TensorRT Samples: CharRNN
以下是参考TensorRT 2.1.2中的sampleCharRNN.cpp文件改写的测试代码,文件(charrnn.cpp)内容如下:
#include <assert.h>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <tuple>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>#include <NvInfer.h>
#include <NvUtils.h>
#include <cuda_runtime_api.h>#include "common.hpp"// reference: TensorRT-2.1.2/samples/sampleMNIST/sampleCharRNN.cpp
// demonstrates how to generate a simple RNN based on the charRNN network using the PTB datasetnamespace {// Information describing the network:
// int: layer count, batch size, hidden size, seq size, data size, output size
// string: input blob name, hidden in blob name, cell in blob name, output blob name, hidden out blob name, cell out blob name
typedef std::tuple<int, int, int, int, int, int, std::string, std::string, std::string, std::string, std::string, std::string> NET_INFO;// These mappings came from training with tensorflow 0.12.1
static std::map<char, int> char_to_id{{'#', 40},{ '$', 31}, { '\'', 28}, { '&', 35}, { '*', 49},{ '-', 32}, { '/', 48}, { '.', 27}, { '1', 37},{ '0', 36}, { '3', 39}, { '2', 41}, { '5', 43},{ '4', 47}, { '7', 45}, { '6', 46}, { '9', 38},{ '8', 42}, { '<', 22}, { '>', 23}, { '\0', 24},{ 'N', 26}, { '\\', 44}, { ' ', 0}, { 'a', 3},{ 'c', 13}, { 'b', 20}, { 'e', 1}, { 'd', 12},{ 'g', 18}, { 'f', 15}, { 'i', 6}, { 'h', 9},{ 'k', 17}, { 'j', 30}, { 'm', 14}, { 'l', 10},{ 'o', 5}, { 'n', 4}, { 'q', 33}, { 'p', 16},{ 's', 7}, { 'r', 8}, { 'u', 11}, { 't', 2},{ 'w', 21}, { 'v', 25}, { 'y', 19}, { 'x', 29},{ 'z', 34}
};// A mapping from index to character.
static std::vector<char> id_to_char{{' ', 'e', 't', 'a','n', 'o', 'i', 's', 'r', 'h', 'l', 'u', 'd', 'c','m', 'f', 'p', 'k', 'g', 'y', 'b', 'w', '<', '>','\0', 'v', 'N', '.', '\'', 'x', 'j', '$', '-', 'q','z', '&', '0', '1', '9', '3', '#', '2', '8', '5','\\', '7', '6', '4', '/', '*'}};// Our weight files are in a very simple space delimited format.
std::map<std::string, nvinfer1::Weights> loadWeights(const std::string& file)
{std::map<std::string, nvinfer1::Weights> weightMap;std::ifstream input(file);if (!input.is_open()) { fprintf(stderr, "Unable to load weight file: %s\n", file.c_str()); return weightMap;}int32_t count;input >> count;if (count <= 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Invalid weight map file: %d\n", count); return weightMap; }while (count--) {nvinfer1::Weights wt{nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT, nullptr, 0};uint32_t type, size;std::string name;input >> name >> std::dec >> type >> size;wt.type = static_cast<nvinfer1::DataType>(type);if (wt.type == nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT) {uint32_t *val = reinterpret_cast<uint32_t*>(malloc(sizeof(val) * size));for (uint32_t x = 0, y = size; x < y; ++x) {input >> std::hex >> val[x];}wt.values = val;} else if (wt.type == nvinfer1::DataType::kHALF) {uint16_t *val = reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*>(malloc(sizeof(val) * size));for (uint32_t x = 0, y = size; x < y; ++x) {input >> std::hex >> val[x];}wt.values = val;}wt.count = size;weightMap[name] = wt;}return weightMap;
}// Reshape plugin to feed RNN into FC layer correctly.
class Reshape : public nvinfer1::IPlugin {
