C++/C++11中std::set用法汇总
一个容器就是一些特定类型对象的集合。顺序容器(sequential container)为程序员提供了控制元素存储和访问顺序的能力。这种顺序不依赖于元素的值,而是与元素加入容器时的位置相对应。与之相对的,有序和无序关联容器,则根据关键字的值来存储元素。
标准库还提供了三种容器适配器,分别为容器操作定义了不同的接口,来与容器类型适配:stack、queue和priority_queue。适配器(adaptor)是标准库中的一个通用概念。容器、迭代器和函数都有适配器。本质上,一个适配器是一种机制,能使某种事物的行为看起来像另外一种事物一样。一个容器适配器接受一种已有的容器类型,使其行为看起来像一种不同的类型。
顺序容器包括vector、deque、list、forward_list、array、string,所有顺序容器都提供了快速顺序访问元素的能力。
关联容器和顺序容器有着根本的不同:关联容器中的元素是按关键字来保存和访问的。与之相对,顺序容器中的元素是按它们在容器中的位置来顺序保存和访问的。
类似顺序容器,关联容器也是模板。
关联容器不支持顺序容器的位置相关的操作。原因是关联容器中元素是根据关键字存储的,这些操作对关联容器没有意义。而且,关联容器也不支持构造函数或插入操作这些接受一个元素值和一个数量值得操作。
关联容器支持高效的关键字查找和访问。两个主要的关联容器(associative container)类型是map和set。map中的元素是一些关键字----值(key--value)对:关键字起到索引的作用,值则表示与索引相关联的数据。set中每个元素只包含一个关键字:set支持高效的关键字查询操作----检查一个给定关键字是否在set中。
标准库提供8个关联容器:
(1)、按关键字有序保存元素:map(关联数组:保存关键字----值对);set(关键字即值,即只保存关键字的容器);multimap(关键字可重复出现的map);multiset(关键字可重复出现的set);
(2)、无序集合:unordered_map(用哈希函数组织的map);unordered_set(用哈希函数组织的set);unordered_multimap(哈希组织的map,关键字可以重复出现);unordered_multiset(哈希组织的sest,关键字可以重复出现)。
map是关键字----值对的集合,与之相对,set就是关键字的简单集合。当只是想知道一个值是否存在时,set是最有用的。
在set中每个元素的值都唯一,而且系统能根据元素的值自动进行排序。Set中元素的值不能直接被改变。set内部采用的是一种非常高效的平衡检索二叉树:红黑树,也称为RB树(Red-Black Tree)。RB树的统计性能要好于一般平衡二叉树。
下面是从cplusplus和cppreference网站摘录的测试代码:
#include "set.hpp"
#include <set>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cassert>
#include <chrono>
#include <functional>
#include <iomanip>// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/set/set/
static bool fncomp(int lhs, int rhs) { return lhs<rhs; }struct classcomp {bool operator() (const int& lhs, const int& rhs) const{return lhs<rhs;}
};int test_set_cplusplus()
{
{ // set:构造函数std::set<int> first; // empty set of intsint myints[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };std::set<int> second(myints, myints + 5); // rangestd::set<int> third(second); // a copy of secondstd::set<int> fourth(second.begin(), second.end()); // iterator ctor.std::set<int, classcomp> fifth; // class as Comparebool(*fn_pt)(int, int) = fncomp;std::set<int, bool(*)(int, int)> sixth(fn_pt); // function pointer as Compare
}{ // begin/end:返回指向第一个元素的迭代/返回指向最后一个元素之后的迭代器,不是最后一个元素int myints[] = { 75, 23, 65, 42, 13 };std::set<int> myset(myints, myints + 5);std::cout << "myset contains:";for (std::set<int>::iterator it = myset.begin(); it != myset.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';
}{ // clear:清除所有元素std::set<int> myset;myset.insert(100);myset.insert(200);myset.insert(300);std::cout << "myset contains:";for (std::set<int>::iterator it = myset.begin(); it != myset.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';myset.clear();myset.insert(1101);myset.insert(2202);std::cout << "myset contains:";for (std::set<int>::iterator it = myset.begin(); it != myset.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';
}{ // count:判断某一个关键字是否在set内,返回0或者1std::set<int> myset;// set some initial values:for (int i = 1; i<5; ++i) myset.insert(i * 3); // set: 3 6 9 12for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {std::cout << i;if (myset.count(i) != 0)std::cout << " is an element of myset.\n";elsestd::cout << " is not an element of myset.\n";}}{ // cbegin/cend(c++11): Returns a const_iterator pointing to the first element in the container/// Returns a const_iterator pointing to the past-the-end element in the containerstd::set<int> myset = { 50, 20, 60, 10, 25 };std::cout << "myset contains:";for (auto it = myset.cbegin(); it != myset.cend(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';
}{ // crbegin/crend(c++11):Return const_reverse_iterator to reverse beginning/// Return const_reverse_iterator to reverse endstd::set<int> myset = { 50, 20, 60, 10, 25 };std::cout << "myset backwards:";for (auto rit = myset.crbegin(); rit != myset.crend(); ++rit)std::cout << ' ' << *rit;std::cout << '\n';
}{ // emplace(c++11):如果新元素的值是唯一的,将插入该元素std::set<std::string> myset;myset.emplace("foo");myset.emplace("bar");auto ret = myset.emplace("foo");if (!ret.second) std::cout << "foo already exists in myset\n";
}{ // emplace_hint(c++11):Construct and insert element with hintstd::set<std::string> myset;auto it = myset.cbegin();myset.emplace_hint(it, "alpha");it = myset.emplace_hint(myset.cend(), "omega");it = myset.emplace_hint(it, "epsilon");it = myset.emplace_hint(it, "beta");std::cout << "myset contains:";for (const std::string& x : myset)std::cout << ' ' << x;std::cout << '\n';
}{ // empty:如果集合为空,返回truestd::set<int> myset;myset.insert(20);myset.insert(30);myset.insert(10);std::cout << "myset contains:";while (!myset.empty()) {std::cout << ' ' << *myset.begin();myset.erase(myset.begin());}std::cout << '\n';
}{ // equal_range:返回集合中与给定值相等的上下限的两个迭代器std::set<int> myset;for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) myset.insert(i * 10); // myset: 10 20 30 40 50std::pair<std::set<int>::const_iterator, std::set<int>::const_iterator> ret;ret = myset.equal_range(30);std::cout << "the lower bound points to: " << *ret.first << '\n';std::cout << "the upper bound points to: " << *ret.second << '\n';
}{ // erase:删除集合中的元素std::set<int> myset;std::set<int>::iterator it;// insert some values:for (int i = 1; i<10; i++) myset.insert(i * 10); // 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90it = myset.begin();++it; // "it" points now to 20myset.erase(it);myset.erase(40);it = myset.find(60);myset.erase(it, myset.end());std::cout << "myset contains:";for (it = myset.begin(); it != myset.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';
}{ // find:返回一个指向被查找到元素的迭代器,如果没找到则返回end()std::set<int> myset;std::set<int>::iterator it;// set some initial values:for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) myset.insert(i * 10); // set: 10 20 30 40 50it = myset.find(20);myset.erase(it);myset.erase(myset.find(40));std::cout << "myset contains:";for (it = myset.begin(); it != myset.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';
