C/C++,FEISTDLIB的部分源代码

1 文本格式
#ifndef _FEISTDLIB_POLY_
#define _FEISTDLIB_POLY_
/*
* This file is part of the fstdlib project.
* Version: Build v0.0.2
* You can check for details at https://github.com/FNatsuka/fstdlib
*/
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
namespace fstdlib {
typedef long long ll;
int mod = 998244353, grt = 3;
class poly {
private:
std::vector<int> data;
void out(void) {
for (int i = 0; i < (int)data.size(); ++i) printf("%d ", data[i]);
puts("");
}
public:
poly(std::size_t len = std::size_t(0)) { data = std::vector<int>(len); }
poly(const std::vector<int>& b) { data = b; }
poly(const poly& b) { data = b.data; }
void resize(std::size_t len, int val = 0) { data.resize(len, val); }
std::size_t size(void) const { return data.size(); }
void clear(void) { data.clear(); }
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
void shrink_to_fit(void) { data.shrink_to_fit(); }
#endif
int& operator[](std::size_t b) { return data[b]; }
const int& operator[](std::size_t b) const { return data[b]; }
poly operator*(const poly& h) const;
poly operator*=(const poly& h);
poly operator*(const int& h) const;
poly operator*=(const int& h);
poly operator+(const poly& h) const;
poly operator+=(const poly& h);
poly operator-(const poly& h) const;
poly operator-=(const poly& h);
poly operator<<(const std::size_t& b) const;
poly operator<<=(const std::size_t& b);
poly operator>>(const std::size_t& b) const;
poly operator>>=(const std::size_t& b);
poly operator/(const int& h) const;
poly operator/=(const int& h);
poly operator==(const poly& h) const;
poly operator!=(const poly& h) const;
poly operator+(const int& h) const;
poly operator+=(const int& h);
poly inv(void) const;
poly inv(const int& h) const;
friend poly sqrt(const poly& h);
friend poly log(const poly& h);
friend poly exp(const poly& h);
};
int qpow(int a, int b, int p = mod) {
int res = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) res = (ll)res * a % p;
a = (ll)a * a % p, b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
std::vector<int> rev;
void dft_for_module(std::vector<int>& f, int n, int b) {
static std::vector<int> w;
w.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (i < rev[i]) std::swap(f[i], f[rev[i]]);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i <<= 1) {
w[0] = 1, w[1] = qpow(grt, (mod - 1) / i);
if (b == -1) w[1] = qpow(w[1], mod - 2);
for (int j = 2; j < i / 2; ++j) w[j] = (ll)w[j - 1] * w[1] % mod;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j += i)
for (int k = 0; k < i / 2; ++k) {
int p = f[j + k], q = (ll)f[j + k + i / 2] * w[k] % mod;
f[j + k] = (p + q) % mod, f[j + k + i / 2] = (p - q + mod) % mod;
}
}
}
poly poly::operator*(const poly& h) const {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(size() + h.size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
std::vector<int> f(this->data), g(h.data);
f.resize(N), g.resize(N);
rev.resize(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? N >> 1 : 0);
dft_for_module(f, N, 1), dft_for_module(g, N, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) f[i] = (ll)f[i] * g[i] % mod;
dft_for_module(f, N, -1), f.resize(size() + h.size() - 1);
for (int i = 0, inv = qpow(N, mod - 2); i < (int)f.size(); ++i)
f[i] = (ll)f[i] * inv % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator*=(const poly& h) { return *this = *this * h; }
poly poly::operator*(const int& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i] = (ll)f[i] * h % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator*=(const int& h) {
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i) data[i] = (ll)data[i] * h % mod;
return *this;
}
poly poly::operator+(const poly& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
if (f.size() < h.size()) f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) f[i] = (f[i] + h[i]) % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator+=(const poly& h) {
std::vector<int>& f = this->data;
if (f.size() < h.size()) f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) f[i] = (f[i] + h[i]) % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator-(const poly& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
if (f.size() < h.size()) f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) f[i] = (f[i] - h[i] + mod) % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator-=(const poly& h) {
std::vector<int>& f = this->data;
if (f.size() < h.size()) f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) f[i] = (f[i] - h[i] + mod) % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator<<(const std::size_t& b) const {
std::vector<int> f(size() + b);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i) f[i + b] = data[i];
return f;
}
poly poly::operator<<=(const std::size_t& b) { return *this = (*this) << b; }
poly poly::operator>>(const std::size_t& b) const {
std::vector<int> f(size() - b);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i] = data[i + b];
return f;
}
poly poly::operator>>=(const std::size_t& b) { return *this = (*this) >> b; }
poly poly::operator/(const int& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
int inv = qpow(h, mod - 2);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i] = (ll)f[i] * inv % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator/=(const int& h) {
int inv = qpow(h, mod - 2);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)data.size(); ++i) data[i] = (ll)data[i] * inv % mod;
return *this;
}
poly poly::inv(void) const {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(size() + size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
std::vector<int> f(N), g(N), d(this->data);
d.resize(N), f[0] = qpow(d[0], mod - 2);
for (int w = 2; w < N; w <<= 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i) g[i] = d[i];
rev.resize(w << 1);
for (int i = 0; i < w * 2; ++i)
rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? w : 0);
dft_for_module(f, w << 1, 1), dft_for_module(g, w << 1, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < w * 2; ++i)
f[i] = (ll)f[i] * (2 + mod - (ll)f[i] * g[i] % mod) % mod;
dft_for_module(f, w << 1, -1);
for (int i = 0, inv = qpow(w << 1, mod - 2); i < w; ++i)
f[i] = (ll)f[i] * inv % mod;
for (int i = w; i < w * 2; ++i) f[i] = 0;
}
f.resize(size());
return f;
}
poly poly::operator==(const poly& h) const {
if (size() != h.size()) return 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i)
if (data[i] != h[i]) return 0;
return 1;
}
poly poly::operator!=(const poly& h) const {
if (size() != h.size()) return 1;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i)
if (data[i] != h[i]) return 1;
return 0;
}
poly poly::operator+(const int& h) const {
poly f(this->data);
f[0] = (f[0] + h) % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator+=(const int& h) { return *this = (*this) + h; }
poly poly::inv(const int& h) const {
poly f(*this);
f.resize(h);
return f.inv();
}
int modsqrt(int h, int p = mod) { return 1; }
poly sqrt(const poly& h) {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(h.size() + h.size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
poly f(N), g(N), d(h);
d.resize(N), f[0] = modsqrt(d[0]);
for (int w = 2; w < N; w <<= 1) {
g.resize(w);
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i) g[i] = d[i];
f = (f + f.inv(w) * g) / 2;
f.resize(w);
}
f.resize(h.size());
return f;
}
poly log(const poly& h) {
poly f(h);
for (int i = 1; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i - 1] = (ll)f[i] * i % mod;
f[f.size() - 1] = 0, f = f * h.inv(), f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = (int)f.size() - 1; i > 0; --i)
f[i] = (ll)f[i - 1] * qpow(i, mod - 2) % mod;
f[0] = 0;
return f;
}
poly exp(const poly& h) {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(h.size() + h.size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
poly f(N), g(N), d(h);
f[0] = 1, d.resize(N);
for (int w = 2; w < N; w <<= 1) {
f.resize(w), g.resize(w);
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i) g[i] = d[i];
f = f * (g + 1 - log(f));
f.resize(w);
}
f.resize(h.size());
return f;
}
struct comp {
long double x, y;
comp(long double _x = 0, long double _y = 0) : x(_x), y(_y) {}
comp operator*(const comp& b) const {
return comp(x * b.x - y * b.y, x * b.y + y * b.x);
}
comp operator+(const comp& b) const { return comp(x + b.x, y + b.y); }
comp operator-(const comp& b) const { return comp(x - b.x, y - b.y); }
comp conj(void) { return comp(x, -y); }
};
const int EPS = 1e-9;
template <typename FLOAT_T>
FLOAT_T fabs(const FLOAT_T& x) {
return x > 0 ? x : -x;
}
template <typename FLOAT_T>
FLOAT_T sin(const FLOAT_T& x, const long double& EPS = fstdlib::EPS) {
FLOAT_T res = 0, delt = x;
int d = 0;
while (fabs(delt) > EPS) {
res += delt, ++d;
delt *= -x * x / ((2 * d) * (2 * d + 1));
}
return res;
