接口响应慢?那是你没用 CompletableFuture 来优化!
转自:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/j1BYnPwUMztajesjmPjqag
前言
大多数程序员在平时工作中,都是增删改查。这里我跟大家讲解如何利用CompletableFuture优化项目代码,使项目性能更佳!
为什么要用异步编程
举个例子:用户登录成功,需要返回前端用户角色,菜单权限,个人信息,用户余额,积分情况等。正常逻辑是依次查询不同表,得到对应的数据封装返回给前端,代码如下:
@Test
public void login(Long userId){
log.info("开始查询用户全部信息---串行!");
// 查询用户角色信息
getUserRole(userId);
// 查询用户菜单信息
getUserMenu(userId);
// 查询用户余额信息
getUserAmount(userId);
// 查询用户积分信息
getUserIntegral(userId);
log.info("封装用户信息返回给前端!");
}
假如查询用户角色,用户菜单,用户余额,用户积分分别耗时500,200,200,100毫秒,则登录接口耗时为1秒。如果采用异步(多线程并行)形式,则登录接口耗时以单个查询最慢的任务为主,为查询用户角色信息500毫秒。相当于登录接口性能提升一倍!查询任务越多,则其性能提升越大!
代码演示(串行):
@Test
public void login() throws InterruptedException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("开始查询用户全部信息!");
log.info("开始查询用户角色信息!");
Thread.sleep(500);
String role = "管理员";
log.info("开始查询用户菜单信息!");
Thread.sleep(200);
String menu = "首页,账户管理,积分管理";
log.info("开始查询查询用户余额信息!");
Thread.sleep(200);
Integer amount = 1999;
log.info("开始查询查询查询用户积分信息!");
Thread.sleep(100);
Integer integral = 1015;
log.info("封装用户信息返回给前端!");
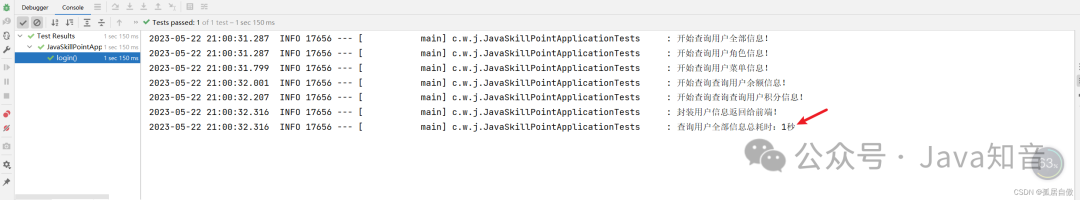
log.info("查询用户全部信息总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
结果:
代码演示(异步):
@Test
public void asyncLogin() {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("开始查询用户角色信息!");
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> roleFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> roleMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
roleMap.put("role", "管理员");
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查询用户角色信息耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒");
return roleMap;
});
log.info("开始查询用户菜单信息!");
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> menuFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> menuMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
menuMap.put("menu", "首页,账户管理,积分管理");
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查询用户菜单信息耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒");
return menuMap;
});
log.info("开始查询用户余额信息!");
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> amountFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 1999);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查询用户余额信息耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒");
return amountMap;
});
log.info("开始查询用户积分信息!");
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> integralFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> integralMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
integralMap.put("integral", 1015);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查询用户积分信息耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒");
return integralMap;
});
roleFuture.join();
menuFuture.join();
amountFuture.join();
integralFuture.join();
log.info("查询用户全部信息总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "毫秒");
}
结果:
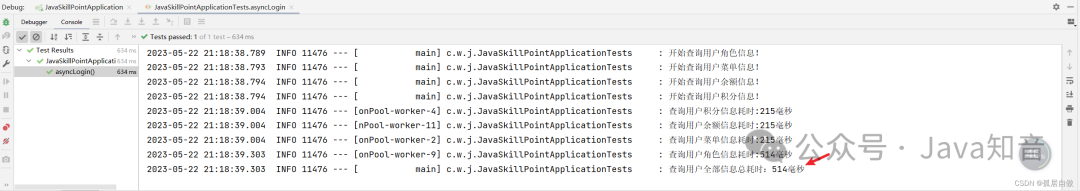
直观的可以看出,异步执行的优势!
回顾Future
Future是什么?
- Java 1.5中引入Callable解决多线程执行无返回值的问题。
- Future是为了配合Callable/Runnable而产生的。简单来讲,我们可以通过future来对任务查询、取消、执行结果的获取,是调用方与异步执行方之间沟通的桥梁。
- FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture接口,同时具有Runnable、Future的能力,即既可以作为Future得到Callable的返回值,又可以作为一个Runnable。
- CompletableFuture实现了Futrue接口。
- Future是Java5新加的一个接口,它提供了一种异步并行计算的功能。如果主线程需要执行一个很耗时的计算任务,我们可以将这个任务通过Future放到异步线程中去执行。主线程继续处理其他任务,处理完成后,再通过Future获取计算结果。
- Future可以在连续流程中满足数据驱动的并发需求,既获得了并发执行的性能提升,又不失连续流程的简洁优雅。
代码演示(不使用自定义线程池):
@Test
public void callable() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Callable amountCall = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(6000);
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 99);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查询金额信息耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
}
};
FutureTask<Map> amountFuture = new FutureTask<>(amountCall);
new Thread(amountFuture).start();
Callable roleCall = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(5000);
Map<String, String> roleMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
roleMap.put("name", "管理员");
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查询角色信息耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return roleMap;
}
};
FutureTask<Map> roleFuture = new FutureTask<>(roleCall);
new Thread(roleFuture).start();
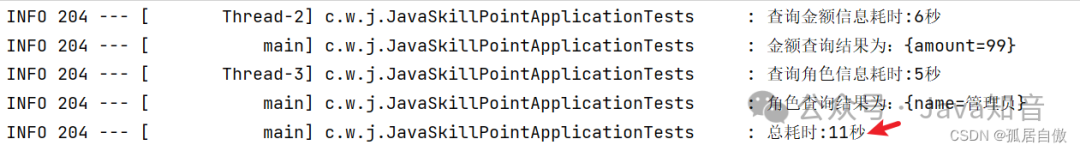
log.info("金额查询结果为:" + amountFuture.get());
log.info("角色查询结果为:" + roleFuture.get());
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("总耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}

“
这里要注意:Future对于结果的获取,不是很友好,只能通过阻塞或者轮询的方式得到任务的结果。
Future.get()就是阻塞调用,在线程获取结果之前get方法会一直阻塞;Future提供了一个isDone方法,可以在程序中轮询这个方法查询执行结果。
这里的 amountFuture.get()如果放到如下图所示的位置,则amountFuture下面的线程将等amountFuture.get()完成后才能执行,没有执行完,则一直阻塞。

结果:
代码演示(使用自定义线程池):
@Test
public void executor() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Callable amountCall = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(6000);
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 99);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查询金额信息耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
}
};
Callable roleCall = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(5000);
Map<String, String> roleMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
roleMap.put("name", "管理员");
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查询用户角色信息耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return roleMap;
}
};
Future amountFuture = executor.submit(amountCall);
Future roleFuture = executor.submit(roleCall);
log.info("金额查询结果为:" + amountFuture.get());
log.info("角色查询结果为:" + roleFuture.get());
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("总耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
结果:

CompletableFuture使用场景
创建异步任务
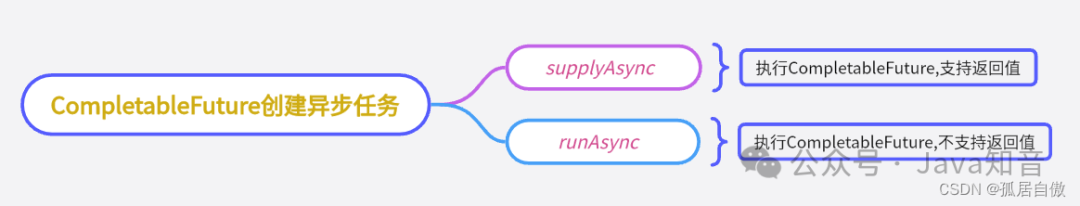
CompletableFuture创建异步任务,一般有supplyAsync和runAsync两个方法:
- supplyAsync执行CompletableFuture任务,支持返回值。
- runAsync执行CompletableFuture任务,没有返回值。
supplyAsync方法
//使用默认内置线程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据supplier构建执行任务
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
//自定义线程,根据supplier构建执行任务
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
runAsync方法
//使用默认内置线程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据runnable构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
//自定义线程,根据runnable构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
代码演示:
@Test
// supplyAsync执行CompletableFuture任务,支持返回值
public void defaultSupplyAsync() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 构建执行任务
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(6000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 99);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查询金额信息耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
});
// 这行代码在这里 则会进行6秒的阻塞 下面代码其他线程无法创建
// 只能等这个线程6秒过后结束才能创建其他线程
// Map<String, Object> userMap = userCompletableFuture.get();
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> roleCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> roleMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
roleMap.put("name", "管理员");
return roleMap;
});
log.info("金额查询结果为:" + amountCompletableFuture.join());
log.info("角色查询结果为:" + roleCompletableFuture.join());
log.info("总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
@Test
// supplyAsync执行CompletableFuture任务,支持返回值
public void customSupplyAsync() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 自定义线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(6000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 99);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查询金额信息耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
}, executorService);
// 这行代码在这里 则会进行6秒的阻塞 下面代码其他线程无法创建
// 只能等这个线程6秒过后结束才能创建其他线程
// Map<String, Object> userMap = userCompletableFuture.get();
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> roleCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> roleMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
roleMap.put("name", "管理员");
return roleMap;
}, executorService);
log.info("金额查询结果为:" + amountCompletableFuture.join());
log.info("角色查询结果为:" + roleCompletableFuture.join());
// 线程池需要关闭
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
@Test
// runAsync执行CompletableFuture任务,没有返回值
public void defaultRunAsync() {
long lordStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Void> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("执行金额增删改操作用时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> roleCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("执行角色增删改操作用时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
});
log.info("金额查询结果为:" + amountCompletableFuture.join());
log.info("角色查询结果为:" + roleCompletableFuture.join());
log.info("总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lordStartTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
@Test
// runAsync执行CompletableFuture任务,没有返回值
public void customRunAsync() {
long lordStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
CompletableFuture<Void> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("执行金额增删改操作用时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> roleCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("执行角色增删改操作用时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}, executor);
log.info("金额查询结果为:" + amountCompletableFuture.join());
log.info("角色查询结果为:" + roleCompletableFuture.join());
// 关闭线程池
executor.shutdown();
log.info("总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lordStartTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
注意:这里的get()与join()都是获取任务线程的返回值。join()方法抛出的是uncheck异常(即RuntimeException),不会强制开发者抛出, 会将异常包装成CompletionException异常 /CancellationException异常,但是本质原因还是代码内存在的真正的异常;
get()方法抛出的是经过检查的异常,ExecutionException, InterruptedException 需要用户手动处理(抛出或者 try catch)。
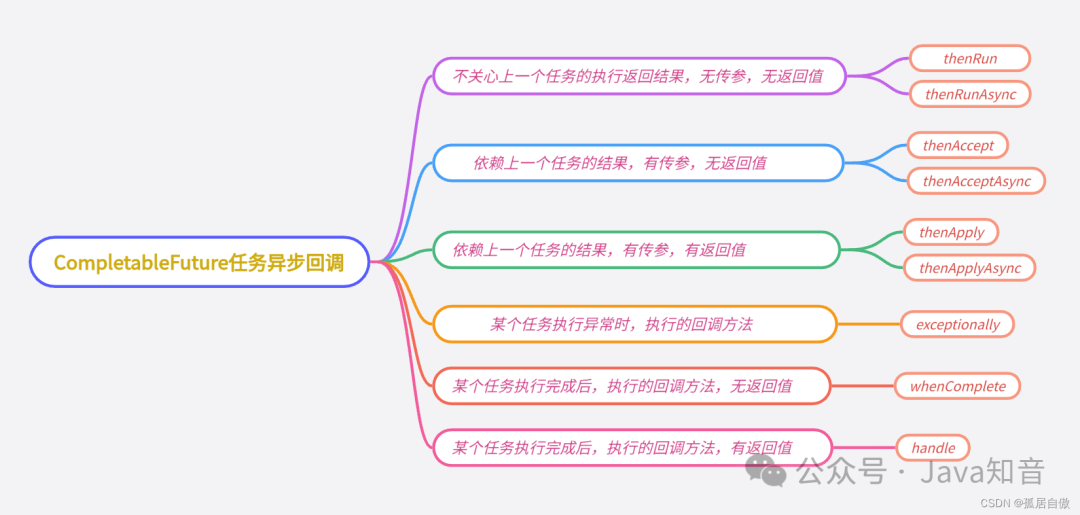
异步任务回调
thenRun / thenRunAsync
CompletableFuture的thenRun方法,通俗点讲就是,做完第一个任务后,再做第二个任务。某个任务执行完成后,执行回调方法;但是前后两个任务没有参数传递,第二个任务也没有返回值。
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
thenRun / thenRunAsync的区别? 源码解释:
private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(null, action);
}
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(asyncPool, action);
}
如果你执行第一个任务的时候,传入了一个自定义线程池:
- 调用thenRun方法执行第二个任务时,则第二个任务和第一个任务是共用同一个线程池。
- 调用thenRunAsync执行第二个任务时,则第一个任务使用的是你自己传入的线程池,第二个任务使用的是ForkJoin线程池。
后面介绍的thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync,thenApply和thenApplyAsync等,它们之间的区别也是这个哈!
代码演示:
@Test
// 执行第一个任务后 可以继续执行第二个任务 两个任务之间无传参 无返回值
public void defaultThenRun() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long lordStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Void> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("执行金额增删改操作用时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> thenCompletableFuture = amountCompletableFuture.thenRun(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("执行角色增删改操作用时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
});
thenCompletableFuture.get();
log.info("总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lordStartTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
结果:

thenAccept / thenAcceptAsync
CompletableFuture的thenAccept方法表示,第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,会将该任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,但是回调方法是没有返回值的。
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);
代码演示:
@Test
// 执行第一个任务后 可以继续执行第二个任务 并携带第一个任务的返回值 第二个任务执行完没有返回值
public void defaultThenAccept() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long lordStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Map> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 90);
log.info("执行金额查询操作用时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> thenCompletableFuture = amountCompletableFuture.thenAccept((map) -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (Integer.parseInt(map.get("amount").toString()) > 90) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("金额充足,可以购买!:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
} else {
log.info("金额不足,无法购买!:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
});
thenCompletableFuture.get();
log.info("总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lordStartTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
结果:

thenApply / thenApplyAsync
CompletableFuture的thenApply方法表示,第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,会将该任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,并且回调方法是有返回值的。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync();
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
代码演示:
@Test
// 执行第一个任务后 可以继续执行第二个任务 并携带第一个任务的返回值 第二个任务执行完有返回值
public void defaultThenApply() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long lordStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Map> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 90);
log.info("执行金额查询操作用时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> thenCompletableFuture = amountCompletableFuture.thenApply((map) -> {
int number = 0;
if (Integer.parseInt(map.get("amount").toString()) > 3) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 可口可乐3元一瓶 看金额一共能购买多少瓶
number = Integer.parseInt(map.get("amount").toString()) / 3;
}
return number;
});
log.info("当前金额一共可以买" + thenCompletableFuture.get() + "瓶可口可乐!");
Integer integer = thenCompletableFuture.get();
log.info("总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lordStartTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
结果:

exceptionally
CompletableFuture的exceptionally方法表示,某个任务执行异常时,执行的回调方法;并且有抛出异常作为参数,传递到回调方法。
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(
Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn) {
return uniExceptionallyStage(fn);
}
代码演示:
@Test
// 某个任务执行异常时,执行的回调方法;并且有抛出异常作为参数,传递到回调方法。
public void exceptionally() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long lordStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Map> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 90);
log.info("执行金额查询操作用时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> thenCompletableFuture = amountCompletableFuture.thenApply((map) -> {
int number = 0;
if (Integer.parseInt(map.get("amount").toString()) > 3) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 可口可乐3元一瓶 看金额一共能购买多少瓶
number = Integer.parseInt(map.get("amount").toString()) / 0;
} catch (ArithmeticException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new ArithmeticException(); // 这里一定要将异常抛除了,不然exceptionally无效
}
}
return number;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> exceptionFuture = thenCompletableFuture.exceptionally((e) -> {
log.error("除数为0,则默认商为0!");
return 0;
});
log.info("当前金额一共可以买" + thenCompletableFuture.get() + "瓶可口可乐!");
exceptionFuture.get();
log.info("总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lordStartTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
“
注意:这里的异常一定要抛出来,不然exceptionally无效!
whenComplete
CompletableFuture的whenComplete方法表示,某个任务执行完成后,执行的回调方法,无返回值;并且whenComplete方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是上个任务的结果。
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(
BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) {
return uniWhenCompleteStage(null, action);
}
代码演示:
@Test
// 某个任务执行完成后,执行的回调方法,无返回值;并且whenComplete方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是上个任务的结果。
public void whenComplete() {
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return "周杰伦";
});
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture1 = stringCompletableFuture.whenComplete((a, throwable) -> {
log.info("周杰伦喜欢唱");
});
log.info("输出结果为第一个任务:" + stringCompletableFuture1.join());
}
结果:

handle
CompletableFuture的handle方法表示,某个QQ账号买号平台地图任务执行完成后,执行回调方法,并且是有返回值的;并且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是回调方法执行的结果。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(
BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) {
return uniHandleStage(null, fn);
}
代码演示:
@Test
// 某个任务执行完成后,执行的回调方法,有返回值;并且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是第二个任务的结果。
public void handle() {
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return "周杰伦";
});
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture1 = stringCompletableFuture.handle((a, throwable) -> {
return "周杰伦喜欢唱歌!";
});
log.info("输出结果为第二个任务:" + stringCompletableFuture1.join());
}
结果:

多个任务组合处理
AND组合关系
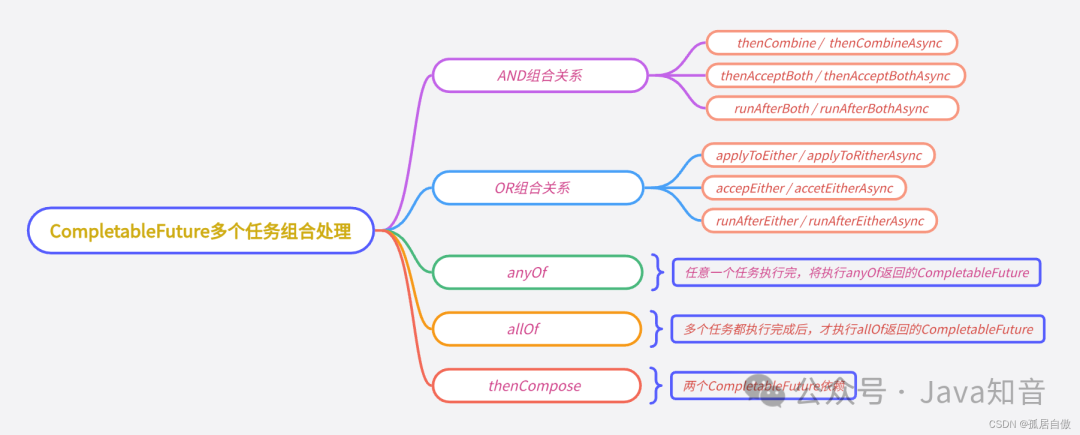
thenCombine / thenAcceptBoth / runAfterBoth都表示:将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只有这两个都正常执行完了,才会执行某个任务。
- thenCombine:会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且有返回值。
- thenAcceptBoth: 会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且无返回值。
- runAfterBoth 不会把执行结果当做方法入参,且没有返回值。
代码演示:
@Test
public void thenCombine() {
CompletableFuture<Integer> first = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 7;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> second = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 2).thenCombine(first, Integer::sum);
log.info("结果为:" + second.join());
}
结果为:

OR组合关系
applyToEither / acceptEither / runAfterEither 都表示:将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只要其中一个执行完了,就会执行某个任务。
- applyToEither:会将已经执行完成的任务,作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且有返回值。
- acceptEither: 会将已经执行完成的任务,作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且无返回值。
- runAfterEither:不会把执行结果当做方法入参,且没有返回值。
代码演示:
@Test
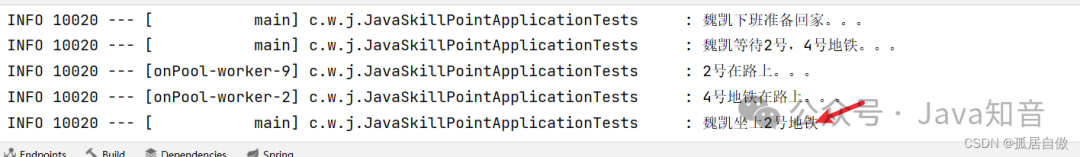
public void applyToEither1() {
log.info("魏凯下班准备回家。。。");
log.info("魏凯等待2号,4号地铁。。。");
CompletableFuture<String> busCF = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("2号在路上。。。");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "2";
}).applyToEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("4号地铁在路上。。。");
try {
Thread.sleep(4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "4";
}), first -> first + "号");
log.info("魏凯坐上" + busCF.join() + "地铁");
}
@Test
// OR
public void applyToEither() {
CompletableFuture<Integer> first = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 7;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> second = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 7;
}).applyToEither(first, num -> num);
log.info("最后结果为:" + second.join());
}
结果演示:
AllOf
所有任务都执行完成后,才执行 allOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果任意一个任务异常,allOf的CompletableFuture,执行get方法,会抛出异常。
代码演示:
@Test
// 所有任务都执行完成后,才执行 allOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果任意一个任务异常,allOf的CompletableFuture,执行get方法,会抛出异常。
// 这里第一次执行没有睡眠的话,是可以直接执行第三个任务的。如果有睡眠,则需要手动join启动。
public void allOf() {
CompletableFuture<Void> first = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// try {
// Thread.sleep(2000);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
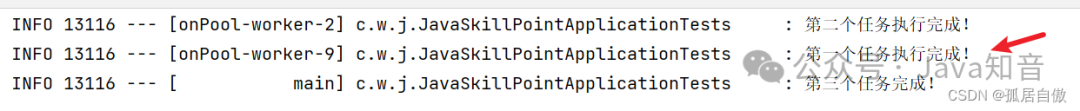
log.info("第一个任务执行完成!");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> second = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// try {
// Thread.sleep(500);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
log.info("第二个任务执行完成!");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(first, second).whenComplete((m, n) -> {
log.info("第三个任务完成!");
});
// voidCompletableFuture.join();
}
结果:
“
注意:这里第一次启动执行没有睡眠的话,是可以直接执行第三个任务的,因为这两个任务都执行完成,启动的瞬间第三个也同时执行完。如果有睡眠,则需要手动join启动,等待最长睡眠任务时间过后,第三个任务完成!
AnyOf
任意一个任务执行完,就执行anyOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果执行的任务异常,anyOf的CompletableFuture,执行get方法,会抛出异常。
代码演示:
@Test
// 前提任务任意执行完一个,则目标任务执行。其他前提任务则不在执行。
// 任意一个任务执行完,就执行anyOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果执行的任务异常,anyOf的CompletableFuture,执行get方法,会抛出异常。
public void anyOf() {
CompletableFuture<Void> first = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("第一个任务执行完成!");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> second = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("第二个任务执行完成!");
});
CompletableFuture<Object> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.anyOf(first, second).whenComplete((m, n) -> {
log.info("第三个任务完成!");
});
voidCompletableFuture.join();
}
结果:

thenCompose
thenCompose方法会在某个任务执行完成后,将该任务的执行结果,作为方法入参,去执行指定的方法。该方法会返回一个新的CompletableFuture实例。
- 如果该CompletableFuture实例的result不为null,则返回一个基于该result新的CompletableFuture实例。
- 如果该CompletableFuture实例为null,然后就执行这个新任务。
代码演示:
@Test
public void thenCompose1() {
CompletableFuture<Integer> stringCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 4)
.thenCompose(value -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// thenCompose方法返回一个新的CompletableFuture
if (Integer.valueOf(4).equals(value)) {
return 66;
} else {
return 99;
}
}));
log.info("结果:" + stringCompletableFuture.join());
}
@Test
public void thenCompose() {
CompletableFuture<String> first = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("第一个任务");
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 4)
.thenCompose((data) -> {
log.info("data为:" + data);
return first;
});
log.info("结果:" + stringCompletableFuture.join());
}
结果:

CompletableFuture注意点
Future需要获取返回值,才能获取异常信息
@Test
public void futureTest(){
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
CompletableFuture<Integer> integerCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int m = 9;
int n = 0;
return m / n;
},executor);
// integerCompletableFuture.join(); // 这行代码不加,则不会抛出异常
}
Future需要获取返回值,才能获取到异常信息。如果不加 get()/join()方法,看不到异常信息。小伙伴们使用的时候,注意一下哈,考虑是否加try…catch…或者使用exceptionally方法。
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的
//反例
CompletableFuture.get();
//正例
CompletableFuture.get(9, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的,如果使用它来获取异步调用的返回值,需要添加超时时间
默认线程池的注意点
CompletableFuture代码中又使用了默认的线程池,处理的线程个数是电脑CPU核数-1。在大量请求过来的时候,处理逻辑复杂的话,响应会很慢。一般建议使用自定义线程池,优化线程池配置参数。
自定义线程池时,注意饱和策略
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的,我们一般建议使用future.get(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)。并且一般建议使用自定义线程池。但是如果线程池拒绝策略是DiscardPolicy或者DiscardOldestPolicy,当线程池饱和时,会直接丢弃任务,不会抛弃异常。
因此建议,CompletableFuture线程池策略最好使用AbortPolicy,然后耗时的异步线程,做好线程池隔离!
相关文章:
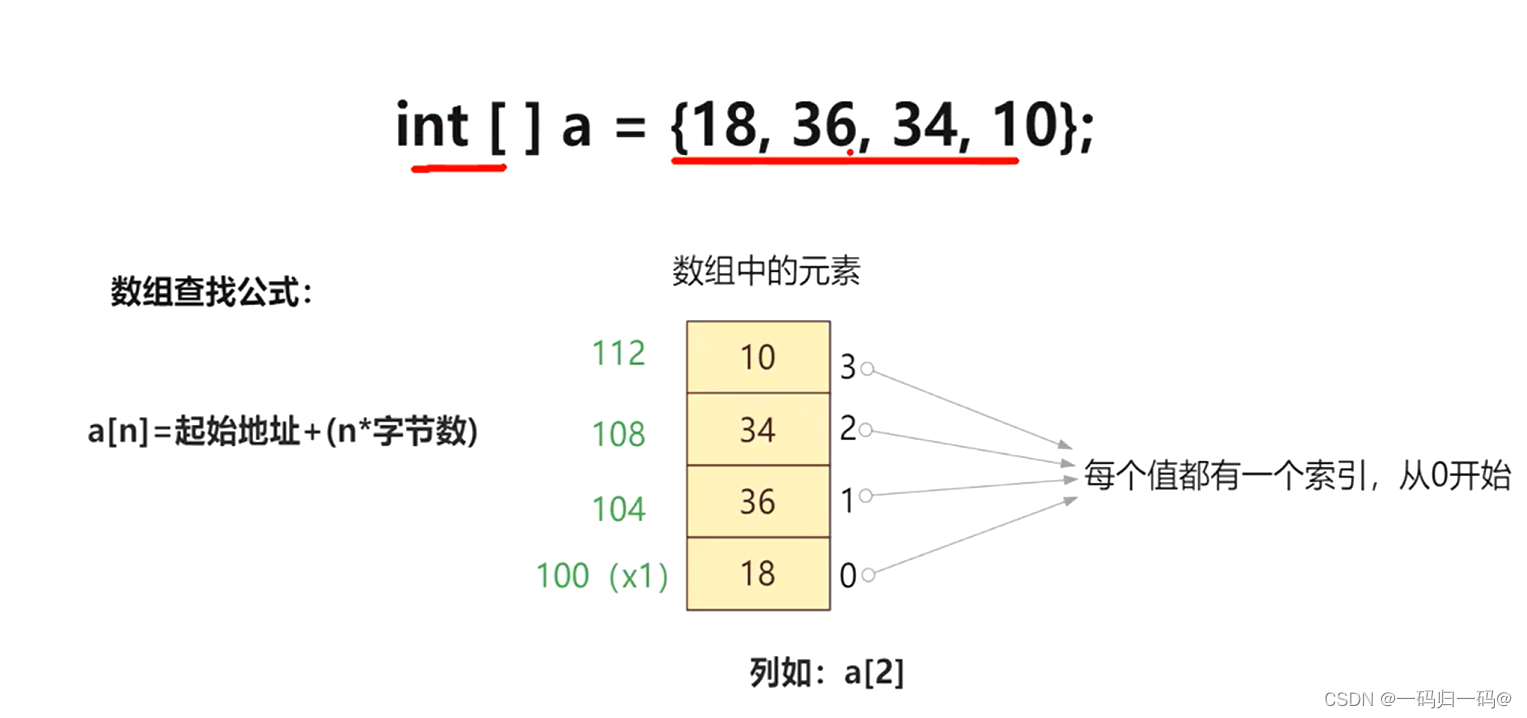
并发编程下的集合:数组寻址、LinkedList、HashMap、ConcurrentHashMap
如果发现hash取模后的数组索引位下无元素则直接新增,若不是空那就说明存在hash冲突,则判断数组索引位链表结构中的第一个元素的key以及hash值是否与新的key一致则直接覆盖,若不一致则判断当前的数组索引下的链表结构是否为红黑树,若为红黑树则走红黑树的新增方法,若不为红黑树则遍历当前链表结构,遍历中发现某个节点元素的next为null是则直接将新元素指针与next进行关联,若在遍历到next为空前判断到,某个节点的key以及key的hash值与新的key与新的keyhash值一致时则走覆盖。

【日常开发之插件篇】IDEA plugins 神器助我!!
今早因为老代码的一些bug让我突然觉得Idea的一些插件特别好用,我准备将我平时所用到的一些插件做个推荐以及记录。

【日常开发之FTP】Windows开启FTP、Java实现FTP文件上传下载
FTP是一个专门进行文件管理的操作服务,一般来讲可以在任意的操作系统之中进行配置,但是如果考虑到简便性,一般来讲可以直接在Linux系统下进行安装。FTP (File Transfer Protocol、文件传输协议)是TCP/IP协议中的一部分,属于应用层协议。使用FTP最主要的功能是对文件进行管理,所以在FTP内部对于文件支持有两种传输模式:文本模式(ASCII、默认)和二进制模式(Binary),通常文本文件使用ASCIl模式,而对于图片、视频、声音、压缩等文件则会使用二进制的方式进行传输。

【Linux之升华篇】Linux内核锁、用户模式与内核模式、用户进程通讯方式
alloc_pages(gfp_mask, order),_ _get_free_pages(gfp_mask, order)等。字符设备描述符 struct cdev,cdev_alloc()用于动态的分配 cdev 描述符,cdev_add()用于注。外,还支持语义符合 Posix.1 标准的信号函数 sigaction(实际上,该函数是基于 BSD 的,BSD。从最初的原子操作,到后来的信号量,从。(2)命名管道(named pipe):命名管道克服了管道没有名字的限制,因此,除具有管道所具有的。

