图像边缘检测之拉普拉斯(Laplacian)C++实现
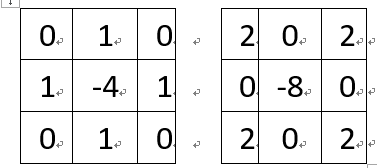
拉普拉斯算子(Laplacian)可应用到图像边缘检测中。在OpenCV中当kernel大小为3*3时,支持两种kernel算子,分别为:
#include "funset.hpp"
#include <limits.h>
#include <chrono>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <memory>
#include "common.hpp"namespace {typedef struct Rect {int x, y, width, height;
} Rect;
typedef struct Size {int width, height;
} Size;
typedef struct Point {int x, y;
} Point;int borderInterpolate(int p, int len)
{if ((unsigned)p < (unsigned)len) {;} else {if (len == 1) return 0;int delta = 1;do {if (p < 0) p = -p - 1 + delta;else p = len - 1 - (p - len) - delta;} while ((unsigned)p >= (unsigned)len);}return p;
}inline unsigned char saturate_cast(float v)
{int iv = (int)(v + (v >= 0 ? 0.5f : -0.5f));return (unsigned char)((unsigned)v <= UCHAR_MAX ? v : v > 0 ? UCHAR_MAX : 0);
}void filter2D(const unsigned char** src, unsigned char* dst, int dststep, int count, int width, int ksize)
{std::vector<Point> coords;std::vector<float> coeffs;if (ksize == 1) {coords = { { 1, 0 }, { 0, 1 }, { 1, 1 }, { 2, 1 }, { 1, 2 } }; // kernel non zero position: (x, y)coeffs = { 1.f, 1.f, -4.f, 1.f, 1.f }; // kernel non zero value: 1, 1, -4, 1, 1} else {coords = { { 0, 0 }, { 2, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, { 0, 2 }, { 2, 2 } }; // kernel non zero position: (x, y)coeffs = { 2.f, 2.f, -8.f, 2.f, 2.f }; // kernel non zero value: 2, 2, -8, 2, 2}std::vector<unsigned char*> ptrs(coords.size());float _delta{ 0.f };const Point* pt = &coords[0];const float* kf = (const float*)&coeffs[0];const unsigned char** kp = (const unsigned char**)&ptrs[0];int nz = (int)coords.size();for (; count > 0; count--, dst += dststep, src++) {unsigned char* D = (unsigned char*)dst;for (int k = 0; k < nz; k++)kp[k] = (const unsigned char*)src[pt[k].y] + pt[k].x;for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) {float s0 = _delta;for (int k = 0; k < nz; k++)s0 += kf[k] * kp[k][i];D[i] = saturate_cast(s0);}}
}int Laplacian_(const unsigned char* src_, unsigned char* dst_, int width_, int height_, int ksize_)
{const unsigned char* src = src_;unsigned char* dst = dst_;const Size ksize{ 3, 3 };const int maxBufRows = ksize.height + 3;const Point anchor{ 1, 1 };const Rect roi{ 0, 0, width_, height_ };const int dx1{ 1 }, dx2{ 1 };int borderLength = std::max(ksize.width - 1, 1);std::vector<int> borderTab(borderLength);borderTab[0] = borderInterpolate(-dx1, width_);borderTab[1] = borderInterpolate(width_, width_);std::vector<unsigned char*> rows(maxBufRows);const int* btab = &borderTab[0];int srcstep{ width_ }, dststep{ width_ };std::vector<unsigned char> ringBuf((width_ + ksize.width - 1) * maxBufRows, 0);int bufStep{ width_ + ksize.width - 1 };int startY = std::max(roi.y - anchor.y, 0), startY0 = startY, rowCount{ 0 }, dstY{ 0 };int endY = std::min(roi.y + roi.height + ksize.height - anchor.y - 1, height_);int esz = 1;unsigned char** brows = &rows[0];int bufRows = (int)rows.size();int kwidth = ksize.width;int kheight = ksize.height, ay = anchor.y;int _dx1 = dx1, _dx2 = dx2;int width1 = roi.width + kwidth - 1;int dy = 0, i = 0;int count = endY - startY;for (;; dst += dststep * i, dy += i) {int dcount = bufRows - ay - startY - rowCount + roi.y;dcount = dcount > 0 ? dcount : bufRows - kheight + 1;dcount = std::min(dcount, count);count -= dcount;for (; dcount-- > 0; src += srcstep) {int bi = (startY - startY0 + rowCount) % bufRows;unsigned char* brow = &ringBuf[0] + bi*bufStep;unsigned char* row = brow;if (++rowCount > bufRows) {--rowCount;++startY;}memcpy(row + _dx1*esz, src, (width1 - _dx2 - _dx1)*esz);for (i = 0; i < _dx1*esz; i++)row[i] = src[btab[i]];for (i = 0; i < _dx2*esz; i++)row[i + (width1 - _dx2)*esz] = src[btab[i + _dx1*esz]];}int max_i = std::min(bufRows, roi.height - (dstY + dy) + (kheight - 1));for (i = 0; i < max_i; i++) {int srcY = borderInterpolate(dstY + dy + i + roi.y - ay, height_);if (srcY < startY) return -1;if (srcY >= startY + rowCount) break;int bi = (srcY - startY0) % bufRows;brows[i] = &ringBuf[0] + bi*bufStep;}if (i < kheight) break;i -= kheight - 1;filter2D((const unsigned char**)brows, dst, dststep, i, roi.width, ksize_);}dstY += dy;if (dstY > roi.height) return -1;return 0;