}
template <typename FLOAT_T>
FLOAT_T cos(const FLOAT_T& x, const long double& EPS = fstdlib::EPS) {
FLOAT_T res = 0, delt = 1;
int d = 0;
while (fabs(delt) > EPS) {
res += delt, ++d;
delt *= -x * x / ((2 * d) * (2 * d - 1));
}
return res;
}
const long double PI = std::acos((long double)(-1));
void dft_for_complex(std::vector<comp>& f, int n, int b) {
static std::vector<comp> w;
w.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (i < rev[i]) std::swap(f[i], f[rev[i]]);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i <<= 1) {
w[0] = comp(1, 0), w[1] = comp(cos(2 * PI / i), b * sin(2 * PI / i));
for (int j = 2; j < i / 2; ++j) w[j] = w[j - 1] * w[1];
for (int j = 0; j < n; j += i)
for (int k = 0; k < i / 2; ++k) {
comp p = f[j + k], q = f[j + k + i / 2] * w[k];
f[j + k] = p + q, f[j + k + i / 2] = p - q;
}
}
}
class arbitrary_module_poly {
private:
std::vector<int> data;
int construct_element(int D, ll x, ll y, ll z) const {
x %= mod, y %= mod, z %= mod;
return ((ll)D * D * x % mod + (ll)D * y % mod + z) % mod;
}
public:
int mod;
arbitrary_module_poly(std::size_t len = std::size_t(0),
int module_value = 1e9 + 7) {
mod = module_value;
data = std::vector<int>(len);
}
arbitrary_module_poly(const std::vector<int>& b, int module_value = 1e9 + 7) {
mod = module_value;
data = b;
}
arbitrary_module_poly(const arbitrary_module_poly& b) {
mod = b.mod;
data = b.data;
}
void resize(std::size_t len, const int& val = 0) { data.resize(len, val); }
std::size_t size(void) const { return data.size(); }
void clear(void) { data.clear(); }
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
void shrink_to_fit(void) { data.shrink_to_fit(); }
#endif
int& operator[](std::size_t b) { return data[b]; }
const int& operator[](std::size_t b) const { return data[b]; }
arbitrary_module_poly operator*(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator*=(const arbitrary_module_poly& h);
arbitrary_module_poly operator*(const int& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator*=(const int& h);
arbitrary_module_poly operator+(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator+=(const arbitrary_module_poly& h);
arbitrary_module_poly operator-(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator-=(const arbitrary_module_poly& h);
arbitrary_module_poly operator<<(const std::size_t& b) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator<<=(const std::size_t& b);
arbitrary_module_poly operator>>(const std::size_t& b) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator>>=(const std::size_t& b);
arbitrary_module_poly operator/(const int& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator/=(const int& h);
arbitrary_module_poly operator==(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator!=(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly inv(void) const;
arbitrary_module_poly inv(const int& h) const;
friend arbitrary_module_poly sqrt(const arbitrary_module_poly& h);
friend arbitrary_module_poly log(const arbitrary_module_poly& h);
};
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator*(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(size() + h.size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
std::vector<comp> f(N), g(N), p(N), q(N);
const int D = std::sqrt(mod);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i)
f[i].x = data[i] / D, f[i].y = data[i] % D;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) g[i].x = h[i] / D, g[i].y = h[i] % D;
rev.resize(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? N >> 1 : 0);
dft_for_complex(f, N, 1), dft_for_complex(g, N, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
p[i] = (f[i] + f[(N - i) % N].conj()) * comp(0.50, 0) * g[i];
q[i] = (f[i] - f[(N - i) % N].conj()) * comp(0, -0.5) * g[i];
}
dft_for_complex(p, N, -1), dft_for_complex(q, N, -1);
std::vector<int> r(size() + h.size() - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)r.size(); ++i)
r[i] = construct_element(D, p[i].x / N + 0.5, (p[i].y + q[i].x) / N + 0.5,
q[i].y / N + 0.5);
return arbitrary_module_poly(r, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator*=(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) {
return *this = *this * h;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator*(const int& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i] = (ll)f[i] * h % mod;
return arbitrary_module_poly(f, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator*=(const int& h) {
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i) data[i] = (ll)data[i] * h % mod;
return *this;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator+(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
if (f.size() < h.size()) f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) f[i] = (f[i] + h[i]) % mod;
return arbitrary_module_poly(f, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator+=(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) {
if (size() < h.size()) resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) data[i] = (data[i] + h[i]) % mod;
return *this;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator-(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
if (f.size() < h.size()) f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) f[i] = (f[i] + mod - h[i]) % mod;
return arbitrary_module_poly(f, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator-=(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) {
if (size() < h.size()) resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i)
data[i] = (data[i] + mod - h[i]) % mod;
return *this;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator<<(
const std::size_t& b) const {
std::vector<int> f(size() + b);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i) f[i + b] = data[i];
return arbitrary_module_poly(f, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator<<=(const std::size_t& b) {
return *this = (*this) << b;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator>>(
const std::size_t& b) const {
std::vector<int> f(size() - b);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i] = data[i + b];
return arbitrary_module_poly(f, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator>>=(const std::size_t& b) {
return *this = (*this) >> b;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::inv(void) const {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(size() + size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
arbitrary_module_poly f(1, mod), g(N, mod), h(*this), f2(1, mod);
f[0] = qpow(data[0], mod - 2, mod), h.resize(N), f2[0] = 2;
for (int w = 2; w < N; w <<= 1) {
g.resize(w);
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i) g[i] = h[i];
f = f * (f * g - f2) * (mod - 1);
f.resize(w);
}
f.resize(size());
return f;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::inv(const int& h) const {
arbitrary_module_poly f(*this);
f.resize(h);
return f.inv();
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator/(const int& h) const {
int inv = qpow(h, mod - 2, mod);
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i] = (ll)f[i] * inv % mod;
return arbitrary_module_poly(f, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator/=(const int& h) {
int inv = qpow(h, mod - 2, mod);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i) data[i] = (ll)data[i] * inv % mod;
return *this;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator==(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const {
if (size() != h.size() || mod != h.mod) return 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i)
if (data[i] != h[i]) return 0;
return 1;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator!=(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const {
if (size() != h.size() || mod != h.mod) return 1;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i)
if (data[i] != h[i]) return 1;
return 0;
}
arbitrary_module_poly sqrt(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(h.size() + h.size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
arbitrary_module_poly f(1, mod), g(N, mod), d(h);
f[0] = modsqrt(h[0], mod), d.resize(N);
for (int w = 2; w < N; w <<= 1) {
g.resize(w);
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i) g[i] = d[i];
f = (f + f.inv(w) * g) / 2;
f.resize(w);
}
f.resize(h.size());
return f;
}
arbitrary_module_poly log(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) {
arbitrary_module_poly f(h);
for (int i = 1; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i - 1] = (ll)f[i] * i % f.mod;
f[f.size() - 1] = 0, f = f * h.inv(), f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = (int)f.size() - 1; i > 0; --i)
f[i] = (ll)f[i - 1] * qpow(i, f.mod - 2, f.mod) % f.mod;
f[0] = 0;
return f;
}
typedef arbitrary_module_poly m_poly;
} // namespace fstdlib
#endif
2 代码格式