public:Reshape(size_t size) : mSize(size) {} Reshape(const void*buf, size_t size){assert(size == sizeof(mSize));mSize = *static_cast<const size_t*>(buf);}int getNbOutputs() const override { return 1; }int initialize() override { return 0; }void terminate() override {}size_t getWorkspaceSize(int) const override { return 0; }int enqueue(int batchSize, const void*const * inputs, void** outputs, void* workspace, cudaStream_t stream){cudaMemcpyAsync(static_cast<float*>(outputs[0]),static_cast<const float*>(inputs[0]),sizeof(float) * mSize * batchSize, cudaMemcpyDefault, stream);return 0;}size_t getSerializationSize() override{return sizeof(mSize);}void serialize(void* buffer) override{(*static_cast<size_t*>(buffer)) = mSize;}void configure(const nvinfer1::Dims*, int, const nvinfer1::Dims*, int, int) override { }// The RNN outputs in {L, N, C}, but FC layer needs {C, 1, 1}, so we can convert RNN// output to {L*N, C, 1, 1} and TensorRT will handle the rest.nvinfer1::Dims getOutputDimensions(int index, const nvinfer1::Dims* inputs, int nbInputDims) override{assert(nbInputDims == 1 && index == 0 && inputs[index].nbDims == 3);return nvinfer1::DimsNCHW(inputs[index].d[1] * inputs[index].d[0], inputs[index].d[2], 1, 1);}private:size_t mSize{0};
};class PluginFactory : public nvinfer1::IPluginFactory
{
public:// deserialization plugin implementationnvinfer1::IPlugin* createPlugin(const char* layerName, const void* serialData, size_t serialLength) override{assert(!strncmp(layerName, "reshape", 7));if (!mPlugin) mPlugin = new Reshape(serialData, serialLength);return mPlugin;}void destroyPlugin(){if (mPlugin) delete mPlugin;mPlugin = nullptr;}private:Reshape *mPlugin{nullptr};
}; // PluginFactory// TensorFlow weight parameters for BasicLSTMCell
nvinfer1::Weights convertRNNWeights(nvinfer1::Weights input, const NET_INFO& info)
{float* ptr = static_cast<float*>(malloc(sizeof(float)*input.count));int indir[4]{ 1, 2, 0, 3 };int order[5]{ 0, 1, 4, 2, 3};int dims[5]{std::get<0>(info), 2, 4, std::get<2>(info), std::get<2>(info)};nvinfer1::utils::reshapeWeights(input, dims, order, ptr, 5);nvinfer1::utils::transposeSubBuffers(ptr, nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT, std::get<0>(info) * 2, std::get<2>(info) * std::get<2>(info), 4);int subMatrix = std::get<2>(info) * std::get<2>(info);int layerOffset = 8 * subMatrix;for (int z = 0; z < std::get<0>(info); ++z) {nvinfer1::utils::reorderSubBuffers(ptr + z * layerOffset, indir, 4, subMatrix * sizeof(float));nvinfer1::utils::reorderSubBuffers(ptr + z * layerOffset + 4 * subMatrix, indir, 4, subMatrix * sizeof(float));}return nvinfer1::Weights{input.type, ptr, input.count};
}// TensorFlow bias parameters for BasicLSTMCell
nvinfer1::Weights convertRNNBias(nvinfer1::Weights input, const NET_INFO& info)
{float* ptr = static_cast<float*>(malloc(sizeof(float)*input.count*2));std::fill(ptr, ptr + input.count*2, 0);const float* iptr = static_cast<const float*>(input.values);int indir[4]{ 1, 2, 0, 3 };for (int z = 0, y = 0; z < std::get<0>(info); ++z)for (int x = 0; x < 4; ++x, ++y)std::copy(iptr + y * std::get<2>(info) , iptr + (y + 1) * std::get<2>(info), ptr + (z * 8 + indir[x]) * std::get<2>(info));return nvinfer1::Weights{input.type, ptr, input.count*2};
}// The fully connected weights from tensorflow are transposed compared to the order that tensorRT expects them to be in.
nvinfer1::Weights transposeFCWeights(nvinfer1::Weights input, const NET_INFO& info)