【Mongdb之数据同步篇】什么是Oplog、Mongodb 开启oplog,java监听oplog并写入关系型数据库、Mongodb动态切换数据源
oplog是local库下的一个固定集合,Secondary就是通过查看Primary 的oplog这个集合来进行复制的。每个节点都有oplog,记录这从主节点复制过来的信息,这样每个成员都可以作为同步源给其他节点。Oplog 可以说是Mongodb Replication的纽带了。
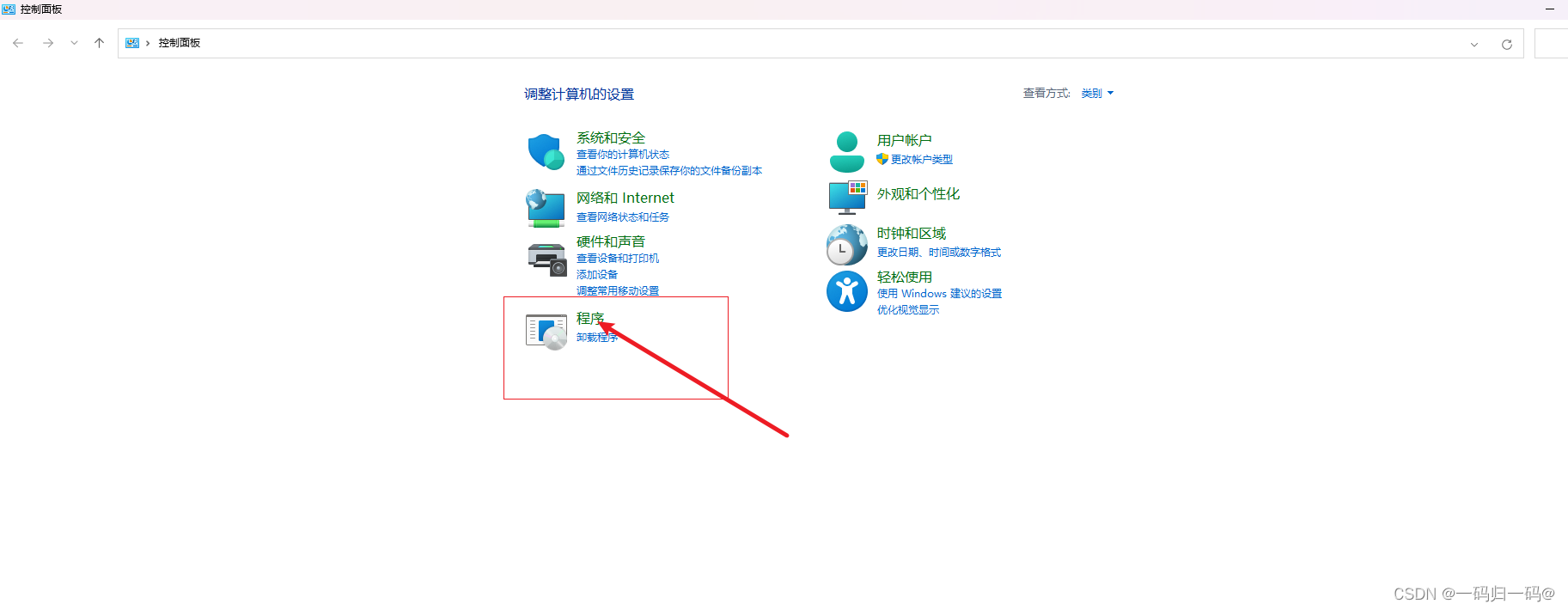
【日常开发之Windows共享文件】Java实现Windows共享文件上传下载
下拉框选择你选择的用户点击添加,然后共享确定。创建一个文件夹然后点击属性界面,点击共享。maven版本存在于SMB协议的兼容问题。首先开启服务,打开控制面板点击程序。点击启用或关闭Windows功能。我这边是专门创建了一个用户。SMB1.0选中红框内的。

CXFServlet类的作用
CXFServlet是Apache CXF框架中的一个核心组件,用于处理HTTP请求并将它们转换为Web服务调用。通过配置CXFServlet,你可以轻松地部署和管理SOAP和RESTful Web服务。

@Scheduled注解的scheduler属性什么作用
注解是 Spring Framework 提供的一种机制,用于定义计划任务,即周期性执行的任务。 注解可以应用于方法上,以指示 Spring 容器在特定的时间间隔或按照某种调度规则来调用该方法。 属性是 注解的一个可选属性,它的作用是允许开发者指定一个自定义的 对象来控制任务的调度方式。默认情况下, 注解使用 Spring 内部的 来执行任务,但如果需要更高级的定制化需求,可以通过 属性指定一个自定义的 实现。自定义调度器:共享调度器资源:高级调度需求:假设你想使用 作为调度器,并且希望所有带有
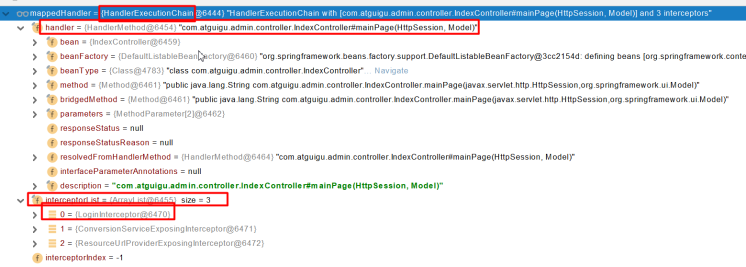
过滤器、拦截器、aop的先后顺序和作用范围&拦截器preHandle(),postHandle(),afterComplation()方法执行顺序
在Spring框架中,过滤器(Filter)、拦截器(Interceptor)和面向切面编程(AOP)都是用于处理请求和处理流程的组件,但它们的作用范围和触发时机有所不同。下面我会解释这三者的先后顺序和作用范围。执行顺序:请注意,这个顺序可能因具体的配置和使用的技术而有所不同。在实际应用中,建议根据项目的具体需求来合理配置和使用这些组件。拦截器执行流程图:实现拦截器需要实现这个接口,这个 接口中有三个默认方法,这三个方法的执行顺序:我们实现接口然后重写这三个方法,就会在对应的时机被自动执行。这里就是调用处理
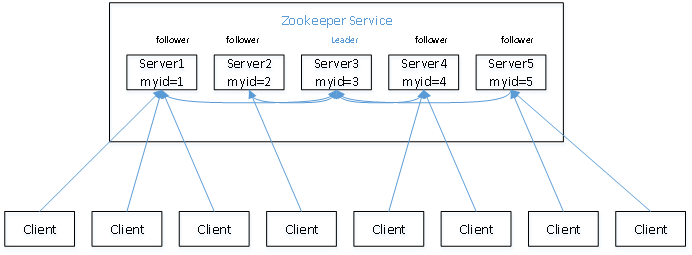
Zookeeper概要、协议、应用场景
Zoopkeeper提供了一套很好的分布式集群管理的机制,就是它这种基于层次型的目录树的数据结构并对树中的节点进行有效管理,从而可以设计出多种多样的分布式的数据管理模型,作为分布式系统的沟通调度桥梁。
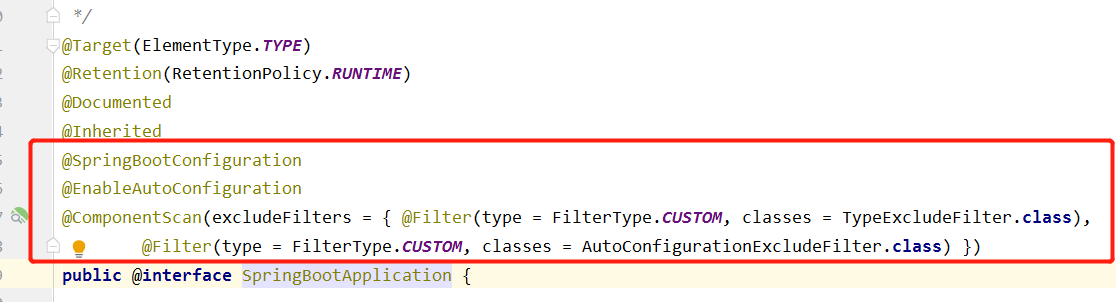
spring.factories文件的作用
即spring.factories文件是帮助spring-boot项目包以外的bean(即在pom文件中添加依赖中的bean)注册到spring-boot项目的spring容器中。在Spring Boot启动时,它会扫描classpath下所有的spring.factories文件,加载其中的自动配置类,并将它们注入到Spring ApplicationContext中,使得项目能够自动运行。spring.factories文件是Spring Boot自动配置的核心文件之一,它的作用是。
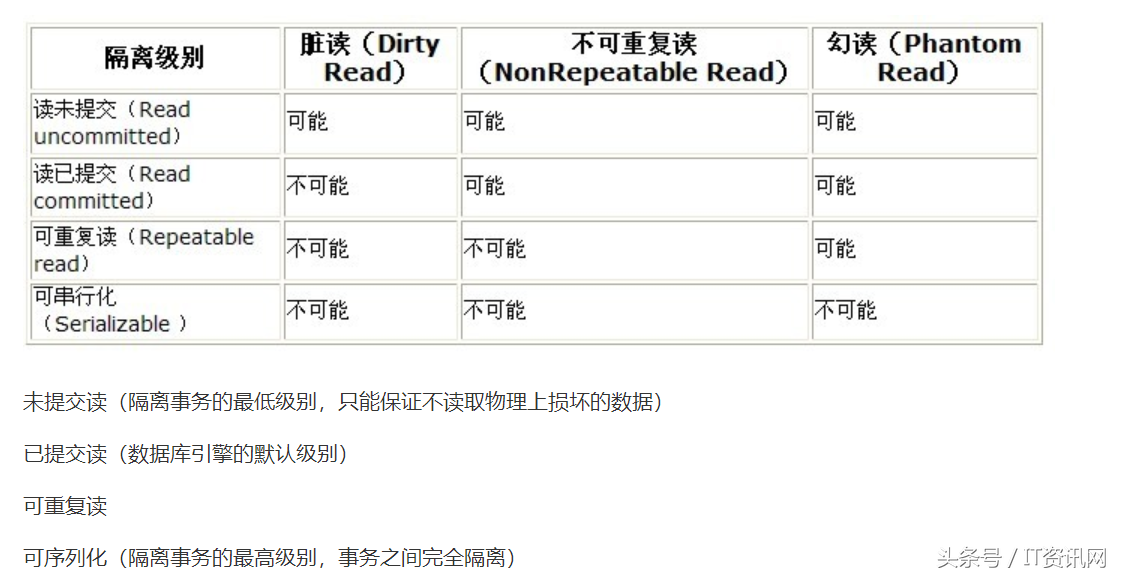
Spring事务七大传播机制与五个隔离级别,嵌套事务
如果当前方法正有一个事务在运行中,则该方法应该运行在一个嵌套事务中,被嵌套的事务可以独立于被封装的事务中进行提交或者回滚。如果封装事务存在,并且外层事务抛出异常回滚,那么内层事务必须回滚,反之,内层事务并不影响外层事务。当前方法必须在一个具有事务的上下文中运行,如有客户端有事务在进行,那么被调用端将在该事务中运行,否则的话重新开启一个事务。当前方法必须运行在它自己的事务中。一个新的事务将启动,而且如果有一个现有的事务在运行的话,则这个方法将在运行期被挂起,直到新的事务提交或者回滚才恢复执行。
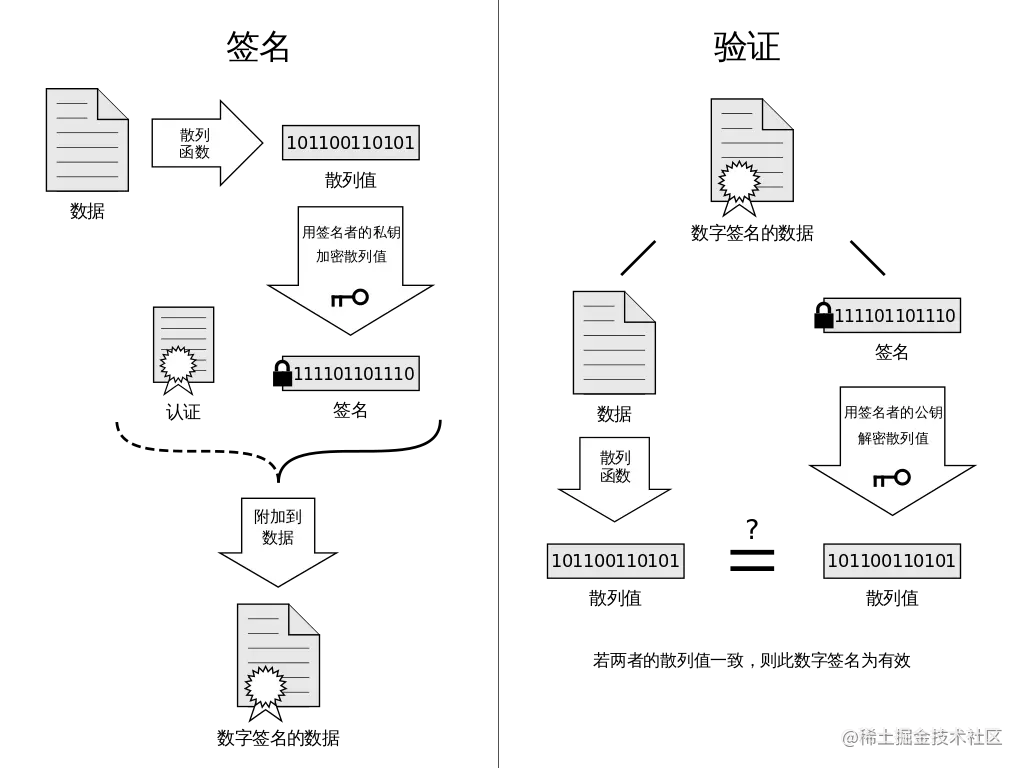
常见的七种加密算法及实现
**数字签名**、**信息加密** 是前后端开发都经常需要使用到的技术,应用场景包括了用户登入、交易、信息通讯、`oauth` 等等,不同的应用场景也会需要使用到不同的签名加密算法,或者需要搭配不一样的 **签名加密算法** 来达到业务目标。这里简单的给大家介绍几种常见的签名加密算法和一些典型场景下的应用。## 正文### 1. 数字签名**数字签名**,简单来说就是通过提供 **可鉴别** 的 **数字信息** 验证 **自身身份** 的一种方式。一套 **数字签名** 通常定义两种 **互补