#ifndef _FEISTDLIB_POLY_
#define _FEISTDLIB_POLY_
/*
* This file is part of the fstdlib project.
* Version: Build v0.0.2
* You can check for details at https://github.com/FNatsuka/fstdlib
*/
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
namespace fstdlib {
typedef long long ll;
int mod = 998244353, grt = 3;
class poly {
private:
std::vector<int> data;
void out(void) {
for (int i = 0; i < (int)data.size(); ++i) printf("%d ", data[i]);
puts("");
}
public:
poly(std::size_t len = std::size_t(0)) { data = std::vector<int>(len); }
poly(const std::vector<int>& b) { data = b; }
poly(const poly& b) { data = b.data; }
void resize(std::size_t len, int val = 0) { data.resize(len, val); }
std::size_t size(void) const { return data.size(); }
void clear(void) { data.clear(); }
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
void shrink_to_fit(void) { data.shrink_to_fit(); }
#endif
int& operator[](std::size_t b) { return data[b]; }
const int& operator[](std::size_t b) const { return data[b]; }
poly operator*(const poly& h) const;
poly operator*=(const poly& h);
poly operator*(const int& h) const;
poly operator*=(const int& h);
poly operator+(const poly& h) const;
poly operator+=(const poly& h);
poly operator-(const poly& h) const;
poly operator-=(const poly& h);
poly operator<<(const std::size_t& b) const;
poly operator<<=(const std::size_t& b);
poly operator>>(const std::size_t& b) const;
poly operator>>=(const std::size_t& b);
poly operator/(const int& h) const;
poly operator/=(const int& h);
poly operator==(const poly& h) const;
poly operator!=(const poly& h) const;
poly operator+(const int& h) const;
poly operator+=(const int& h);
poly inv(void) const;
poly inv(const int& h) const;
friend poly sqrt(const poly& h);
friend poly log(const poly& h);
friend poly exp(const poly& h);
};
int qpow(int a, int b, int p = mod) {
int res = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) res = (ll)res * a % p;
a = (ll)a * a % p, b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
std::vector<int> rev;
void dft_for_module(std::vector<int>& f, int n, int b) {
static std::vector<int> w;
w.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (i < rev[i]) std::swap(f[i], f[rev[i]]);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i <<= 1) {
w[0] = 1, w[1] = qpow(grt, (mod - 1) / i);
if (b == -1) w[1] = qpow(w[1], mod - 2);
for (int j = 2; j < i / 2; ++j) w[j] = (ll)w[j - 1] * w[1] % mod;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j += i)
for (int k = 0; k < i / 2; ++k) {
int p = f[j + k], q = (ll)f[j + k + i / 2] * w[k] % mod;
f[j + k] = (p + q) % mod, f[j + k + i / 2] = (p - q + mod) % mod;
}
}
}
poly poly::operator*(const poly& h) const {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(size() + h.size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
std::vector<int> f(this->data), g(h.data);
f.resize(N), g.resize(N);
rev.resize(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? N >> 1 : 0);
dft_for_module(f, N, 1), dft_for_module(g, N, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) f[i] = (ll)f[i] * g[i] % mod;
dft_for_module(f, N, -1), f.resize(size() + h.size() - 1);
for (int i = 0, inv = qpow(N, mod - 2); i < (int)f.size(); ++i)
f[i] = (ll)f[i] * inv % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator*=(const poly& h) { return *this = *this * h; }
poly poly::operator*(const int& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i] = (ll)f[i] * h % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator*=(const int& h) {
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i) data[i] = (ll)data[i] * h % mod;
return *this;
}
poly poly::operator+(const poly& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
if (f.size() < h.size()) f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) f[i] = (f[i] + h[i]) % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator+=(const poly& h) {
std::vector<int>& f = this->data;
if (f.size() < h.size()) f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) f[i] = (f[i] + h[i]) % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator-(const poly& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
if (f.size() < h.size()) f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) f[i] = (f[i] - h[i] + mod) % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator-=(const poly& h) {
std::vector<int>& f = this->data;
if (f.size() < h.size()) f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) f[i] = (f[i] - h[i] + mod) % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator<<(const std::size_t& b) const {
std::vector<int> f(size() + b);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i) f[i + b] = data[i];
return f;
}
poly poly::operator<<=(const std::size_t& b) { return *this = (*this) << b; }
poly poly::operator>>(const std::size_t& b) const {
std::vector<int> f(size() - b);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i] = data[i + b];
return f;
}
poly poly::operator>>=(const std::size_t& b) { return *this = (*this) >> b; }
poly poly::operator/(const int& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
int inv = qpow(h, mod - 2);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i] = (ll)f[i] * inv % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator/=(const int& h) {
int inv = qpow(h, mod - 2);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)data.size(); ++i) data[i] = (ll)data[i] * inv % mod;
return *this;
}
poly poly::inv(void) const {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(size() + size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
std::vector<int> f(N), g(N), d(this->data);
d.resize(N), f[0] = qpow(d[0], mod - 2);
for (int w = 2; w < N; w <<= 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i) g[i] = d[i];
rev.resize(w << 1);
for (int i = 0; i < w * 2; ++i)
rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? w : 0);
dft_for_module(f, w << 1, 1), dft_for_module(g, w << 1, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < w * 2; ++i)
f[i] = (ll)f[i] * (2 + mod - (ll)f[i] * g[i] % mod) % mod;
dft_for_module(f, w << 1, -1);
for (int i = 0, inv = qpow(w << 1, mod - 2); i < w; ++i)
f[i] = (ll)f[i] * inv % mod;
for (int i = w; i < w * 2; ++i) f[i] = 0;
}
f.resize(size());
return f;
}
poly poly::operator==(const poly& h) const {
if (size() != h.size()) return 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i)
if (data[i] != h[i]) return 0;
return 1;
}
poly poly::operator!=(const poly& h) const {
if (size() != h.size()) return 1;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i)
if (data[i] != h[i]) return 1;
return 0;
}
poly poly::operator+(const int& h) const {
poly f(this->data);
f[0] = (f[0] + h) % mod;
return f;
}
poly poly::operator+=(const int& h) { return *this = (*this) + h; }
poly poly::inv(const int& h) const {
poly f(*this);
f.resize(h);
return f.inv();
}
int modsqrt(int h, int p = mod) { return 1; }
poly sqrt(const poly& h) {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(h.size() + h.size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
poly f(N), g(N), d(h);
d.resize(N), f[0] = modsqrt(d[0]);
for (int w = 2; w < N; w <<= 1) {
g.resize(w);
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i) g[i] = d[i];
f = (f + f.inv(w) * g) / 2;
f.resize(w);
}
f.resize(h.size());
return f;
}
poly log(const poly& h) {
poly f(h);
for (int i = 1; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i - 1] = (ll)f[i] * i % mod;
f[f.size() - 1] = 0, f = f * h.inv(), f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = (int)f.size() - 1; i > 0; --i)
f[i] = (ll)f[i - 1] * qpow(i, mod - 2) % mod;
f[0] = 0;
return f;
}
poly exp(const poly& h) {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(h.size() + h.size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
poly f(N), g(N), d(h);
f[0] = 1, d.resize(N);
for (int w = 2; w < N; w <<= 1) {
f.resize(w), g.resize(w);
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i) g[i] = d[i];
f = f * (g + 1 - log(f));
f.resize(w);
}
f.resize(h.size());
return f;
}
struct comp {
long double x, y;
comp(long double _x = 0, long double _y = 0) : x(_x), y(_y) {}
comp operator*(const comp& b) const {
return comp(x * b.x - y * b.y, x * b.y + y * b.x);
}
comp operator+(const comp& b) const { return comp(x + b.x, y + b.y); }
comp operator-(const comp& b) const { return comp(x - b.x, y - b.y); }
comp conj(void) { return comp(x, -y); }
};
const int EPS = 1e-9;
template <typename FLOAT_T>
FLOAT_T fabs(const FLOAT_T& x) {
return x > 0 ? x : -x;
}
template <typename FLOAT_T>
FLOAT_T sin(const FLOAT_T& x, const long double& EPS = fstdlib::EPS) {
FLOAT_T res = 0, delt = x;
int d = 0;
while (fabs(delt) > EPS) {
res += delt, ++d;
delt *= -x * x / ((2 * d) * (2 * d + 1));
}
return res;
}
template <typename FLOAT_T>