}{ // get_allocator:返回集合set的分配器std::set<int> myset;int * p;unsigned int i;// allocate an array of 5 elements using myset's allocator:p = myset.get_allocator().allocate(5);// assign some values to arrayfor (i = 0; i<5; i++) p[i] = (i + 1) * 10;std::cout << "The allocated array contains:";for (i = 0; i<5; i++) std::cout << ' ' << p[i];std::cout << '\n';myset.get_allocator().deallocate(p, 5);
}{ // insert:在集合中插入元素std::set<int> myset;std::set<int>::iterator it;std::pair<std::set<int>::iterator, bool> ret;// set some initial values:for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) myset.insert(i * 10); // set: 10 20 30 40 50ret = myset.insert(20); // no new element insertedif (ret.second == false) it = ret.first; // "it" now points to element 20myset.insert(it, 25); // max efficiency insertingmyset.insert(it, 24); // max efficiency insertingmyset.insert(it, 26); // no max efficiency insertingint myints[] = { 5, 10, 15 }; // 10 already in set, not insertedmyset.insert(myints, myints + 3);std::cout << "myset contains:";for (it = myset.begin(); it != myset.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';
}{ // key_comp:Returns a copy of the comparison object used by the containerstd::set<int> myset;int highest;std::set<int>::key_compare mycomp = myset.key_comp();for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) myset.insert(i);std::cout << "myset contains:";highest = *myset.rbegin();std::set<int>::iterator it = myset.begin();do {std::cout << ' ' << *it;} while (mycomp(*(++it), highest));std::cout << '\n';
}{ // lower_bond:返回指向大于(或等于)某值的第一个元素的迭代器std::set<int> myset;std::set<int>::iterator itlow, itup;for (int i = 1; i<10; i++) myset.insert(i * 10); // 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90itlow = myset.lower_bound(30); // ^itup = myset.upper_bound(60); // ^myset.erase(itlow, itup); // 10 20 70 80 90std::cout << "myset contains:";for (std::set<int>::iterator it = myset.begin(); it != myset.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';
}{ // max_size:返回集合能容纳的元素的最大限值int i;std::set<int> myset;if (myset.max_size() > 1000) {for (i = 0; i<1000; i++) myset.insert(i);std::cout << "The set contains 1000 elements.\n";} elsestd::cout << "The set could not hold 1000 elements.\n";
}{ // operator =:Assigns new contents to the container, replacing its current contentint myints[] = { 12, 82, 37, 64, 15 };std::set<int> first(myints, myints + 5); // set with 5 intsstd::set<int> second; // empty setsecond = first; // now second contains the 5 intsfirst = std::set<int>(); // and first is emptystd::cout << "Size of first: " << int(first.size()) << '\n';std::cout << "Size of second: " << int(second.size()) << '\n';
}{ // rbegin/rend:返回指向集合中最后一个元素的反向迭代器/返回指向集合中第一个元素的反向迭代器int myints[] = { 21, 64, 17, 78, 49 };std::set<int> myset(myints, myints + 5);std::set<int>::reverse_iterator rit;std::cout << "myset contains:";for (rit = myset.rbegin(); rit != myset.rend(); ++rit)std::cout << ' ' << *rit;std::cout << '\n';
}{ // size:集合中元素的数目std::set<int> myints;std::cout << "0. size: " << myints.size() << '\n';for (int i = 0; i<10; ++i) myints.insert(i);std::cout << "1. size: " << myints.size() << '\n';myints.insert(100);std::cout << "2. size: " << myints.size() << '\n';myints.erase(5);std::cout << "3. size: " << myints.size() << '\n';
}{ // swap:交换两个集合变量int myints[] = { 12, 75, 10, 32, 20, 25 };std::set<int> first(myints, myints + 3); // 10,12,75std::set<int> second(myints + 3, myints + 6); // 20,25,32first.swap(second);std::cout << "first contains:";for (std::set<int>::iterator it = first.begin(); it != first.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';std::cout << "second contains:";for (std::set<int>::iterator it = second.begin(); it != second.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';
}{ // upper_bound:返回大于某个值元素的迭代器std::set<int> myset;std::set<int>::iterator itlow, itup;for (int i = 1; i<10; i++) myset.insert(i * 10); // 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90itlow = myset.lower_bound(30); // ^itup = myset.upper_bound(60); // ^myset.erase(itlow, itup); // 10 20 70 80 90std::cout << "myset contains:";for (std::set<int>::iterator it = myset.begin(); it != myset.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';
}{ // value_comp:Returns a copy of the comparison object used by the containerstd::set<int> myset;std::set<int>::value_compare mycomp = myset.value_comp();for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) myset.insert(i);std::cout << "myset contains:";int highest = *myset.rbegin();std::set<int>::iterator it = myset.begin();do {std::cout << ' ' << *it;} while (mycomp(*(++it), highest));std::cout << '\n';
}{ // relational operators:==/!=/</<=/>/>=std::set<int> foo, bar;foo.insert(10);bar.insert(20);bar.insert(30);foo.insert(40);// foo ({10,40}) vs bar ({20,30}):if (foo == bar) std::cout << "foo and bar are equal\n";if (foo != bar) std::cout << "foo and bar are not equal\n";if (foo< bar) std::cout << "foo is less than bar\n";if (foo> bar) std::cout << "foo is greater than bar\n";if (foo <= bar) std::cout << "foo is less than or equal to bar\n";if (foo >= bar) std::cout << "foo is greater than or equal to bar\n";
}return 0;
}// reference: http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container/set
struct Point { double x, y; };
struct PointCmp {bool operator()(const Point& lhs, const Point& rhs) const {return std::hypot(lhs.x, lhs.y) < std::hypot(rhs.x, rhs.y);}
};static void display_sizes(const std::set<int> &nums1, const std::set<int> &nums2, const std::set<int> &nums3)