7min到40s:SpringBoot 启动优化实践
然后重点排查这些阶段的代码。先看下。

SpringBoot系列教程之Bean之指定初始化顺序的若干姿势
之前介绍了@Order注解的常见错误理解,它并不能指定 bean 的加载顺序,那么问题来了,如果我需要指定 bean 的加载顺序,那应该怎么办呢?本文将介绍几种可行的方式来控制 bean 之间的加载顺序。

在Java中使用WebSocket
WebSocket是一种协议,用于在Web应用程序和服务器之间建立实时、双向的通信连接。它通过一个单一的TCP连接提供了持久化连接,这使得Web应用程序可以更加实时地传递数据。WebSocket协议最初由W3C开发,并于2011年成为标准。
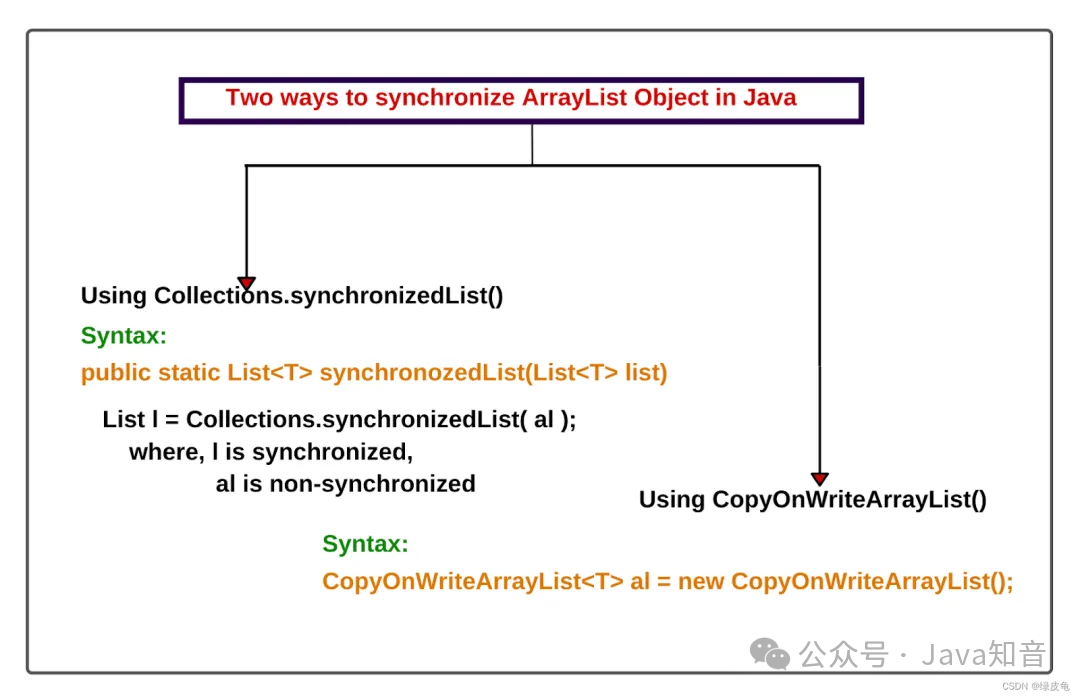
3种方案,模拟两个线程抢票
在多线程编程中,资源竞争是一个常见的问题。资源竞争发生在多个线程试图同时访问或修改共享资源时,可能导致数据不一致或其他并发问题。在模拟两个线程抢票的场景中,我们需要考虑如何公平地分配票,并确保每个线程都有机会成功获取票。本篇文章将通过三种方式来模拟两个线程抢票的过程,以展示不同的并发控制策略。使用 Synchronized 来确保一次只有一个线程可以访问票资源。使用 ReentrantLock 来实现线程间的协调。使用 Semaphore 来限制同时访问票的线程数量。
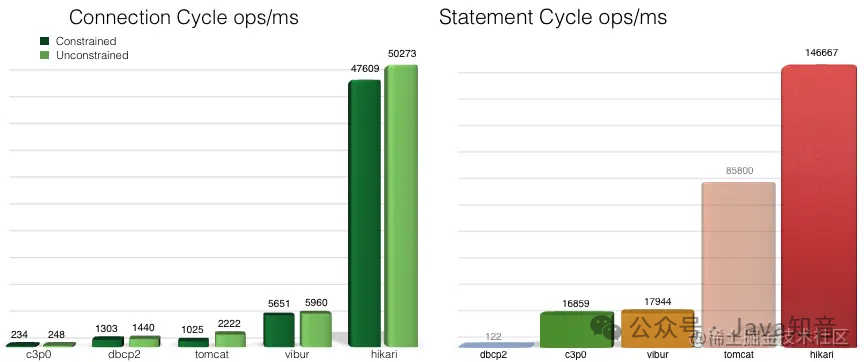
替代Druid,HakariCP 为什么这么快?
这次源码探究,真的感觉看到了无数个小细节,无数个小优化,积少成多。平时开发过程中,一些小的细节也一定要“扣”。

