夕颜 责编 | 唐小引 出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100) 如今,大数据和 AI 已经成为两个分不开的词汇,没有大数据,AI 就失去了根基;没有 AI,数据不会呈现爆发式的增长。如何将 AI 与大…

关于JavaScript的闭包(closure)
(转载自阮一峰博客) 闭包(closure)是Javascript语言的一个难点,也是它的特色,更是函数式编程的重要思想之一,很多高级应用都要依靠闭包实现。 下面就是我的学习笔记,对于Javascript初…
Vagrant控制管理器——“Hobo”
Hobo是控制Vagrant盒子和在Mac上编辑Vagrantfiles的最佳和最简单的方法。您可以快速启动,停止和重新加载您的Vagrant机器。您可以从头开始轻松创建新的Vagrantfile。点击进入,尽享Hobo for Mac全部功能! Hobo做什么? 启动…

微众银行AI团队开源联邦学习框架,并发布《联邦学习白皮书1.0》
(图片由AI科技大本营付费下载自视觉中国)编辑 | Jane来源 | 《联邦学习白皮书1.0》出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)【导语】2019年,联邦学习成为业界技术研究与应用的焦点。近日,微众银行 AI 项目组编制…

C++11中头文件atomic的使用
原子库为细粒度的原子操作提供组件,允许无锁并发编程。涉及同一对象的每个原子操作,相对于任何其他原子操作是不可分的。原子对象不具有数据竞争(data race)。原子类型对象的主要特点就是从不同线程访问不会导致数据竞争。因此从不同线程访问某个原子对象…

Oracle回收站
回收站是删除对象使用的存储空间。可以使用实例参数recyclebin禁用回收站,默认是on,可以为某个会话或系统设置为off或on。所有模式都有一个回收站。 当表空间不足时可以自动重用回收站对象占用的表空间(此后不可能恢复对象)&#…
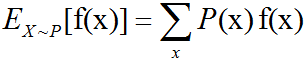
协方差矩阵介绍及C++/OpenCV/Eigen的三种实现
函数f(x)关于某分布P(x)的期望(expectation)或者期望值(expected value)是指,当x由P产生,f作用于x时,f(x)的平均值。对于离散型随机变量,这可以通过求和得到:对于连续型随机变量可以通过求积分得到:当概率分…
10分钟搭建你的第一个图像识别模型 | 附完整代码
(图片由AI科技大本营付费下载自视觉中国)作者 | Pulkit Sharma译者 | 王威力来源 | 数据派THU(ID:DatapiTHU)【导读】本文介绍了图像识别的深度学习模型的建立过程,通过陈述实际比赛的问题、介绍模型框架和…

Rancher 2.2.2 发布,优化 Kubernetes 集群运维
开发四年只会写业务代码,分布式高并发都不会还做程序员? >>> Rancher 2.2.2 发布了。Rancher 是一个开源的企业级 Kubernetes 平台,可以管理所有云上、所有发行版、所有 Kubernetes集群,解决了生产环境中企业用户可能面…

EXP/EXPDP, IMP/IMPDP应用
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> EXP/EXPDP, IMP/IMPDP应用 exp name/pwddbname filefilename.dmp tablestablename rowsy indexesn triggersn grantsn $ sqlplus username/passwordhostname:port/SERVICENAME OR $ sqlplus username Enter password:…

微软语音AI技术与微软听听文档小程序实践 | AI ProCon 2019
演讲嘉宾 | 赵晟、张鹏整理 | 伍杏玲来源 | CSDN(ID:CSDNnews)【导语】9 月 7 日,在CSDN主办的「AI ProCon 2019」上,微软(亚洲)互联网工程院人工智能语音团队首席研发总监赵晟、微软࿰…

C++11中std::condition_variable的使用
<condition_variable>是C标准程序库中的一个头文件,定义了C11标准中的一些用于并发编程时表示条件变量的类与方法等。条件变量是并发程序设计中的一种控制结构。多个线程访问一个共享资源(或称临界区)时,不但需要用互斥锁实现独享访问以避免并发错…

docker基础文档(链接,下载,安装)
一、docker相关链接1.docker中国区官网(包含部分中文文档,下载安装包,镜像加速器):https://www.docker-cn.com/2.docker官方镜像仓库:https://cloud.docker.com/3.docker下载:https://www.docker-cn.com/community-edi…