{float* ptr = static_cast<float*>(malloc(sizeof(float)*input.count));const float* iptr = static_cast<const float*>(input.values);assert(input.count == std::get<2>(info) * std::get<5>(info));for (int z = 0; z < std::get<2>(info); ++z)for (int x = 0; x < std::get<5>(info); ++x)ptr[x * std::get<2>(info) + z] = iptr[z * std::get<5>(info) + x];return nvinfer1::Weights{input.type, ptr, input.count};
}int APIToModel(std::map<std::string, nvinfer1::Weights> &weightMap, nvinfer1::IHostMemory** modelStream, const NET_INFO& info, Logger logger)
{// create the buildernvinfer1::IBuilder* builder = nvinfer1::createInferBuilder(logger);// create the model to populate the network, then set the outputs and create an enginenvinfer1::INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetwork();auto data = network->addInput(std::get<6>(info).c_str(), nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT, nvinfer1::DimsCHW{ std::get<3>(info), std::get<1>(info), std::get<4>(info)});CHECK(data != nullptr);auto hiddenIn = network->addInput(std::get<7>(info).c_str(), nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT, nvinfer1::DimsCHW{ std::get<0>(info), std::get<1>(info), std::get<2>(info)});CHECK(hiddenIn != nullptr);auto cellIn = network->addInput(std::get<8>(info).c_str(), nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT, nvinfer1::DimsCHW{ std::get<0>(info), std::get<1>(info), std::get<2>(info)});CHECK(cellIn != nullptr);// Create an RNN layer w/ 2 layers and 512 hidden statesauto tfwts = weightMap["rnnweight"];nvinfer1::Weights rnnwts = convertRNNWeights(tfwts, info);auto tfbias = weightMap["rnnbias"];nvinfer1::Weights rnnbias = convertRNNBias(tfbias, info);auto rnn = network->addRNN(*data, std::get<0>(info), std::get<2>(info), std::get<3>(info),nvinfer1::RNNOperation::kLSTM, nvinfer1::RNNInputMode::kLINEAR, nvinfer1::RNNDirection::kUNIDIRECTION, rnnwts, rnnbias);CHECK(rnn != nullptr);rnn->getOutput(0)->setName("RNN output");rnn->setHiddenState(*hiddenIn);if (rnn->getOperation() == nvinfer1::RNNOperation::kLSTM)rnn->setCellState(*cellIn);Reshape reshape(std::get<3>(info) * std::get<1>(info) * std::get<2>(info));nvinfer1::ITensor *ptr = rnn->getOutput(0);auto plugin = network->addPlugin(&ptr, 1, reshape);plugin->setName("reshape");// Add a second fully connected layer with 50 outputs.auto tffcwts = weightMap["rnnfcw"];auto wts = transposeFCWeights(tffcwts, info);auto bias = weightMap["rnnfcb"];auto fc = network->addFullyConnected(*plugin->getOutput(0), std::get<5>(info), wts, bias);CHECK(fc != nullptr);fc->getOutput(0)->setName("FC output");// Add a softmax layer to determine the probability.auto prob = network->addSoftMax(*fc->getOutput(0));CHECK(prob != nullptr);prob->getOutput(0)->setName(std::get<9>(info).c_str());network->markOutput(*prob->getOutput(0));rnn->getOutput(1)->setName(std::get<10>(info).c_str());network->markOutput(*rnn->getOutput(1));if (rnn->getOperation() == nvinfer1::RNNOperation::kLSTM) {rnn->getOutput(2)->setName(std::get<11>(info).c_str());network->markOutput(*rnn->getOutput(2));}// Build the enginebuilder->setMaxBatchSize(1);builder->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1 << 25);// Store the transformed weights in the weight map so the memory can be properly released later.weightMap["rnnweight2"] = rnnwts;weightMap["rnnbias2"] = rnnbias;weightMap["rnnfcw2"] = wts;auto engine = builder->buildCudaEngine(*network);CHECK(engine != nullptr);// we don't need the network any morenetwork->destroy();// serialize the engine, then close everything down(*modelStream) = engine->serialize();engine->destroy();builder->destroy();return 0;