}int Laplacian(const unsigned char* src_, unsigned char* dst_, int width_, int height_, int ksize_)
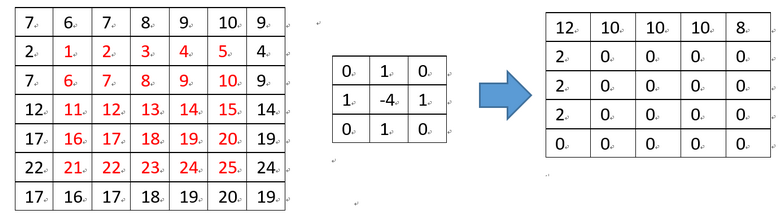
{const int kernel_size{ 3 };std::vector<float> kernel;if (ksize_ == 1) kernel = { 0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f, -4.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f, 0.f };else kernel = { 2.f, 0.f, 2.f, 0.f, -8.f, 0.f, 2.f, 0.f, 2.f };int new_width = width_ + kernel_size - 1, new_height = height_ + kernel_size - 1;std::unique_ptr<unsigned char[]> data(new unsigned char[new_width * new_height]);unsigned char* p = data.get();for (int y = 0; y < new_height; ++y) {if (y != 0 && y != new_height - 1) {for (int x = 0; x < new_width; ++x) {if (x == 0) {p[y * new_width + x] = src_[(y - 1) * width_ + 1];} else if (x == new_width - 1) {p[y * new_width + x] = src_[(y - 1) * width_ + (width_ - 1 - 1)];} else {p[y * new_width + x] = src_[(y - 1) * width_ + (x - 1)];}}}if (y == new_height - 1) {for (int x = 0; x < new_width; ++x) {p[y * new_width + x] = p[(y - 2) * new_width + x];}for (int x = 0; x < new_width; ++x) { // y = 0p[x] = p[2 * new_width + x];}}}for (int y = 1; y < new_height - 1; ++y) {for (int x = 1; x < new_width - 1; ++x) {float value{ 0.f };int count{ 0 };for (int m = -1; m <= 1; ++m) {for (int n = -1; n <= 1; ++n) {value += p[(y + m) * new_width + (x + n)] * kernel[count++];}}if (value < 0.) dst_[(y - 1) * width_ + (x - 1)] = 0;else if (value > 255.) dst_[(y - 1) * width_ + (x - 1)] = 255;else dst_[(y - 1) * width_ + (x - 1)] = static_cast<unsigned char>(value);}}return 0;
}} // namespaceint laplacian_cpu(const unsigned char* src, int width, int height, int ksize, unsigned char* dst, float* elapsed_time)
{int ret{ -1 };// ksize == 1: kernel={ 0, 1, 0, 1, -4, 1, 0, 1, 0 }// ksize == 3: kernel={ 2, 0, 2, 0, -8, 0, 2, 0, 2 }CHECK(ksize == 1 || ksize == 3);//TIME_START_CPUret = Laplacian(src, dst, width, height, ksize);//TIME_END_CPUreturn ret;
}#include "funset.hpp"
#include <random>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include "common.hpp"int test_image_process_laplacian()
{cv::Mat src = cv::imread("E:/GitCode/CUDA_Test/test_data/images/lena.png", 0);if (!src.data || src.channels() != 1) {fprintf(stderr, "read image fail\n");return -1;}int width{ 400 }, height{ 400 };cv::resize(src, src, cv::Size(width, height));std::unique_ptr<unsigned char[]> data1(new unsigned char[width * height]), data2(new unsigned char[width * height]);float elapsed_time1{ 0.f }, elapsed_time2{ 0.f }; // millisecondsint ksize{ 1 };CHECK(laplacian_cpu(src.data, width, height, ksize, data1.get(), &elapsed_time1) == 0);//CHECK(laplacian_gpu(src.data, width, height, data2.get(), &elapsed_time2) == 0);//fprintf(stdout, "gray image edge detection: laplacian: cpu run time: %f ms, gpu run time: %f ms\n", elapsed_time1, elapsed_time2);cv::Mat dst;cv::Laplacian(src, dst, src.depth(), ksize);cv::imwrite("E:/GitCode/CUDA_Test/test_data/images/laplacian.png", dst);CHECK(compare_result(data1.get(), dst.data, width*height) == 0);//CHECK(compare_result(data1.get(), data2.get(), width*height) == 0);save_image(src, dst, width, height / 2, "E:/GitCode/CUDA_Test/test_data/images/laplacian_result.png");return 0;
}