FLOAT_T cos(const FLOAT_T& x, const long double& EPS = fstdlib::EPS) {
FLOAT_T res = 0, delt = 1;
int d = 0;
while (fabs(delt) > EPS) {
res += delt, ++d;
delt *= -x * x / ((2 * d) * (2 * d - 1));
}
return res;
}
const long double PI = std::acos((long double)(-1));
void dft_for_complex(std::vector<comp>& f, int n, int b) {
static std::vector<comp> w;
w.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (i < rev[i]) std::swap(f[i], f[rev[i]]);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i <<= 1) {
w[0] = comp(1, 0), w[1] = comp(cos(2 * PI / i), b * sin(2 * PI / i));
for (int j = 2; j < i / 2; ++j) w[j] = w[j - 1] * w[1];
for (int j = 0; j < n; j += i)
for (int k = 0; k < i / 2; ++k) {
comp p = f[j + k], q = f[j + k + i / 2] * w[k];
f[j + k] = p + q, f[j + k + i / 2] = p - q;
}
}
}
class arbitrary_module_poly {
private:
std::vector<int> data;
int construct_element(int D, ll x, ll y, ll z) const {
x %= mod, y %= mod, z %= mod;
return ((ll)D * D * x % mod + (ll)D * y % mod + z) % mod;
}
public:
int mod;
arbitrary_module_poly(std::size_t len = std::size_t(0),
int module_value = 1e9 + 7) {
mod = module_value;
data = std::vector<int>(len);
}
arbitrary_module_poly(const std::vector<int>& b, int module_value = 1e9 + 7) {
mod = module_value;
data = b;
}
arbitrary_module_poly(const arbitrary_module_poly& b) {
mod = b.mod;
data = b.data;
}
void resize(std::size_t len, const int& val = 0) { data.resize(len, val); }
std::size_t size(void) const { return data.size(); }
void clear(void) { data.clear(); }
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
void shrink_to_fit(void) { data.shrink_to_fit(); }
#endif
int& operator[](std::size_t b) { return data[b]; }
const int& operator[](std::size_t b) const { return data[b]; }
arbitrary_module_poly operator*(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator*=(const arbitrary_module_poly& h);
arbitrary_module_poly operator*(const int& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator*=(const int& h);
arbitrary_module_poly operator+(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator+=(const arbitrary_module_poly& h);
arbitrary_module_poly operator-(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator-=(const arbitrary_module_poly& h);
arbitrary_module_poly operator<<(const std::size_t& b) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator<<=(const std::size_t& b);
arbitrary_module_poly operator>>(const std::size_t& b) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator>>=(const std::size_t& b);
arbitrary_module_poly operator/(const int& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator/=(const int& h);
arbitrary_module_poly operator==(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly operator!=(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const;
arbitrary_module_poly inv(void) const;
arbitrary_module_poly inv(const int& h) const;
friend arbitrary_module_poly sqrt(const arbitrary_module_poly& h);
friend arbitrary_module_poly log(const arbitrary_module_poly& h);
};
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator*(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(size() + h.size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
std::vector<comp> f(N), g(N), p(N), q(N);
const int D = std::sqrt(mod);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i)
f[i].x = data[i] / D, f[i].y = data[i] % D;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) g[i].x = h[i] / D, g[i].y = h[i] % D;
rev.resize(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? N >> 1 : 0);
dft_for_complex(f, N, 1), dft_for_complex(g, N, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
p[i] = (f[i] + f[(N - i) % N].conj()) * comp(0.50, 0) * g[i];
q[i] = (f[i] - f[(N - i) % N].conj()) * comp(0, -0.5) * g[i];
}
dft_for_complex(p, N, -1), dft_for_complex(q, N, -1);
std::vector<int> r(size() + h.size() - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)r.size(); ++i)
r[i] = construct_element(D, p[i].x / N + 0.5, (p[i].y + q[i].x) / N + 0.5,
q[i].y / N + 0.5);
return arbitrary_module_poly(r, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator*=(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) {
return *this = *this * h;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator*(const int& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i] = (ll)f[i] * h % mod;
return arbitrary_module_poly(f, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator*=(const int& h) {
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i) data[i] = (ll)data[i] * h % mod;
return *this;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator+(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
if (f.size() < h.size()) f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) f[i] = (f[i] + h[i]) % mod;
return arbitrary_module_poly(f, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator+=(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) {
if (size() < h.size()) resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) data[i] = (data[i] + h[i]) % mod;
return *this;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator-(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const {
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
if (f.size() < h.size()) f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i) f[i] = (f[i] + mod - h[i]) % mod;
return arbitrary_module_poly(f, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator-=(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) {
if (size() < h.size()) resize(h.size());
for (int i = 0; i < (int)h.size(); ++i)
data[i] = (data[i] + mod - h[i]) % mod;
return *this;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator<<(
const std::size_t& b) const {
std::vector<int> f(size() + b);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i) f[i + b] = data[i];
return arbitrary_module_poly(f, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator<<=(const std::size_t& b) {
return *this = (*this) << b;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator>>(
const std::size_t& b) const {
std::vector<int> f(size() - b);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i] = data[i + b];
return arbitrary_module_poly(f, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator>>=(const std::size_t& b) {
return *this = (*this) >> b;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::inv(void) const {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(size() + size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
arbitrary_module_poly f(1, mod), g(N, mod), h(*this), f2(1, mod);
f[0] = qpow(data[0], mod - 2, mod), h.resize(N), f2[0] = 2;
for (int w = 2; w < N; w <<= 1) {
g.resize(w);
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i) g[i] = h[i];
f = f * (f * g - f2) * (mod - 1);
f.resize(w);
}
f.resize(size());
return f;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::inv(const int& h) const {
arbitrary_module_poly f(*this);
f.resize(h);
return f.inv();
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator/(const int& h) const {
int inv = qpow(h, mod - 2, mod);
std::vector<int> f(this->data);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i] = (ll)f[i] * inv % mod;
return arbitrary_module_poly(f, mod);
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator/=(const int& h) {
int inv = qpow(h, mod - 2, mod);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i) data[i] = (ll)data[i] * inv % mod;
return *this;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator==(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const {
if (size() != h.size() || mod != h.mod) return 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i)
if (data[i] != h[i]) return 0;
return 1;
}
arbitrary_module_poly arbitrary_module_poly::operator!=(
const arbitrary_module_poly& h) const {
if (size() != h.size() || mod != h.mod) return 1;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)size(); ++i)
if (data[i] != h[i]) return 1;
return 0;
}
arbitrary_module_poly sqrt(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) {
int N = 1;
while (N < (int)(h.size() + h.size() - 1)) N <<= 1;
arbitrary_module_poly f(1, mod), g(N, mod), d(h);
f[0] = modsqrt(h[0], mod), d.resize(N);
for (int w = 2; w < N; w <<= 1) {
g.resize(w);
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i) g[i] = d[i];
f = (f + f.inv(w) * g) / 2;
f.resize(w);
}
f.resize(h.size());
return f;
}
arbitrary_module_poly log(const arbitrary_module_poly& h) {
arbitrary_module_poly f(h);
for (int i = 1; i < (int)f.size(); ++i) f[i - 1] = (ll)f[i] * i % f.mod;
f[f.size() - 1] = 0, f = f * h.inv(), f.resize(h.size());
for (int i = (int)f.size() - 1; i > 0; --i)
f[i] = (ll)f[i - 1] * qpow(i, f.mod - 2, f.mod) % f.mod;
f[0] = 0;
return f;
}
typedef arbitrary_module_poly m_poly;
} // namespace fstdlib
#endif
相关文章:

23种设计模式之单例模式(懒汉,饿汉,线程安全懒汉)
我们知道设计模式分为23种但是具体划分的话,又分为三大类①:创建型②:结构型③:行为型,本文会介绍创建型的单例模式希望各位能够简单的去了解单例模式以及能够在正常的开发中得到运用,单例模式常见的有饿汉型单例模式、懒汉型单例模式、懒汉线程安全型单例模式,实际上单例模式有七种左右,本文仅介绍常见的三种。从具体实现角度来说,就是以下三点:一是单例模式的类只提供私有的构造函数,二是类定义中含有一个该类的静态私有对象,三是该类提供了一个静态的公有的函数用于创建或获取它本身的静态私有对象。显然单例模式的要点有三个;
23种设计模式之代理模式(抽象层,代理者,被代理者)
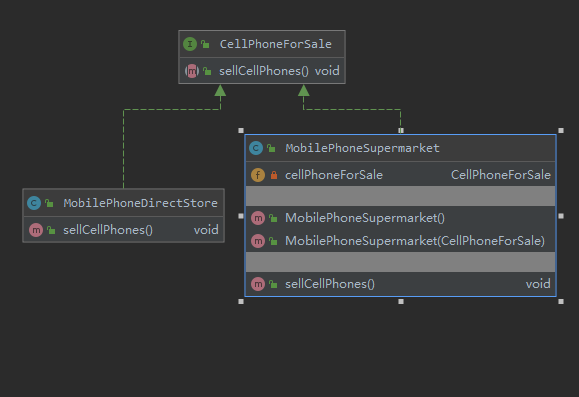
设计模式原则之一开闭原则简而言之就是扩展开发修改关闭以上面的案例来说扩展开发当我们将手机直营店代理后,只要抽象层手机出售接口拥有的行为 我们的手机超市都可以拥有,当手机直营店行为不是特别满足需求时,我们也可以在手机超市上去为手机直营店进行扩展。修改关闭手机超市并不能改变手机直营店的出售手机行为,能对原有的业务进行扩展,并且不修改原有的代码,这就是开闭原则。异变代理模式个人认为 代理模式只是为了控制外界对被代理对象的访问,不应该因为业务需求强行在代理类中增加业务代码,不然跟装饰者模式有什么区别呢?
spring 笔记一 spring快速入门和配置文件详解
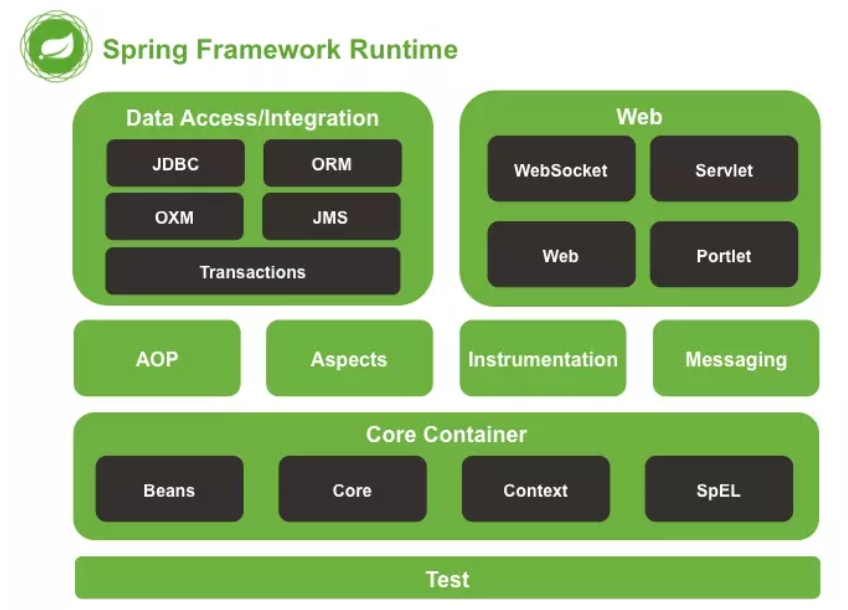
Spring是分层的 Java SE/EE应用full-stack 轻量级开源框架,以 IoC(Inverse Of Control:反转控制)和AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming:面向切面编程)为内核。提供了展现层SpringMVC 和持久层 Spring JDBCTemplate以及业务层事务管理等众多的企业级应用技术,还能整合开源世界众多著名的第三方框架和类库,逐渐成为使用最多的Java EE 企业应用开源框架。