}void stepOnce(float** data, void** buffers, int* sizes, int* indices,int numBindings, cudaStream_t& stream, nvinfer1::IExecutionContext &context)
{for (int z = 0, w = numBindings/2; z < w; ++z)cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[indices[z]], data[z], sizes[z] * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream);// Execute asynchronouslycontext.enqueue(1, buffers, stream, nullptr);// DMA the input from the GPUfor (int z = numBindings/2, w = numBindings; z < w; ++z)cudaMemcpyAsync(data[z], buffers[indices[z]], sizes[z] * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream);// Copy Ct/Ht to the Ct-1/Ht-1 slots.cudaMemcpyAsync(data[1], buffers[indices[4]], sizes[1] * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream);cudaMemcpyAsync(data[2], buffers[indices[5]], sizes[2] * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream);
}bool doInference(nvinfer1::IExecutionContext& context, const std::string& input, const std::string& expected, std::map<std::string, nvinfer1::Weights>&weightMap, const NET_INFO& info)
{const nvinfer1::ICudaEngine& engine = context.getEngine();// We have 6 outputs for LSTM, this needs to be changed to 4 for any other RNN typestatic const int numBindings = 6;assert(engine.getNbBindings() == numBindings);void* buffers[numBindings];float* data[numBindings];std::fill(buffers, buffers + numBindings, nullptr);std::fill(data, data + numBindings, nullptr);const char* names[numBindings] = {std::get<6>(info).c_str(), std::get<7>(info).c_str(), std::get<8>(info).c_str(),std::get<9>(info).c_str(), std::get<10>(info).c_str(), std::get<11>(info).c_str() };int indices[numBindings];std::fill(indices, indices + numBindings, -1);int sizes[numBindings] = { std::get<3>(info) * std::get<1>(info) * std::get<4>(info),std::get<0>(info) * std::get<1>(info) * std::get<2>(info),std::get<0>(info) * std::get<1>(info) * std::get<2>(info),std::get<5>(info),std::get<0>(info) * std::get<1>(info) * std::get<2>(info),std::get<0>(info) * std::get<1>(info) * std::get<2>(info) };for (int x = 0; x < numBindings; ++x) {// In order to bind the buffers, we need to know the names of the input and output tensors.// note that indices are guaranteed to be less than IEngine::getNbBindings()indices[x] = engine.getBindingIndex(names[x]);if (indices[x] == -1) continue;// create GPU buffers and a streamassert(indices[x] < numBindings);cudaMalloc(&buffers[indices[x]], sizes[x] * sizeof(float));data[x] = new float[sizes[x]];}cudaStream_t stream;cudaStreamCreate(&stream);// Initialize input/hidden/cell state to zerofor (int x = 0; x < numBindings; ++x) std::fill(data[x], data[x] + sizes[x], 0.0f);auto embed = weightMap["embed"];std::string genstr;assert(std::get<1>(info) == 1 && "This code assumes batch size is equal to 1.");// Seed the RNN with the input.for (auto &a : input) {std::copy(reinterpret_cast<const float*>(embed.values) + char_to_id[a]*std::get<4>(info),reinterpret_cast<const float*>(embed.values) + char_to_id[a]*std::get<4>(info) + std::get<4>(info),data[0]);stepOnce(data, buffers, sizes, indices, 6, stream, context);cudaStreamSynchronize(stream);genstr.push_back(a);}// Now that we