相关文章:

从0到1,Airbnb的深度学习实践经验总结
作者 | Haldar译者 | 陆离出品 | AI科技大本营(ID: rgznai100)此前,AI科技大本营发布了关于希望通过介绍的研究成果为读者提供一些有用的帮助和指引。模型中的生态系统本文要讨论的机器学习现实应用,是关于根据用户预约的可能性来…

高并发大流量专题---8、动态语言的并发处理
高并发大流量专题---8、动态语言的并发处理 一、总结 一句话总结: 和本科毕业论文连起来了:基于消息中间件Rocket MQ的研究;用于并发处理的消息队列 1、什么是进程、线程、协程? 进程(Process)是计算机中的…

1. 文件系统——磁盘分区、各目录功能、硬盘
一、磁盘分区及文件访问入口在前文中介绍过,Linux的整个文件系统像一棵倒置的数,最顶层的是根文件系统,其下有很多一级子目录,一级子目录下面是二级子目录,依此类推:/:根目录/bin,/s…
吴恩达老师深度学习视频课笔记:逻辑回归公式推导及C++实现
逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)是一个二分分类算法。逻辑回归的目标是最小化其预测与训练数据之间的误差。为了训练逻辑回归模型中的参数w和b,需要定义一个成本函数(cost function)。成本函数(cost function):它是针对整个训练集的。衡量参数w和b在整个训…

网络运行时间提高100倍,Google使用的AI视频理解架构有多强?
译者 | 刘畅出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)视频理解是一个很有挑战性的问题。由于视频包含时空数据,因此图像的特征表示需要同时提取图像和运动信息。这不仅对自动理解视频语义内容有重要性,还对机器人的感知和学习也至关重要…

iOS学习笔记(十三)——获取手机信息(UIDevice、NSBundle、NSLocale)
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> iOS的APP的应用开发的过程中,有时为了bug跟踪或者获取用反馈的需要自动收集用户设备、系统信息、应用信息等等,这些信息方便开发者诊断问题,当然这些信息是用户的非隐私信息࿰…