{std::cout << "nums1: " << nums1.size()<< " nums2: " << nums2.size()<< " nums3: " << nums3.size() << '\n';
}class Dew
{
private:int a;int b;int c;public:Dew(int _a, int _b, int _c): a(_a), b(_b), c(_c){}bool operator<(const Dew &other) const{if (a < other.a)return true;if (a == other.a && b < other.b)return true;return (a == other.a && b == other.b && c < other.c);}
};const int nof_operations = 120;int set_emplace() {std::set<Dew> set;for (int i = 0; i < nof_operations; ++i)for (int j = 0; j < nof_operations; ++j)for (int k = 0; k < nof_operations; ++k)set.emplace(i, j, k);return set.size();
}int set_insert() {std::set<Dew> set;for (int i = 0; i < nof_operations; ++i)for (int j = 0; j < nof_operations; ++j)for (int k = 0; k < nof_operations; ++k)set.insert(Dew(i, j, k));return set.size();
}void timeit(std::function<int()> set_test, std::string what = "") {auto start = std::chrono::system_clock::now();int setsize = set_test();auto stop = std::chrono::system_clock::now();std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli> time = stop - start;if (what.size() > 0 && setsize > 0) {std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2)<< time.count() << " ms for " << what << '\n';}
}int test_set_cppreference()
{
{ // constructor: constructs the set // (1) Default constructorstd::set<std::string> a;a.insert("cat");a.insert("dog");a.insert("horse");for (auto& str : a) std::cout << str << ' ';std::cout << '\n';// (2) Iterator constructorstd::set<std::string> b(a.find("dog"), a.end());for (auto& str : b) std::cout << str << ' ';std::cout << '\n';// (3) Copy constructorstd::set<std::string> c(a);c.insert("another horse");for (auto& str : c) std::cout << str << ' ';std::cout << '\n';// (4) Move constructorstd::set<std::string> d(std::move(a));for (auto& str : d) std::cout << str << ' ';std::cout << '\n';std::cout << "moved-from set is ";for (auto& str : a) std::cout << str << ' ';std::cout << '\n';// (5) Initializer list constructorstd::set<std::string> e{ "one", "two", "three", "five", "eight" };for (auto& str : e) std::cout << str << ' ';std::cout << '\n';// custom comparisonstd::set<Point, PointCmp> z = { { 2, 5 }, { 3, 4 }, { 1, 1 } };z.insert({ 1, -1 }); // this fails because the magnitude of 1,-1 equals 1,1for (auto& p : z) std::cout << '(' << p.x << ',' << p.y << ") ";std::cout << '\n';
}{ // operator = : assigns values to the container std::set<int> nums1{ 3, 1, 4, 6, 5, 9 };std::set<int> nums2;std::set<int> nums3;std::cout << "Initially:\n";display_sizes(nums1, nums2, nums3);// copy assignment copies data from nums1 to nums2nums2 = nums1;std::cout << "After assigment:\n";display_sizes(nums1, nums2, nums3);// move assignment moves data from nums1 to nums3,// modifying both nums1 and nums3nums3 = std::move(nums1);std::cout << "After move assigment:\n";display_sizes(nums1, nums2, nums3);
}{ // get_allocator: returns the associated allocator
}{ // begin/end(cbegin/cend): returns an iterator to the beginning /returns an iterator to the endstd::set<int> set = { 6, 1, 3, 4, 2, 5 };for (auto it = set.begin(); it != set.end(); ++it)std::cout << *it << "\n";
}{ // rbegin/rend(crbegin/crend): returns a reverse iterator to the beginning /returns a reverse iterator to the end
}{ // empty: checks whether the container is empty std::set<int> numbers;std::cout << "Initially, numbers.empty(): " << numbers.empty() << '\n';numbers.insert(42);numbers.insert(13317);std::cout << "After adding elements, numbers.empty(): " << numbers.empty() << '\n';
}{ // size: returns the number of elements std::set<int> nums{ 1, 3, 5, 7 };std::cout << "nums contains " << nums.size() << " elements.\n";
}{ // max_size: returns the maximum possible number of elements std::set<char> s;std::cout << "Maximum size of a 'set' is " << s.max_size() << "\n";
}{ // clear: clears the contents
}{ // insert: inserts elementsstd::set<int> set;auto result_1 = set.insert(3);assert(result_1.first != set.end()); // it's a valid iteratorassert(*result_1.first == 3);if (result_1.second)std::cout << "insert done\n";auto result_2 = set.insert(3);assert(result_2.first == result_1.first); // same iteratorassert(*result_2.first == 3);if (!result_2.second)std::cout << "no insertion\n";
}{ // emplace(c++11): constructs element in-place set_insert();timeit(set_insert, "insert");timeit(set_emplace, "emplace");timeit(set_insert, "insert");timeit(set_emplace, "emplace");
}{ // emplace_hint(c++11): constructs elements in-place using a hint // reference: http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container/set/emplace_hint
}{ // erase: erases elements std::set<int> c = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };// erase all odd numbers from cfor (auto it = c.begin(); it != c.end();)if (*it % 2 == 1)it = c.erase(it);else++it;for (int n : c)std::cout << n << ' ';
}{ // swap: swaps the contents
}{ // count: returns the number of elements matching specific key
}{ // find: finds element with specific key std::set<int> example = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };auto search = example.find(2);if (search != example.end()) {std::cout << "Found " << (*search) << '\n';}else {std::cout << "Not found\n";}
}{ // equal_range: returns range of elements matching a specific key
}{ // lower_bound: returns an iterator to the first element not less than the given key
}{ // upper_bound: returns an iterator to the first element greater than the given key
}{ // key_comp: returns the function that compares keys
}{ // value_comp: returns the function that compares keys in objects of type value_type
}return 0;
}GitHub: https://github.com/fengbingchun/Messy_Test
相关文章:

值得收藏!基于激光雷达数据的深度学习目标检测方法大合集(下)
作者 | 黄浴来源 | 转载自知乎专栏自动驾驶的挑战和发展【导读】在近日发布的《值得收藏!基于激光雷达数据的深度学习目标检测方法大合集(上)》一文中,作者介绍了一部分各大公司和机构基于激光雷达的目标检测所做的工作࿰…

java B2B2C源码电子商务平台 -commonservice-config配置服务搭建
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> Spring Cloud Config为分布式系统中的外部配置提供服务器和客户端支持。使用Config Server,您可以在所有环境中管理应用程序的外部属性。客户端和服务器上的概念映射与Spring Environment和PropertySource抽象…

Topshelf:一款非常好用的 Windows 服务开发框架
背景 多数系统都会涉及到“后台服务”的开发,一般是为了调度一些自动执行的任务或从队列中消费一些消息,开发 windows service 有一点不爽的是:调试麻烦,当然你还需要知道 windows service 相关的一些开发知识(也不难&…

C++中nothrow的介绍及使用
在C中,使用malloc等分配内存的函数时,一定要检查其返回值是否为”空指针”,并以此作为检查内存操作是否成功的依据,这种Test-for-NULL代码形式是一种良好的编程习惯,也是编写可靠程序所必需的。在C中new在申请内存失败…

你猜猜typeof (typeof 1) 会返回什么值(类型)?!
typeof typeof操作符返回一个字符串,表示未经计算的操作数的类型。 语法: var num a; console.log(typeof (num)); 或console.log(typeof num) 复制代码typeof 可以返回的类型为:number、string、boolean、undefined、null、object、functi…

阿里云智能运维的自动化三剑客
整理 | 王银出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)近日,2019 AI开发者大会在北京举行。会上,近百位中美顶尖AI专家、知名企业代表以及千余名AI开发者进行技术解读和产业论证。而在AIDevOps论坛上,阿里巴巴高级技术专家滕圣…