have gone through the initial sequence, lets make sure that we get the sequence out that// we are expecting.for (size_t x = 0, y = expected.size(); x < y; ++x) {std::copy(reinterpret_cast<const float*>(embed.values) + char_to_id[*genstr.rbegin()]*std::get<4>(info),reinterpret_cast<const float*>(embed.values) + char_to_id[*genstr.rbegin()]*std::get<4>(info) + std::get<4>(info),data[0]);stepOnce(data, buffers, sizes, indices, 6, stream, context);cudaStreamSynchronize(stream);float* probabilities = reinterpret_cast<float*>(data[indices[3]]);ptrdiff_t idx = std::max_element(probabilities, probabilities + sizes[3]) - probabilities;genstr.push_back(id_to_char[idx]);}fprintf(stdout, "Received: %s\n", genstr.c_str() + input.size());// release the stream and the bufferscudaStreamDestroy(stream);for (int x = 0; x < numBindings; ++x) {cudaFree(buffers[indices[x]]);if (data[x]) delete [] data[x];}return genstr == (input + expected);
}} // namespaceint test_charrnn()
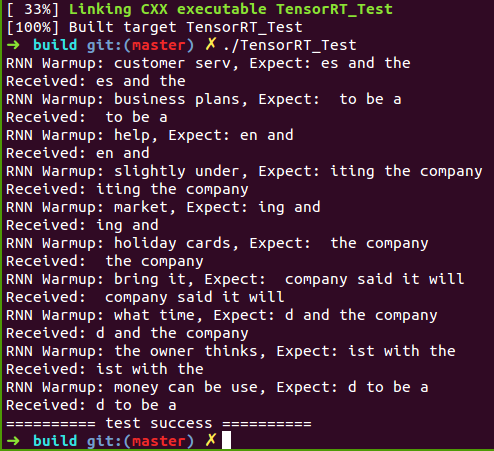
{const NET_INFO info(2, 1, 512, 1, 512, 50, "data", "hiddenIn", "cellIn", "prob", "hiddenOut", "cellOut");Logger logger; // multiple instances of IRuntime and/or IBuilder must all use the same logger// create a model using the API directly and serialize it to a streamnvinfer1::IHostMemory* modelStream{ nullptr };std::map<std::string, nvinfer1::Weights> weightMap = loadWeights("models/char-rnn.wts");APIToModel(weightMap, &modelStream, info, logger);const std::vector<std::string> in_strs {"customer serv", "business plans", "help", "slightly under", "market","holiday cards", "bring it", "what time", "the owner thinks", "money can be use"};const std::vector<std::string> out_strs { "es and the", " to be a", "en and", "iting the company", "ing and"," the company", " company said it will", "d and the company", "ist with the", "d to be a"};CHECK(in_strs.size() == out_strs.size());PluginFactory pluginFactory;nvinfer1::IRuntime* runtime = nvinfer1::createInferRuntime(logger);nvinfer1::ICudaEngine* engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(modelStream->data(), modelStream->size(), &pluginFactory);nvinfer1::IExecutionContext* context = engine->createExecutionContext();for (int num = 0; num < in_strs.size(); ++num) {bool pass {false};fprintf(stdout, "RNN Warmup: %s, Expect: %s\n", in_strs[num].c_str(), out_strs[num].c_str());pass = doInference(*context, in_strs[num], out_strs[num], weightMap, info);if (!pass) fprintf(stderr, "Failure!\n");}if (modelStream) modelStream->destroy();for (auto& mem : weightMap) {free((void*)(mem.second.values));}// destroy the enginecontext->destroy();engine->destroy();runtime->destroy();pluginFactory.destroyPlugin();return 0;
}测试代码编译步骤如下(ReadMe.txt):
在Linux下通过CMake编译TensorRT_Test中的测试代码步骤:
1. 将终端定位到CUDA_Test/prj/linux_tensorrt_cmake,依次执行如下命令:$ mkdir build$ cd build$ cmake ..$ make (生成TensorRT_Test执行文件)$ ln -s ../../../test_data/models ./ (将models目录软链接到build目录下)$ ln -s ../../../test_data/images ./ (将images目录软链接到build目录下)$ ./TensorRT_Test
2. 对于有需要用OpenCV参与的读取图像的操作,需要先将对应文件中的图像路径修改为Linux支持的路径格式GitHub: https://github.com/fengbingchun/CUDA_Test
相关文章:
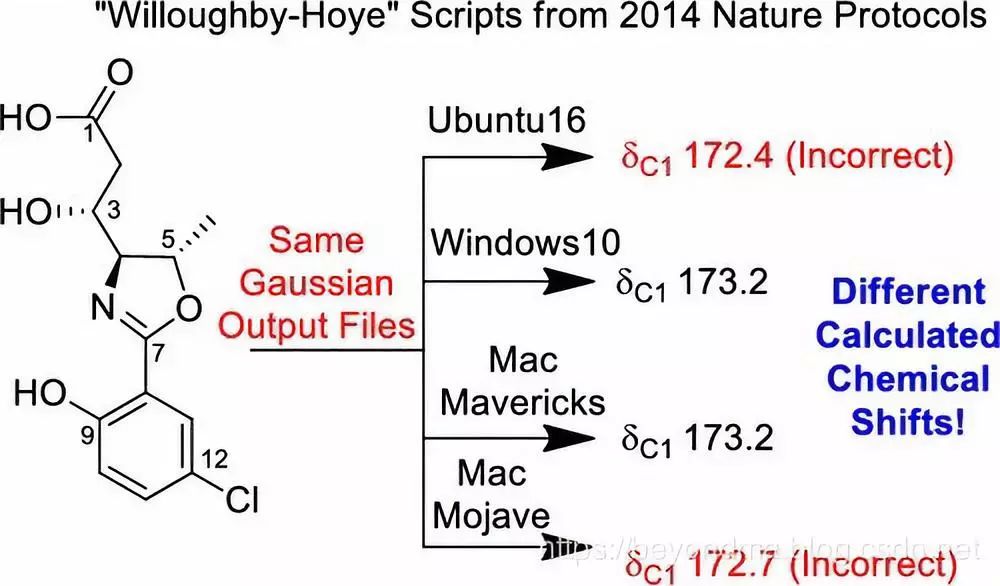
Python脚本BUG引发学界震动,影响有多大?
作者 | beyondma编辑 | Jane来源 | CSDN博客近日一篇“A guide to small-molecule structure assignment through computation of (1H and 13C) NMR chemical shifts”文章火爆网络,据作者看到的资料上看这篇论文自身的结果没有什么问题,但是,…