一个JS对话框,可以显示其它页面,
还不能自适应大小 garyBox.js // JavaScript Document// gary 2014-3-27// 加了 px 在google浏览器没加这个发现设置width 和height没有用 //gary 2014-3-27 //实在不会用那些JS框架,自己弄个,我只是想要个可以加载其它页面的对话框而以,这里用了别人的…

只需4秒,这个算法就能鉴别你的LV是真是假
(图片付费下载自视觉中国)导语:假冒奢侈品制造这个屡禁不止的灰色产业,每年给正品商家和消费者造成上千亿的损失,对企业和消费者造成伤害。作为全球奢侈品巨头,LVMH 对假冒奢侈品的打击十分重视。LVMH 其旗…
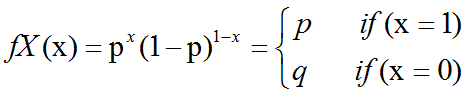
概率论中伯努利分布(bernoulli distribution)介绍及C++11中std::bernoulli_distribution的使用
Bernoulli分布(Bernoulli distribution):是单个二值随机变量的分布。它由单个参数∈[0,1],给出了随机变量等于1的概率。它具有如下的一些性质:P(x1) P(x0)1-P(xx) x(1-)1-xEx[x] Varx(x) (1-)伯努力分布(Bernoulli distribution,又…

关于View测量中的onMeasure函数
在自定义View中我们通常会重写onMeasure,下面来说说这个onMeasure有什么作用 onMeasure主要用于对于View绘制时进行测量 Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);…

zabbix二次开发之从mysql取值在运维平台js图表展现
前沿:集群控制平台已经要慢慢的灰度上线了,出问题的时候,才找点bug,时间有点空闲。正好看了下zabbix的数据库,产生了自己想做一套能更好的展现zabbix的页面。更多内容请到我的个人的博客站点,blog.xiaorui.…
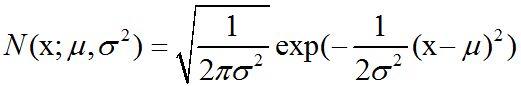
概率论中高斯分布(正态分布)介绍及C++11中std::normal_distribution的使用
高斯分布:最常用的分布是正态分布(normal distribution),也称为高斯分布(Gaussian distribution):正态分布N(x;μ,σ2)呈现经典的”钟形曲线”的形状,其中中心峰的x坐标由μ给出,峰的宽度受σ控制。正态分布由两个参数…

AI落地遭“卡脖子”困境:为什么说联邦学习是解决良方?
作者 | Just出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)毋庸置疑,在业界对人工智能(AI)应用落地备受期待的时期,数据这一重要支点却越来越成为一个“卡脖子”的难题。AI落地需要数据来优化模型效果,但大…

Linux下截取指定时间段日志并输出到指定文件
sed -n /2019-04-22 16:10:/,/2019-04-22 16:20:/p log.log > bbb.txt 转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/mrwuzs/p/10752037.html

nginx+keepalive主从双机热备+自动切换解决方案
环境采集cenots 6.3 64位迷你安装,因为安装前,你需要做一些工作yum install -y make wget如果你愿意可以更新下系统,更换下yum源.1.安装keepalive官方最新版 keepalived-1.2.7tar zxvf keepalived-1.2.7.tar.gzcd keepalived-1.2.7在此之前。…
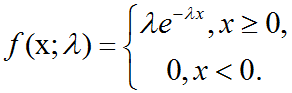
概率论中指数分布介绍及C++11中std::exponential_distribution的使用
指数分布:在深度学习中,我们经常会需要一个在x0点处取得边界点(sharp point)的分布。为了实现这一目的,我们可以使用指数分布(exponential distribution): p(x;λ) λlx≥0exp(-λx)指数分布使用指示函数(indicator function) lx≥…
肖仰华:知识图谱构建的三要素、三原则和九大策略 | AI ProCon 2019
演讲嘉宾 | 肖仰华(复旦大学教授、博士生导师,知识工场实验室负责人) 编辑 | Jane 出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100) 近两年,知识图谱技术得到了各行各业的关注,无论是企业公司还…