Sublime Text2.0.2注册码
直接输入注册码就可以了 ----- BEGIN LICENSE ----- Andrew Weber Single User License EA7E-855605 813A03DD 5E4AD9E6 6C0EEB94 BC99798F 942194A6 02396E98 E62C9979 4BB979FE 91424C9D A45400BF F6747D88 2FB88078 90F5CC94 1CDC92DC 8457107A F151657B 1D22E383 A997F016 …
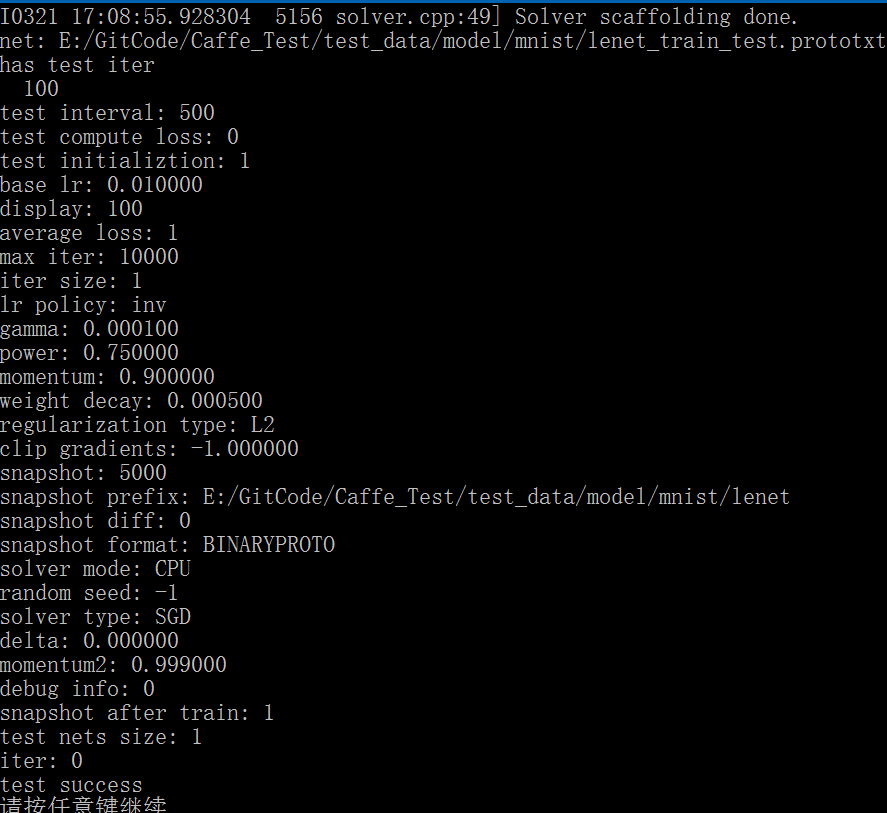
Caffe源码中Solver文件分析
Caffe源码(caffe version commit: 09868ac , date: 2015.08.15)中有一些重要的头文件,这里介绍下include/caffe/solver.hpp文件的内容:1. include文件: <caffe/solver.hpp>:此文件的介绍可以参考: http://b…
百度大脑金秋九月CV盛典,人脸识别新产品及伙伴计划发布会压轴开启
提起人脸识别你最先想到的是什么?是告别排队,刷脸就能支付的超市;还是告别黄牛,刷脸就能自助挂号建档的医院?其实,“刷脸”的时代早已到来,并且人脸识别技术的发展已经超越你的想象,…

BIML 101 - ETL数据清洗 系列 - BIML 快速入门教程 - 序
BIML 101 - BIML 快速入门教程 做大数据的项目,最花时间的就是数据清洗。 没有一个相对可靠的数据,数据分析就是无木之舟,无水之源。 如果你已经进了ETL这个坑,而且预算有限,并且有大量的活要做; 时间紧&am…
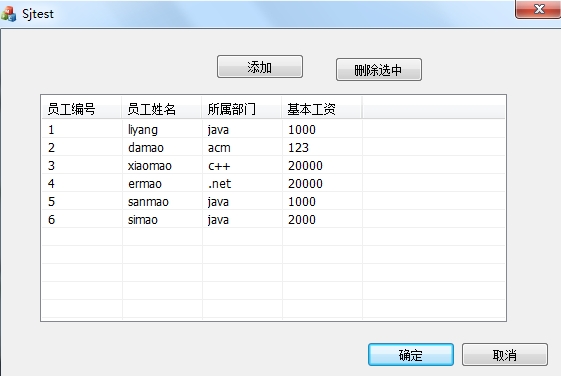
ADO数据库操作
void CSjtestDlg::OnBnClickedButtonAdd() {// TODO: 在此添加控件通知处理程序代码this->ShowWindow(SW_HIDE);DigAdd dig ;dig.DoModal() ;this->ShowWindow(SW_SHOW);m_Grid.DeleteAllItems() ;ADOConn m_Adoconn ;m_Adoconn.OnInitADOConn() ;CString sql ;sql.Forma…
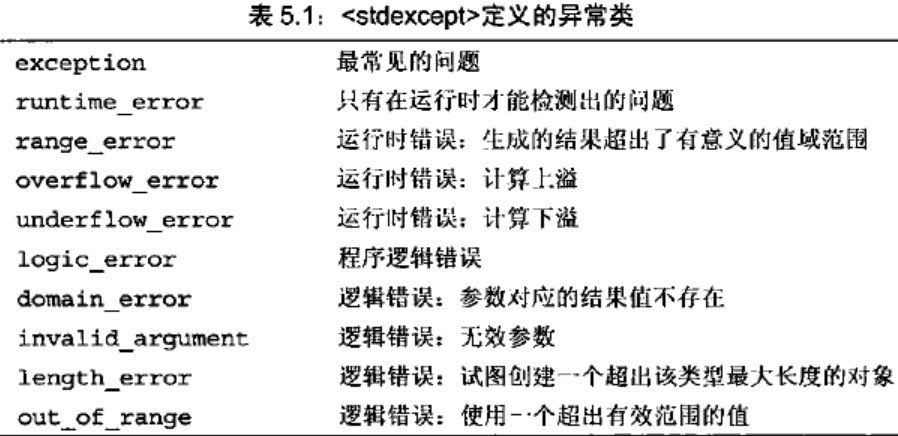
C++中try/catch/throw的使用
C异常是指在程序运行时发生的反常行为,这些行为超出了函数正常功能的范围。当程序的某部分检测到一个它无法处理的问题时,需要用到异常处理。异常提供了一种转移程序控制权的方式。C异常处理涉及到三个关键字:try、catch、throw。 在C语言中…