C++中public、protect和private用法区别
Calsspig : public animal,意思是外部代码可以随意访问 Classpig : protect animal ,意思是外部代码无法通过该子类访问基类中的public Classpig : private animal ,意思是告诉编译器从基类继承的每一个成员都当成private,即只有这个子类可以访问 转载于:https://blog.51cto.…
TensorRT Samples: MNIST(Plugin, add a custom layer)
关于TensorRT的介绍可以参考:http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/78469551 以下是参考TensorRT 2.1.2中的samplePlugin.cpp文件改写的通过IPlugin添加一个全连接层实现对手写数字0-9识别的测试代码,plugin.cpp文件内容如下:…
AutoML很火,过度吹捧的结果?
作者 | Denis Vorotyntsev译者 | Shawnice编辑 | Jane出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)【导语】现在,很多企业都很关注AutoML领域,很多开发者也开始接触和从事AutoML相关的研究与应用工作,作者也是&#…

tomcat6 配置web管理端访问权限
配置tomcat 管理端登陆 /apache-tomcat-6.0.35/conf/tomcat-users.xml 配置文件,使用时需要把注释去掉<!-- <!-- <role rolename"tomcat"/> <role rolename"role1"/> <user username"tomcat" password"…

@程序员:Python 3.8正式发布,重要新功能都在这里
整理 | Jane、夕颜出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)【导读】最新版本的Python发布了!今年夏天,Python 3.8发布beta版本,但在2019年10月14日,第一个正式版本已准备就绪。现在,我们都…
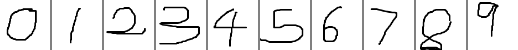
TensorRT Samples: MNIST(serialize TensorRT model)
关于TensorRT的介绍可以参考: http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/78469551 这里实现在构建阶段将TensorRT model序列化存到本地文件,然后在部署阶段直接load TensorRT model序列化的文件进行推理,mnist_infer.cpp文件内容…