spring 笔记二 spring配置数据源和整合测试功能
• 数据源(连接池)是提高程序性能如出现的• 事先实例化数据源,初始化部分连接资源• 使用连接资源时从数据源中获取• 使用完毕后将连接资源归还给数据源常见的数据源(连接池):DBCP、C3P0、BoneCP、Druid① 导入数据源的坐标和数据库驱动坐标② 创建数据源对象③ 设置数据源的基本连接数据④ 使用数据源获取连接资源和归还连接资源。
【Spring boot】RedisTemplate中String、Hash、List设置过期时间
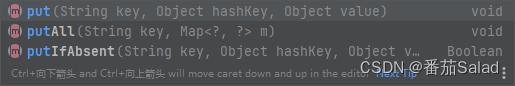
putIfAbsent 指的是如果传入key对应的value已经存在,就返回存在的value,不进行替换。如果不存在,就添加key和value,返回null。如果传入key对应的value已经存在,就返回存在的value,不进行替换。如果不存在,就添加key和value,返回null。下面这两句话,可以实现向Redis插入Hash数据,并且设置整个Hash的过期时间。TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS:毫秒。TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS:微秒。TimeUnit.MINUTES:分。

【Harmony】鸿蒙操作系统架构
鸿蒙操作系统以其微内核架构、分布式能力和全场景覆盖的设计理念,成为当前技术领域一颗璀璨的明星。其架构设计满足了当前多样化的设备需求,注重了设备之间的协同工作和开发者的友好体验。随着鸿蒙操作系统的不断演进和生态系统的丰富,我们对于这个在全球范围内掀起一场科技变革的产物充满期待。在未来的智能互联时代,鸿蒙操作系统必将发挥更为重要的作用,引领技术的潮流。_鸿蒙系统的架构