掌握这些步骤,机器学习模型问题药到病除
作者 | Cecelia Shao编译 | ronghuaiyang来源 | AI公园(ID:AI_Paradise)【导读】这篇文章提供了切实可行的步骤来识别和修复机器学习模型的训练、泛化和优化问题。众所周知,调试机器学习代码非常困难。即使对于简单的前馈神经网络也是这样&am…

How to list/dump dm thin pool metadata device?
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> See: How to create metadata-snap for thin tools using? I dont think LVM provides any support for metadata snapshots so you will need to drive this process through dmsetup. The kernel interface is descri…

Linux基础(二)--基础的命令ls和date的详细用法
本文中主要介绍了linu系统下一些基础命令的用法,重点介绍了ls和date的用法。1.basename:作用:返回一个字符串参数的基本文件名称。用法:basename PATH例如:basename /usr/share/doc 返回结果为doc2.dirname:作用:返回一…
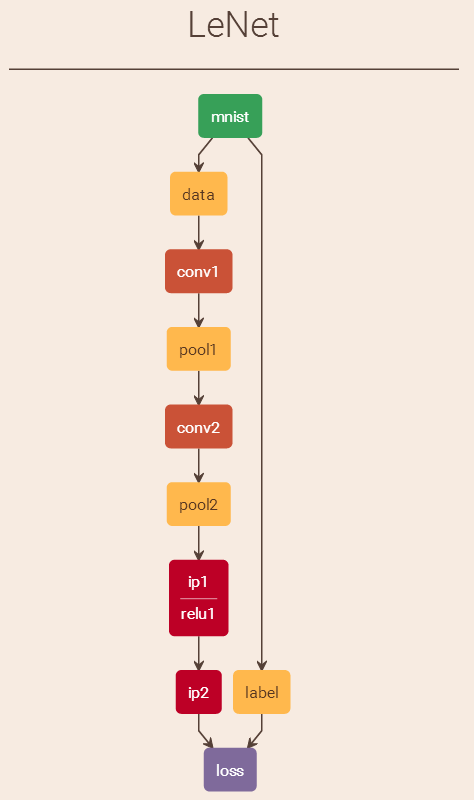
Caffe中对MNIST执行train操作执行流程解析
之前在 http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/49849225 中简单介绍过使用Caffe train MNIST的文章,当时只是仿照caffe中的example实现了下,下面说一下执行流程,并精简代码到仅有10余行:1. 先注册所有层&…
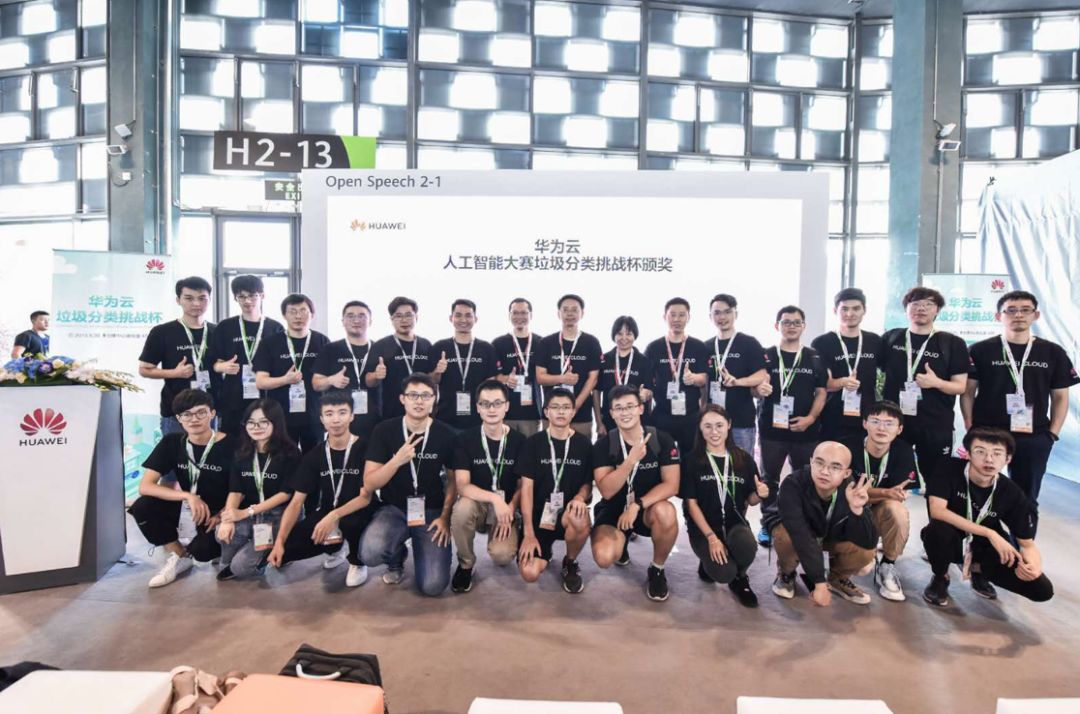