【mysql错误】用as别名 做where条件,报未知的列 1054 - Unknown column 'name111' in 'field list'...
需求:SELECT a AS b WHRER b1; //这样使用会报错,说b不存在。 因为mysql底层跑SQL语句时:where 后的筛选条件在先, as B的别名在后。所以机器看到where 后的别名是不认的,所以会报说B不存在。 这个b只是字段a查询结…

C++2年经验
网络 sql 基础算法 最多到图和树 常用的几种设计模式,5以内即可转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/liujin2012/p/3766106.html
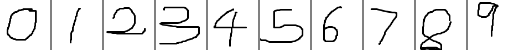
在Caffe中调用TensorRT提供的MNIST model
在TensorRT 2.1.2中提供了MNIST的model,这里拿来用Caffe的代码调用实现,原始的mnist_mean.binaryproto文件调整为了纯二进制文件mnist_tensorrt_mean.binary,测试结果与使用TensorRT调用(http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/…

142页ICML会议强化学习笔记整理,值得细读
作者 | David Abel编辑 | DeepRL来源 | 深度强化学习实验室(ID: Deep-RL)ICML 是 International Conference on Machine Learning的缩写,即国际机器学习大会。ICML如今已发展为由国际机器学习学会(IMLS)主办的年度机器…

CF1148F - Foo Fighters
CF1148F - Foo Fighters 题意:你有n个物品,每个都有val和mask。 你要选择一个数s,如果一个物品的mask & s含有奇数个1,就把val变成-val。 求一个s使得val总和变号。 解:分步来做。发现那个奇数个1可以变成&#x…

html传參中?和amp;
<a href"MealServlet?typefindbyid&mid<%m1.getMealId()%> 在这句传參中?之后的代表要传递的參数当中有两个參数第一个为type第二个为mid假设是一个參数就不用加&假设是多个參数须要加上&来传递

实战:手把手教你实现用语音智能控制电脑 | 附完整代码
作者 | 叶圣出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)导语:本篇文章将基于百度API实现对电脑的语音智能控制,不需要任何硬件上的支持,仅仅依靠一台电脑即可以实现。作者经过测试,效果不错,同时可以依据…

C++/C++11中左值、左值引用、右值、右值引用的使用
C的表达式要不然是右值(rvalue),要不然就是左值(lvalue)。这两个名词是从C语言继承过来的,原本是为了帮助记忆:左值可以位于赋值语句的左侧,右值则不能。 在C语言中,二者的区别就没那么简单了。一个左值表达式的求值结…

Could not create the view: An unexpected exception was thrown. Myeclipse空间报错
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/82654993/1424339

Banknote Dataset(钞票数据集)介绍
Banknote Dataset(钞票数据集):这是从纸币鉴别过程中的图像里提取的数据,用来预测钞票的真伪的数据集。该数据集中含有1372个样本,每个样本由5个数值型变量构成,4个输入变量和1个输出变量。小波变换工具用于从图像中提取特征。这是…
快速适应性很重要,但不是元学习的全部目标
作者 | Khurram Javed, Hengshuai Yao, Martha White译者 | Monanfei出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)实践证明,基于梯度的元学习在学习模型初始化、表示形式和更新规则方面非常有效,该模型允许从少量样本中进行快速适应。这些方…

面试题-自旋锁,以及jvm对synchronized的优化
背景 想要弄清楚这些问题,需要弄清楚其他的很多问题。 比如,对象,而对象本身又可以延伸出很多其他的问题。 我们平时不过只是在使用对象而已,怎么使用?就是new 对象。这只是语法层面的使用,相当于会了一门编…