Redis的opsForValue()和boundValueOps()区别
该模板的序列化机制改变起来也很容易,并且Redis模块在org.springframework.data.redis.serializer包中提供了多种可用的实现,详情请参考Serializers。大部分的用户都喜欢用RedisTemplate,它相应的包是org.springframework.data.redis.core。虽然RedisConnection提供接受和返回二进制值(字节数组)的低级方法,但该模板可以处理序列化和连接管理,使得用户不需要处理太多的细节。如果 两者是实现的效果是相同的。

C/C++,动态 DP 问题的计算方法与源程序
C/C++,动态 DP 问题的计算方法与源程序

软路由R4S+iStoreOS如何实现公网远程桌面本地电脑
本文主要讲解如何使用软路由R4S和iStoreOS实现公网远程桌面本地电脑

将labelme标注的人体姿态Json文件转成训练Yolov8-Pose的txt格式
最近在训练Yolov8-Pose时遇到一个问题,就是如何将自己使用labelme标注的Json文件转化成可用于Yolov8-Pose训练的txt文件。

【redis】Redis中AOF的重写机制
为了避免子进程在重写过程过程中,主进程中的数据发生变化,导致AOF文件里面的数据和redis内存中的数据不一致,redis中还做了一个优化,也就是说在子进程在做这个重写的过程中,主进程中的数据变更,需要追加到AOF的重写缓冲区中,等到AOF重写完成以后,再把AOF重写缓冲区的数据,追加到新的AOF文件里面,这样意料就能保证新的AOF文件里面的数据和当前Redis中的数据保持一致。子进程在进行重写的过程中,主进程依然可以去处理客户端的一个请求,这样一来子进程在重写的过程中,不耽误客户端的使用。

【redis】为什么Redis集群的最大槽数是16384个?
对网络同学开销的平衡:redis集群中的每个节点,会发送心跳消息,而心跳包中会携带节点的完整配置,他能够以幂等的方式来实现配置的更新。但是修改集群的槽位数量需要进行数据迁移和重新均衡,会对集群产生较大的影响,因此一般情况下建议使用默认的 16384 个槽位。可用性和容错性:16384 是一个较大的数字,可以提供足够的槽位数量来分布数据,从而提高集群的可用性和容错性。应用程序去存储一个key的时候会通过,对key进行一个CRC16去计算,再取模,然后路由到hash slot所在的节点。
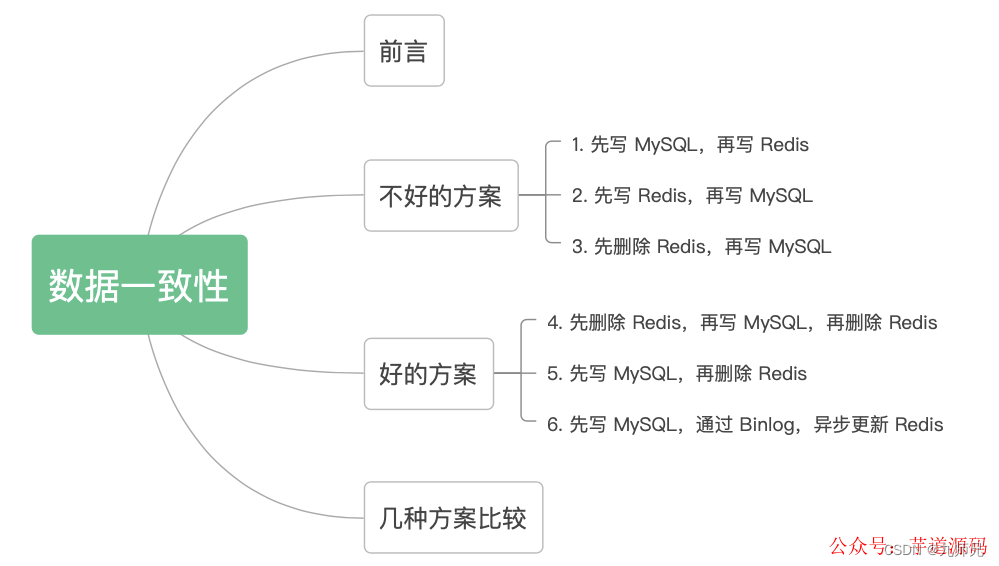
【redis】技术派中的缓存一致性解决方案
对于上面这种情况,对于第一次查询,请求 B 查询的数据是 10,但是 MySQL 的数据是 11,只存在这一次不一致的情况,对于不是强一致性要求的业务,可以容忍。这个图已经画的很清晰了,我就不用再去啰嗦了吧,不过这里有个前提,就是对于读请求,先去读 Redis,如果没有,再去读 DB,但是读请求不会再回写 Redis。请求 A、B 都是先写 MySQL,然后再写 Redis,在高并发情况下,如果请求 A 在写 Redis 时卡了一会,请求 B 已经依次完成数据的更新,就会出现图中的问题。

讲解cv2.setNumThreads
本文讲解了 cv2.setNumThreads 函数的作用和用法。通过设置并行处理的线程数目,我们可以控制 OpenCV 在图像和视频处理中使用的线程数量,从而提高程序的性能和效率。了解和正确使用 cv2.setNumThreads 函数对于优化计算机视觉应用程序的性能非常重要。希望本文能对读者理解并正确使用 cv2.setNumThreads 函数提供帮助。

讲解undefined reference to symbol ‘_ZN2cv7imwriteERKNS_6StringERKNS_11_InputArrayERKSt6vectorIiSaIiEE‘
在本文中,我们讨论了一个常见的错误信息,并解释了它的含义以及可能的解决方法。请记住,在遇到这种错误时,你应该首先确认是否正确链接库文件,包含正确的头文件,正确配置环境以及检查版本兼容性。通过采取适当的措施,你应该能够解决这个错误并顺利编译和链接你的程序。当遇到这个错误时,通常是因为在编译和链接时没有正确地指定OpenCV库文件。下面是一个示例代码,展示了如何使用OpenCV的imwrite函数来保存图像。首先,你需要确保你的系统已经安装了OpenCV,并正确配置了环境。// 读取图像if (!