华为云垃圾分类AI大赛三强出炉,ModelArts2.0让行业按下AI开发“加速键”
9月20日,华为云人工智能大赛垃圾分类挑战杯决赛在上海世博中心2019华为全联接大会会场顺利举办。经过近两个月赛程的层层筛选,入围决赛阵列的11支战队的高光时刻也如期而至。最终华为云垃圾分类挑战杯三强出炉。本次华为云人工智能大赛垃圾分类挑战杯聚焦…

王坚十年前的坚持,才有了今天世界顶级大数据计算平台MaxCompute...
如果说十年前,王坚创立阿里云让云计算在国内得到了普及,那么王坚带领团队自主研发的大数据计算平台MaxCompute则推动大数据技术向前跨越了一大步。数据是企业的核心资产,但十年前阿里巴巴的算力已经无法满足当时急剧增长数据量的需求。基于Ha…

tomcat简单配置
-----------------------------------------一、前言二、环境三、安装JDK四、安装tomcat五、安装mysql六、安装javacenter七、tomcat后台管理-----------------------------------------一、前言Tomcat是Apache 软件基金会(Apache Software Foundation)的…
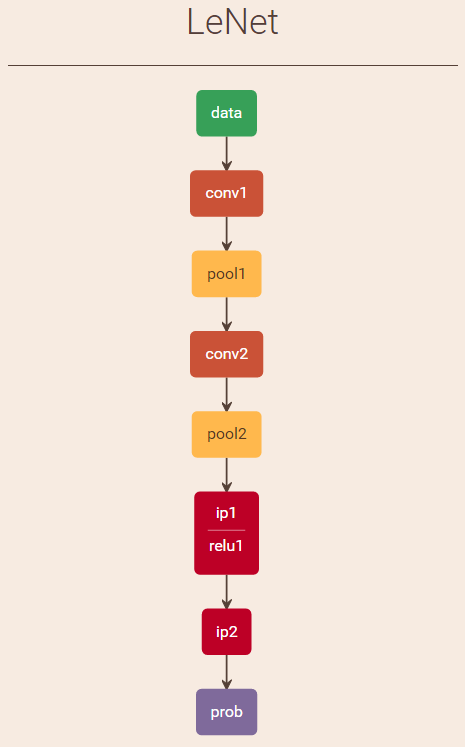
使用Caffe进行手写数字识别执行流程解析
之前在 http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/50987185 中仿照Caffe中的examples实现对手写数字进行识别,这里详细介绍下其执行流程并精简了实现代码,使用Caffe对MNIST数据集进行train的文章可以参考 http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/…
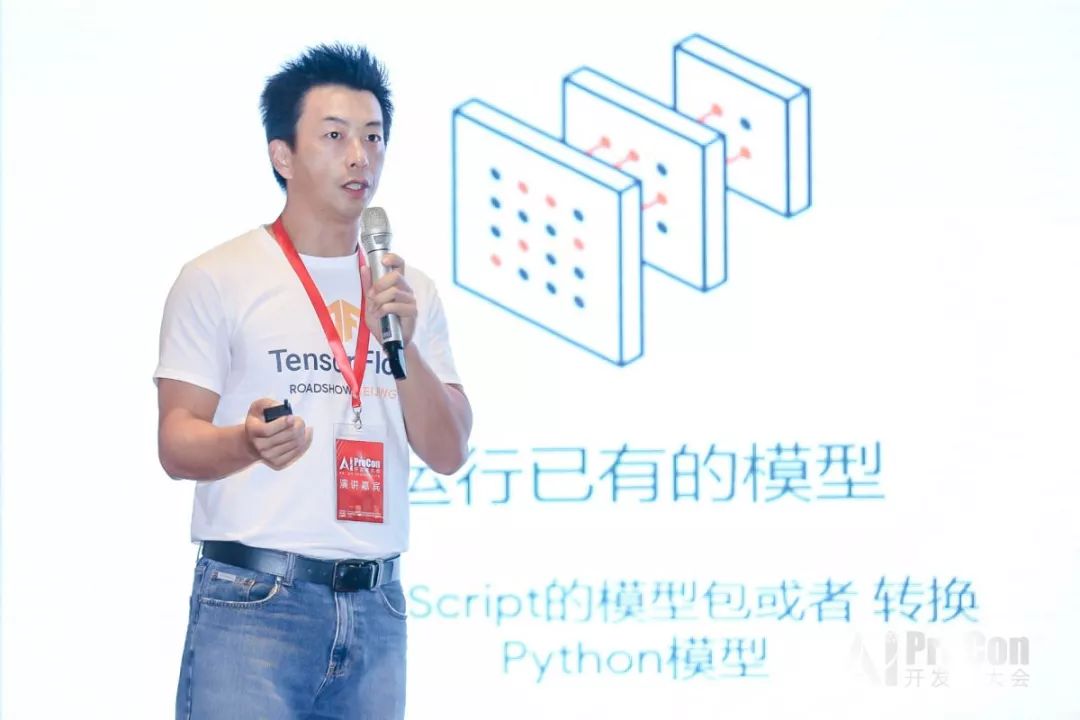