DNS解析故障
在实际应用过程中可能会遇到DNS解析错误的问题,就是说当我们访问一个域名时无法完成将其解析到IP地址的工作,而直接输入网站IP却可以正常访问,这就是因为DNS解析出现故障造成的。这个现象发生的机率比较大,所以本文将从零起步教给…
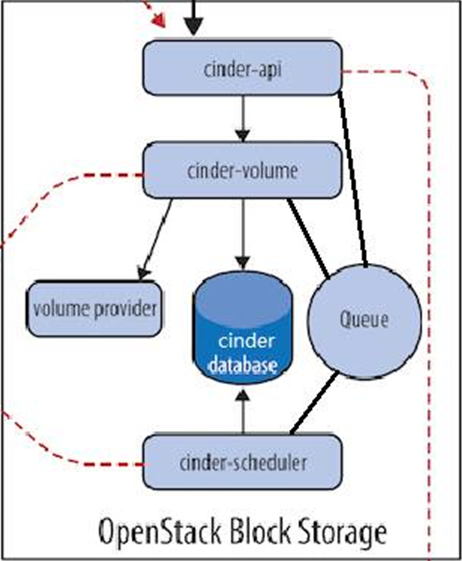
cinder存储服务
一、cinder 介绍: 理解 Block Storage 操作系统获得存储空间的方式一般有两种: 1、通过某种协议(SAS,SCSI,SAN,iSCSI 等)挂接裸硬盘,然后分区、格式化、创建文件系统;或者直接使用裸硬盘存储数据࿰…
Ubuntu 14.04 64位机上配置Android Studio操作步骤
Android Studio是一个为Android平台开发程序的集成开发环境。2013年5月16日在Google I/O上发布,可供开发者免费使用。Android Studio基于JetBrains IntelliJ IDEA,为Android开发特殊定制,并在Windows、OS X和Linux平台上均可运行。1. 从 htt…
大规模1.4亿中文知识图谱数据,我把它开源了
作者 | Just出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)人工智能从感知阶段逐步进入认知智能的过程中,知识图谱技术将为机器提供认知思维能力和关联分析能力,可以应用于机器人问答系统、内容推荐等系统中。不过要降低知识图谱技术应用的门…

使用CSS 3创建不规则图形
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 前言 CSS 创建复杂图形的技术即将会被广泛支持,并且应用到实际项目中。本篇文章的目的是为大家开启它的冰山一角。我希望这篇文章能让你对不规则图形有一个初步的了解。 现在,我们已经可以使用CSS…

谷歌丰田联合成果ALBERT了解一下:新轻量版BERT,参数小18倍,性能依旧SOTA
作者 | Less Wright编译 | ronghuaiyang来源 | AI公园(ID:AI_Paradise)【导读】这是来自Google和Toyota的新NLP模型,超越Bert,参数小了18倍。你以前的NLP模型参数效率低下,而且有些过时。祝你有美好的一天。谷歌Resear…

C++中extern C的使用
C程序有时需要调用其它语言编写的函数,最常见的是调用C语言编写的函数。像所有其它名字一样,其它语言中的函数名字也必须在C中进行声明,并且该声明必须指定返回类型和形参列表。对于其它语言编写的函数来说,编译器检查…

Linux之tmpwatch命令
1、tmpwatch命令功能简介[rootvms002 /]# whatis tmpwatch tmpwatch (8) - removes files which havent been accessed for a period of... #删除一段时间内未被访问的文件tmpwatch删除最近一段时间内没有被访问的文件,时间以小时为单位,节省磁盘空间。…

你不得不知道的Visual Studio 2012(1)- 每日必用功能
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> Visual Studio 2012已经正式发布,有很多花哨的新特性,也有很多方便使用者的新功能,当然也有负面声音。对于我们程序员,最关心的还是如何快速掌握VS2012,用于平时…

C++11中std::unique_lock的使用
std::unique_lock为锁管理模板类,是对通用mutex的封装。std::unique_lock对象以独占所有权的方式(unique owership)管理mutex对象的上锁和解锁操作,即在unique_lock对象的声明周期内,它所管理的锁对象会一直保持上锁状态;而unique…

为何Google将几十亿行源代码放在一个仓库?| CSDN博文精选
作者 | Rachel Potvin,Josh Levenberg译者 | 张建军编辑 | apddd【AI科技大本营导读】与大多数开发者的想象不同,Google只有一个代码仓库——全公司使用不同语言编写的超过10亿文件,近百TB源代码都存放在自行开发的版本管理系统Piper中&#…