Docker mongo副本集环境搭建
1、MongoDB Docker 镜像安装 docker pull mongo 2、Docker容器创建 MongoDB Docker 容器创建有以下几个问题: 1- MongoDB 容器基本创建方法和数据目录挂载 2- MongoDB 容器的数据迁移 3- MongoDB 设置登录权限问题docker run -p 27017:27017 -v <LocalDirectoryP…

菜鸟学习HTML5+CSS3(一)
主要内容: 1.新的文档类型声明(DTD) 2.新增的HTML5标签 3.删除的HTML标签 4.重新定义的HTML标签 一、新的文档类型声明(DTD) HTML 5的DTD声明为:<!doctype html>、<!DOCTYPE html>、<!DOCTY…
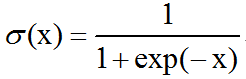
激活函数之logistic sigmoid函数介绍及C++实现
logistic sigmoid函数:logistic sigmoid函数通常用来产生Bernoulli分布中的参数,因为它的范围是(0,1),处在的有效取值范围内。logisitic sigmoid函数在变量取绝对值非常大的正值或负值时会出现饱和(saturate)现象,意味着函数会变得…

NLP重要模型详解,换个方式学(内附资源)
(图片有AI科技大本营付费下载自视觉中国)作者 | Jaime Zornoza,马德里技术大学译者 | 陈之炎校对 | 王威力编辑 | 黄继彦来源 | 数据派THU(ID:DatapiTHU)【导语】本文带你以前所未有的方式了解深度学习神经…
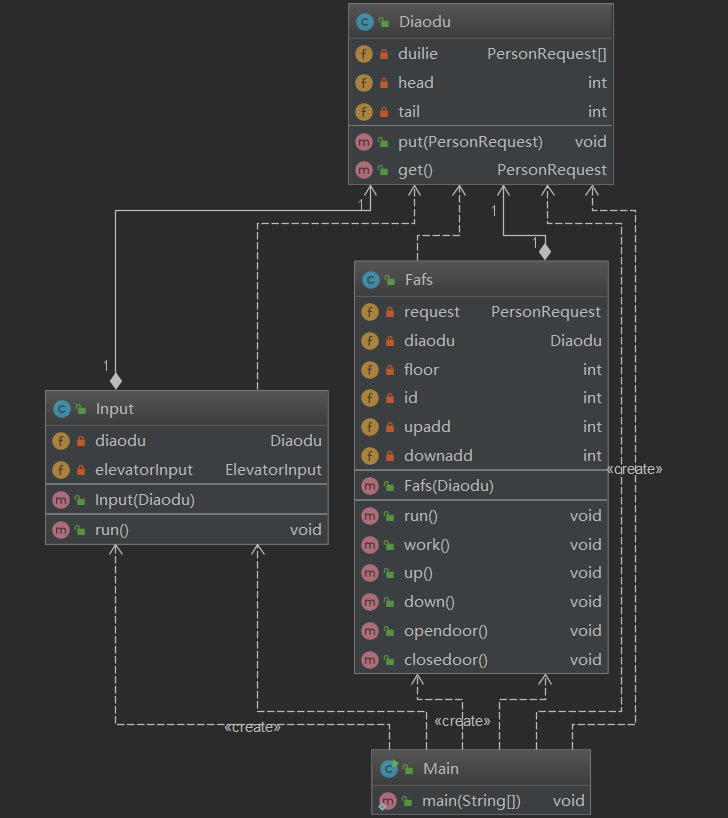
大闸蟹的OO第二单元总结
OO的第二单元是讲多线程的协作与控制,三次作业分别为FAFS电梯,ALS电梯和三部需要协作的电梯。三次作业由浅入深,让我们逐渐理解多线程的工作原理和运行状况。 第一次作业: 第一次作业是傻瓜电梯,也就是完全不需要考虑捎…