前端也能玩转机器学习?Google Brain 工程师来支招
演讲嘉宾 | 俞玶编辑 | 伍杏玲来源 | CSDN(ID:CSDNnews)导语:9 月 7 日,在CSDN主办的「AI ProCon 2019」上,Google Brain 工程师,TensorFlow.js 项目负责人俞玶发表《TensorFlow.js 遇到小程序》的主题演讲,…

mongoDB设置用户名密码的一个要点
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 增加用户之前, 先选好库 use <库名> #选择admin库后可查看system.users里面的用户数据 db.system.users.find() db.createUser 这个函数填写用户名密码与权限就行了, 在这里设置库的名称没用. 一定要用用use选择好…

基于HTML5的电信网管3D机房监控应用
先上段视频,不是在玩游戏哦,是规规矩矩的电信网管企业应用,嗯,全键盘的漫游3D机房:随着PC端支持HTML5浏览器的普及,加上主流移动终端Android和iOS都已支持HTML5技术,新一代的电信网管应用几乎一致性的首选H…

从原理到实现,详解基于朴素ML思想的协同过滤推荐算法
作者丨gongyouliu编辑丨Zandy来源 | 大数据与人工智能(ID: ai-big-data)作者在《协同过滤推荐算法》、《矩阵分解推荐算法》这两篇文章中介绍了几种经典的协同过滤推荐算法。我们在本篇文章中会继续介绍三种思路非常简单朴素的协同过滤算法,这…

C++/C++11中引用的使用
引用(reference)是一种复合类型(compound type)。引用为对象起了另外一个名字,引用类型引用(refer to)另外一种类型。通过将声明符写成&d的形式来定义引用类型,其中d是声明的变量名。 一、一般引用:一般在初始化变量时,初始值…

node.js学习5--------------------- 返回html内容给浏览器
/*** http服务器的搭建,相当于php中的Apache或者java中的tomcat服务器*/ // 导包 const httprequire("http"); const fsrequire("fs"); //创建服务器 /*** 参数是一个回调函数,回调函数2个参数,1个是请求参数,一个是返回参数*/ let serverhttp.createServe…

内核分析阅读笔记
内核分析阅读笔记 include/Linux/stddef.h中macro offsetof define,list: #define offsetof(TYPE,MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER) offsetof macro对于上述示例的展开剂分析:&((struct example_struct *)0)->list表示当结构example_struct正好在地址0上…

杨强教授力荐,快速部署落地深度学习应用的实践手册
香港科技大学计算机科学与工程学系讲座教授、国际人工智能联合会(IJCAI)理事会主席(2017—2019)、深圳前海微众银行首席AI 官 杨强为《深度学习模型及应用详解》一书撰序,他提到现在亟需一本介绍深度学习技术实践的图书…
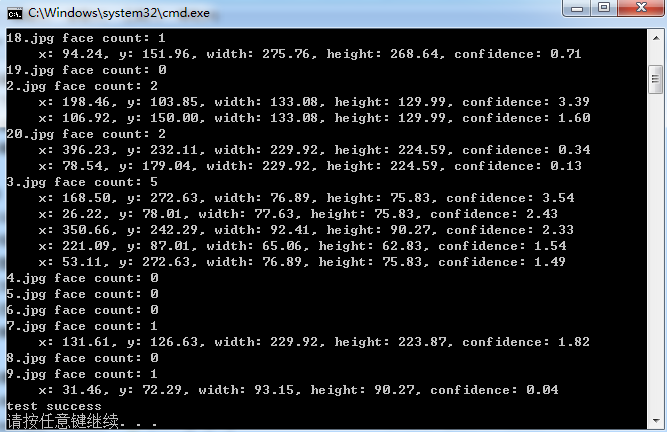
OpenFace库(Tadas Baltrusaitis)中基于HOG进行正脸人脸检测的测试代码
Tadas Baltrusaitis的OpenFace是一个开源的面部行为分析工具,它的源码可以从https://github.com/TadasBaltrusaitis/OpenFace下载。OpenFace主要包括面部关键点检测(facial landmard detection)、头部姿势估计(head pose estimation)、面部动作单元识别(facial acti…

nginx conf 文件配置
打印输出: location / { default_type text/plain; return 502 "$uri"; } $remode_addr 获取访问者的ID$request_method 判断提交方式 GET POST$http_user_agent 获取浏览器软件 if (条件) {} #if之后要有空格 条件3种写法: 1: 来判断相等,用于字符串比较 …