Java中volatile 的使用场景有哪些?
volatile是一种轻量级的同步机制,它能保证共享变量的可见性,同时禁止重排序保证了操作的有序性,但是它无法保证原子性。所以使用volatilevolatile。
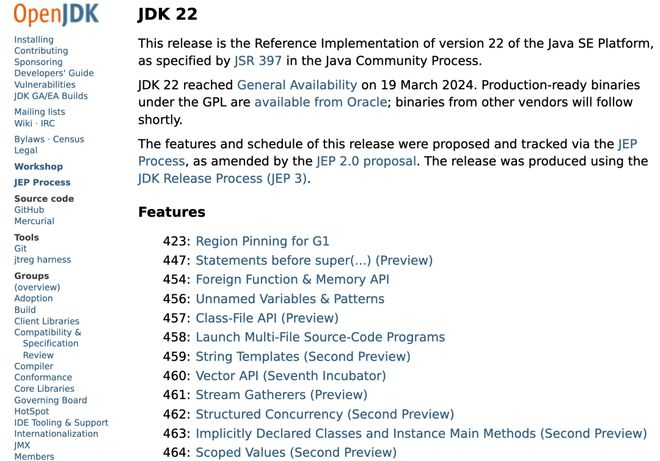
JDK22 正式发布了 !
Java 22 除了推出了新的增强功能和特性,也获得 Java Management Service (JMS) 的支持,这是一项新的 Oracle 云基础设施远程软件服务(Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, OCI) 原生服务,提供统一的控制台和仪表盘,帮助企业管理本地或云端的 Java 运行时和应用。使包含运行时计算值的字符串更容易表达,简化 Java 程序的开发工作,同时提高将用户提供的值编写成字符串,并将字符串传递给其他系统的程序的安全性。支持开发人员自由地表达构造器的行为。

Jackson 用起来!
你可以创建自定义序列化器和反序列化器以自定义特定字段或类的序列化和反序列化行为。为此,请创建一个实现或接口的类,并在需要自定义的字段或类上使用和注解。@Override// ...其他代码...优势性能优异:Jackson在序列化和反序列化过程中表现出优秀的性能,通常比其他Java JSON库更快。灵活性:通过注解、自定义序列化器/反序列化器等功能,Jackson提供了丰富的配置选项,允许你根据需求灵活地处理JSON数据。易于使用:Jackson的API设计简洁明了,易于学习和使用。

拜托!别再滥用 ! = null 判空了!!
另外,也许受此习惯影响,他们总潜意识地认为,所有的返回都是不可信任的,为了保护自己程序,就加了大量的判空。如果你养成习惯,都是这样写代码(返回空collections而不返回null),你调用自己写的方法时,就能大胆地忽略判空)这种情况下,null是个”看上去“合理的值,例如,我查询数据库,某个查询条件下,就是没有对应值,此时null算是表达了“空”的概念。最终,项目中会存在大量判空代码,多么丑陋繁冗!,而不要返回null,这样调用侧就能大胆地处理这个返回,例如调用侧拿到返回后,可以直接。

详解Java Math类的toDegrees()方法:将参数从弧度转换为角度
Java Math 类的 toDegrees() 方法是将一个角度的弧度表示转换为其度表示,返回值为double类型,表示从弧度数转换而来的角度数。这就是Java Math 类的 toDegrees() 方法的攻略。我们已经了解了该方法的基本概念、语法、注意事项以及两个示例。希望这篇攻略对你有所帮助。