讲解Expected more than 1 value per channel when training, got input size torch.Size
在训练深度学习模型时,遇到错误消息"Expected more than 1 value per channel when training, got input size torch.Size"时,我们需要检查数据预处理的过程,确保输入数据的形状满足模型的要求。通过检查数据形状、数据预处理代码和模型的输入层,我们可以找出错误的原因并进行修复。这样,我们就可以成功训练模型并获得预期的结果。

讲解RuntimeError: cudnn64_7.dll not found.
"RuntimeError: cudnn64_7.dll not found" 错误是在使用GPU加速深度学习过程中的常见错误之一。本文介绍了解决这个错误的几种常见方法,包括检查CUDA和cuDNN的安装、确认环境变量配置、检查软件依赖关系以及重新安装CUDA和cuDNN。通过按照以上步骤逐一排查和解决,您应该能够成功地解决这个错误,并顺利进行GPU加速的深度学习任务。祝您顺利完成深度学习项目!

讲解Attempting to deserialize object on a CUDA device but torch.cuda.is_available() is False
"Attempting to deserialize object on a CUDA device but torch.cuda.is_available() is False" 错误提示表明您的代码尝试将一个在 CUDA 设备上训练好的模型加载到不支持 CUDA 的设备上,或者是将其加载到 CPU 上。在 PyTorch 中,当您试图将一个已经在 CUDA 设备上训练好的模型加载到 CPU 上时,或者当尝试将一个在 CUDA 设备上训练好的模型加载到不支持 CUDA 的设备上时,就会出现这个错误。

C/C++,图算法——Dinic最大流量算法
C/C++,图算法——Dinic最大流量算法
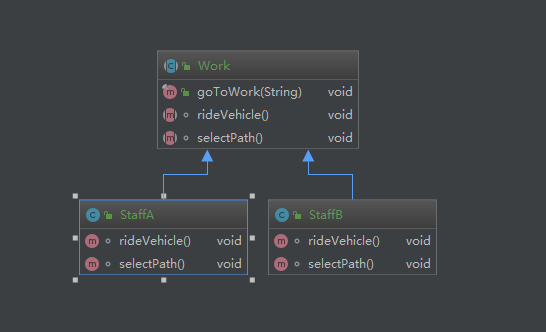
23种设计模式之模板方法模式(模板模式)
分别运行StaffA以及StaffB这两个类我们可以看到整个的步骤顺序是没有变的,只有交通工具以及路线发生了变化,个人认为代码已经诠释了模板模式的精髓,我们平时出现多个类似的功能功能点比如解析DOC文件或者XLSX等不同的文件,前期一些初始化的操作可以封装到模板方法中,到了具体解析哪一种类型的文件,再去交给子类实现。比如,在 Hibernate 中,Session 是一个抽象类,它定义了一系列的模板方法,如 save()、update() 和 delete(),用于执行数据库操作。②:出行交通工具的选择。
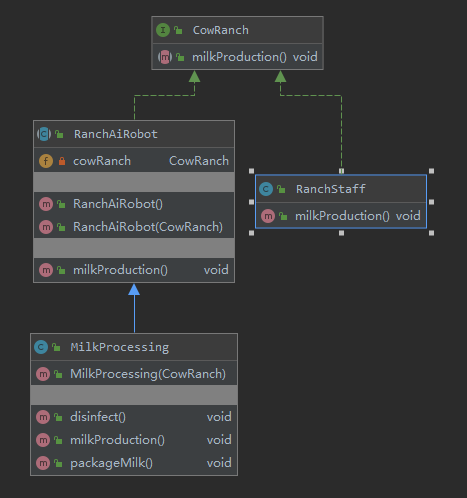
23种设计模式之装饰者模式(被装饰者,接口层,装饰抽象层,具体装饰者)
装饰者模式 其核心就是为了增强方法,对原业务的扩展,以上面的场景来说,牧场工作人员只做牛奶的生产,但是想要对牛奶进行销售,只生产是不够的,生产前后都需要增加其他的行为。装饰抽象层存在的意义抽象类实现接口,可以选择性的去实现接口的抽象方法,并不需要重写接口所有方法,装饰抽象层可以精确的让具体装饰者去装饰某一个行为。异变代理模式。

Java 线程的基本概念
当 Context Switch 发生时,需要由操作系统保存当前线程的状态,并恢复另一个线程的状态,Java 中对应的概念就是程序计数器(Program Counter Register),它的作用是记住下一条 jvm 指令的执行地址,是线程私有的。有一种特殊的线程叫做守护线程,只要其它非守护线程运行结束了,即使守护线程的代码没有执行完,也会强制结束.程序在 t1 线程运行,FileReader.read() 方法调用是异步的。打断 sleep 的线程, 会清空打断状态,以 sleep 为例。

【Redis】Redis的事务碰上Spring的事务 @Transactional导致问题
建议大家去看原文,这里是学到了,记录一下。最近项目的生产环境遇到一个奇怪的问题:现象 :每天早上客服人员在后台创建客服事件时,都会创建失败。当我们重启 这个微服务后,后台就可以正常创建了客服事件了。到第二天早上又会创建失败,又得重启这个微服务才行。初步排查 :创建一个客服事件时,会用到 Redis 的递增操作来生成一个唯一的分布式 ID 作为事件 id。而恰巧每天早上这个递增操作都会返回 null,进而导致后面的一系列逻辑出错,保存客服事件失败。当重启微服务后,这个递增操作又正常了。

【redis】bitmap技术解析:redis与roaringBitmap
然后再看这个好理解一些。bitmap的表象意义是,使用一个01标识位来表示是否的状态,可以达到节省空间和高效判定的效果。在我们的实际工作中,也有着许多的应用场景,相信了解bitmap定会给你带来一些额外的收获。

【Linux系统化学习】进程的父子关系 | fork 进程
本篇文章介绍了进程的父子关系和使用fork函数创建一个进程!

【Linux系统化学习】探索进程的奥秘 | 第一个系统调用
本片文章主要介绍了Linux下的进程和第一个系统调用。

【C++干货铺】解密vector底层逻辑
本片文章主要是vector的介绍使用和手撕模拟实现!!!!

【C++干货铺】剖析string | 底层实现
探索string底层,模拟实现string。

【Linux系统化学习】冯诺依曼体系结构 | 操作系统
本篇文章介绍了冯诺依曼体系结构,描述了操作系统。

【C++干货铺】STL简述 | string类的使用指南
STL简述!!! string类接口使用指南!!!