SpringBoot接口防抖(防重复提交)的一些实现方案
作为一名老码农,在开发后端Java业务系统,包括各种管理后台和小程序等。在这些项目中,我设计过单/多租户体系系统,对接过许多开放平台,也搞过消息中心这类较为复杂的应用,但幸运的是,我至今还没有遇到过线上系统由于代码崩溃导致资损的情况。这其中的原因有三点:一是业务系统本身并不复杂;二是我一直遵循某大厂代码规约,在开发过程中尽可能按规约编写代码;三是经过多年的开发经验积累,我成为了一名熟练工,掌握了一些实用的技巧。啥是防抖所谓防抖,一是防用户手抖,二是防网络抖动。
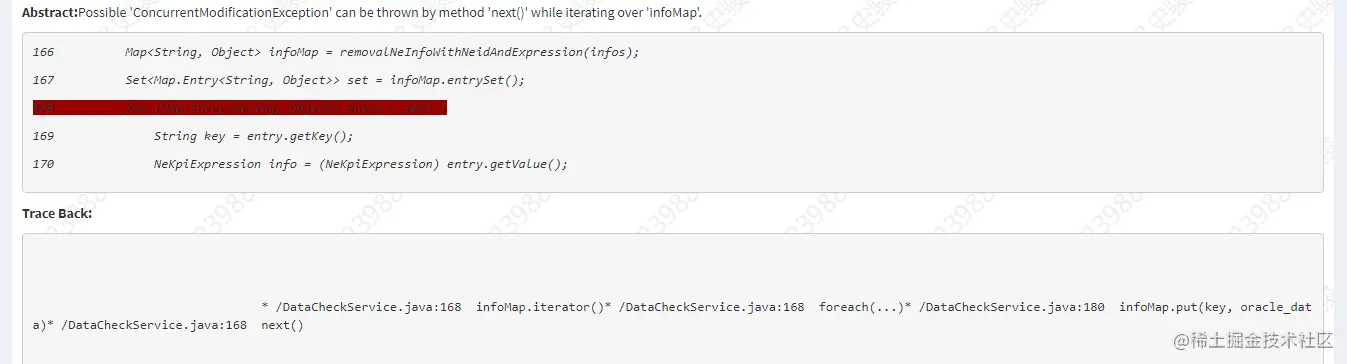
公司新来一个同事:为什么 HashMap 不能一边遍历一边删除?一下子把我问懵了!
前段时间,同事在代码中KW扫描的时候出现这样一条:上面出现这样的原因是在使用foreach对HashMap进行遍历时,同时进行put赋值操作会有问题,异常ConcurrentModificationException。于是帮同简单的看了一下,印象中集合类在进行遍历时同时进行删除或者添加操作时需要谨慎,一般使用迭代器进行操作。于是告诉同事,应该使用迭代器Iterator来对集合元素进行操作。同事问我为什么?这一下子把我问蒙了?对啊,只是记得这样用不可以,但是好像自己从来没有细究过为什么?
每天一个摆脱if-else工程师的技巧——优雅的参数校验
在日常的开发工作中,为了程序的健壮性,大部分方法都需要进行入参数据校验。最直接的当然是在相应方法内对数据进行手动校验,但是这样代码里就会有很多冗余繁琐的if-else。throw new IllegalArgumentException("用户姓名不能为空");throw new IllegalArgumentException("性别不能为空");throw new IllegalArgumentException("性别错误");
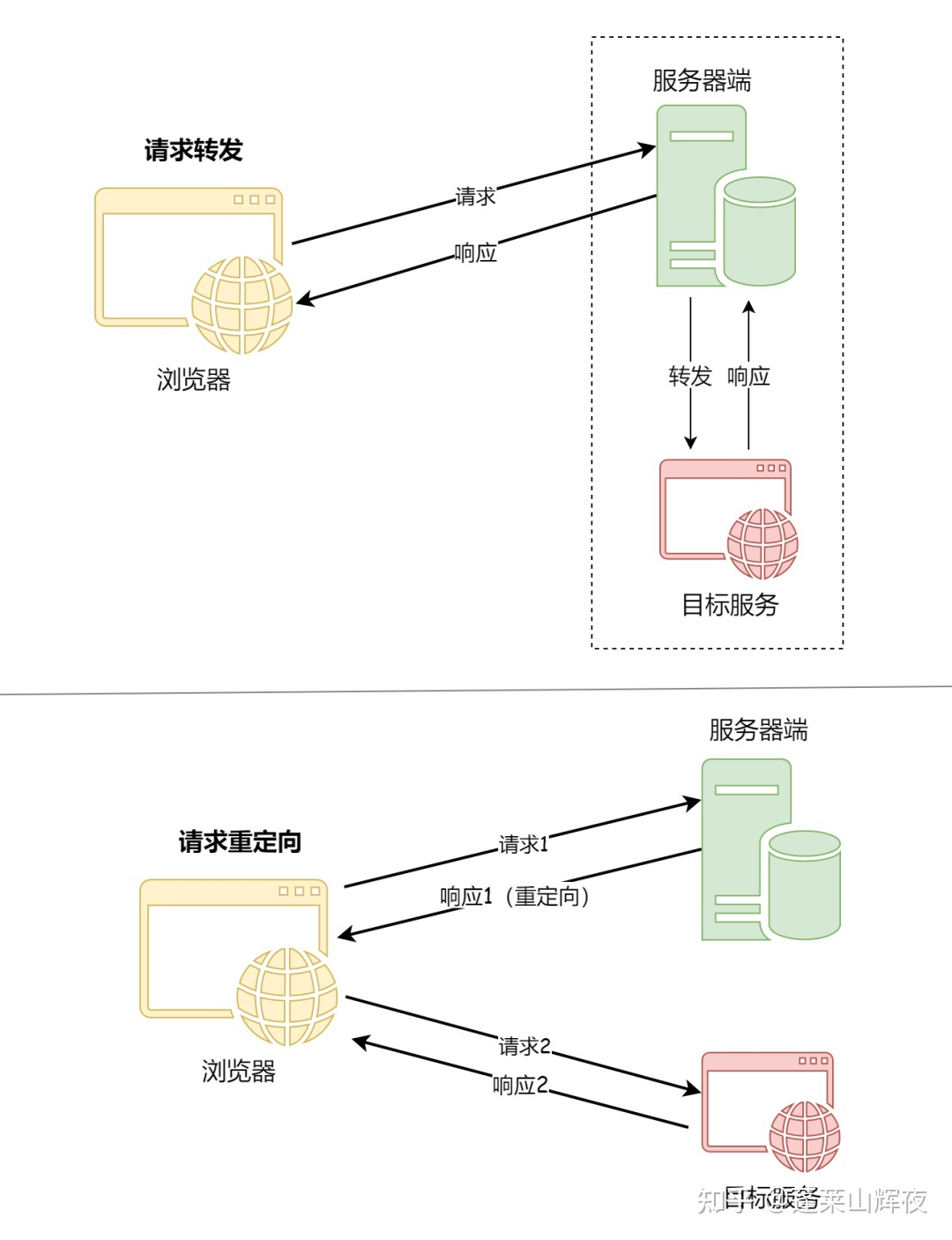
SpringBoot请求转发与重定向
但是可能由于B网址相对于A网址过于复杂,这样搜索引擎就会觉得网址A对用户更加友好,因而在重定向之后任然显示旧的网址A,但是显示网址B的内容。在平常使用手机的过程当中,有时候会发现网页上会有浮动的窗口,或者访问的页面不是正常的页面,这就可能是运营商通过某种方式篡改了用户正常访问的页面。重定向,是指在Nginx中,重定向是指通过修改URL地址,将客户端的请求重定向到另一个URL地址的过程,Nginx中实现重定向的方式有多种,比如使用rewrite模块、return指令等。使用场景:在返回视图的前面加上。

SSO 单点登录和 OAuth2.0 有何区别?
此方法的缺点是它依赖于浏览器和会话状态,对于分布式或者微服务系统而言,可能需要在服务端做会话共享,但是服务端会话共享效率比较低,这不是一个好的方案。在单点登录的上下文中,OAuth 可以用作一个中介,用户在一个“授权服务器”上登录,并获得一个访问令牌,该令牌可以用于访问其他“资源服务器”上的资源。首先,SSO 主要关注用户在多个应用程序和服务之间的无缝切换和保持登录状态的问题。这种方法通过将登录认证和业务系统分离,使用独立的登录中心,实现了在登录中心登录后,所有相关的业务系统都能免登录访问资源。
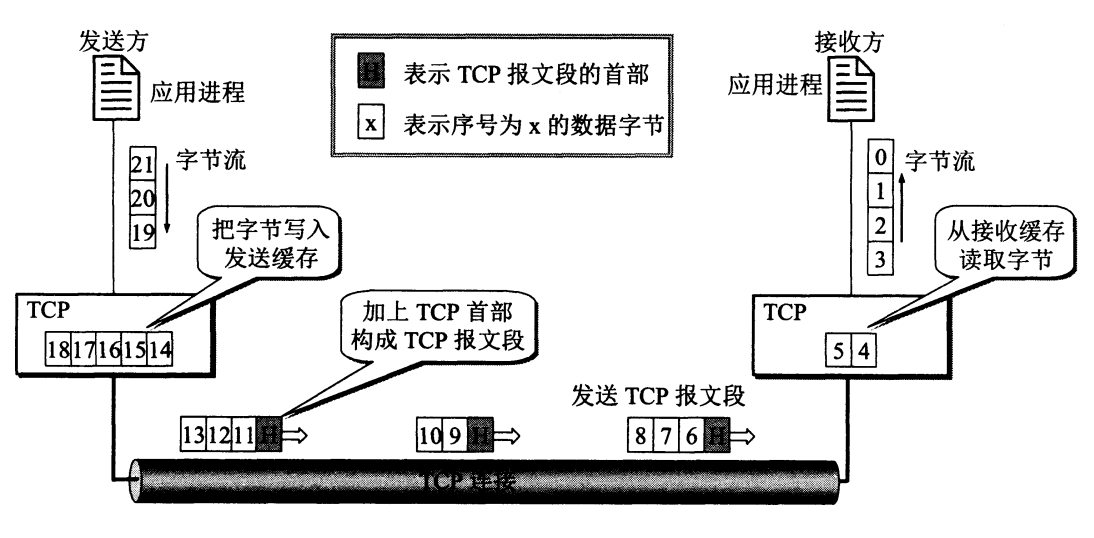
TCP协议-TCP连接管理
TCP协议是 TCP/IP 协议族中一个非常重要的协议。它是一种面向连接、提供可靠服务、面向字节流的传输层通信协议。TCP(Transmission Control Protocol,传输控制协议)。
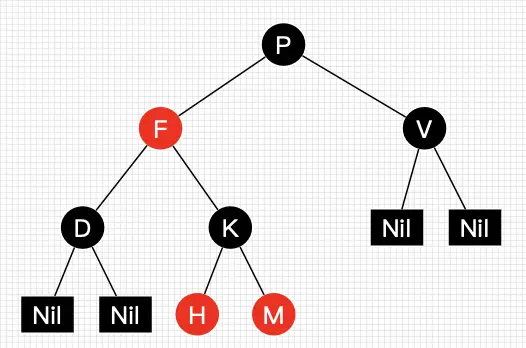
30张图带你彻底理解红黑树
当在10亿数据进行不到30次比较就能查找到目标时,不禁感叹编程之魅力!人类之伟大呀!—— 学红黑树有感。终于,在学习了几天的红黑树相关的知识后,我想把我所学所想和所感分享给大家。红黑树是一种比较难的数据结构,要完全搞懂非常耗时耗力,红黑树怎么自平衡?什么时候需要左旋或右旋?插入和删除破坏了树的平衡后怎么处理?等等一连串的问题在学习前困扰着我。如果你在学习过程中也会存在我的疑问,那么本文对你会有帮助,本文帮助你全面、彻底地理解红黑树!