吴恩达老师深度学习视频课笔记:单隐含层神经网络公式推导及C++实现(二分类)
关于逻辑回归的公式推导和实现可以参考: http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/79346691 下面是在逻辑回归的基础上,对单隐含层的神经网络进行公式推导:选择激活函数时的一些经验:不同层的激活函数可以不一样。如果…

「2019中国大数据技术大会」超值学生票来啦!
大会官网:https://t.csdnimg.cn/U1wA经过11年的沉淀与发展,中国大数据技术大会见证了大数据技术生态在中国的建立、发展和成熟,已经成为国内大数据行业极具影响力的盛会,也是大数据人非常期待的年度深度分享盛会。在新的时代背景下…

校验正确获取对象或者数组的属性方法(babel-plugin-idx/_.get)
背景: 开发中经常遇到取值属性的时候,需要校验数值的有效性。 例如: 获取props对象里面的friends属性 props.user && props.user.friends && props.user.friends[0] && props.user.friends[0].friends 对于深层的对…

Ring Tone Manager on Windows Mobile
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 手机铃声经常能够体现一个人的个性,有些哥们儿在自习室不把手机设置成震动,一来电就#$^%^&^%#$&$*,声音还很大,唯恐别人听不到。 Windows Mobile设备上如何来设置手…

OpenCV3.3中K-Means聚类接口简介及使用
OpenCV3.3中给出了K-均值聚类(K-Means)的实现,即接口cv::kmeans,接口的声明在include/opencv2/core.hpp文件中,实现在modules/core/src/kmeans.cpp文件中,其中:下面对此接口中的参数作个简单说明:(1)、data:…

一文读懂对抗机器学习Universal adversarial perturbations | CSDN博文精选
作者 | Icoding_F2014来源 | CSDN博客本文提出一种 universal 对抗扰动,universal 是指同一个扰动加入到不同的图片中,能够使图片被分类模型误分类,而不管图片到底是什么。示意图:形式化的定义:对于d维数据分布 μ&…
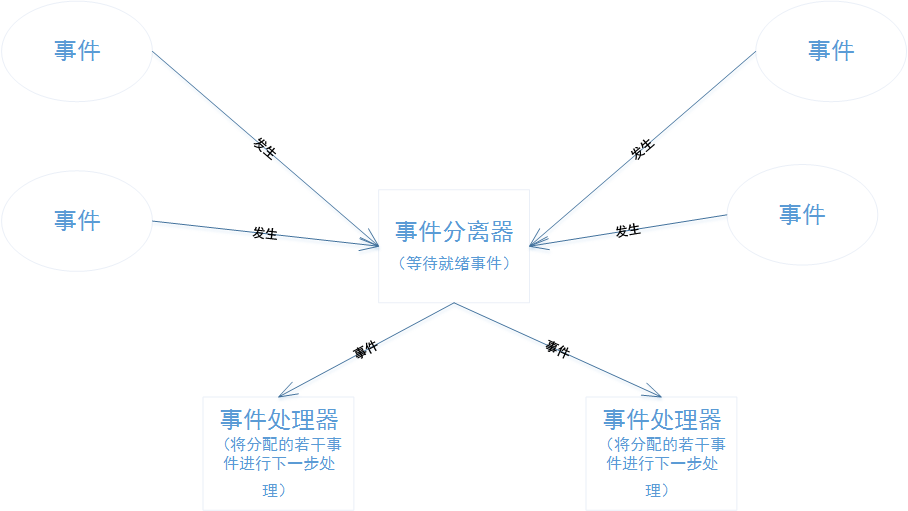
Reactor模式与Proactor模式
博主一脚刚踏进分布式的大门(看《分布式Java应用》,如果大家有啥推荐的书欢迎留言~),发现书中对NIO采用的Reactor模式、AIO采用的Proactor模式一笔带过,好奇心趋势我找了一下文章,发现两篇挺不错的文章&…

linux下使profile和.bash_profile立即生效的方法
使profile生效的方法1.source /etc/profile使用.bash_profile生效的方法1 . .bash_profile2 source .bash_profile3 exec bash --login转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/shine20/1436473
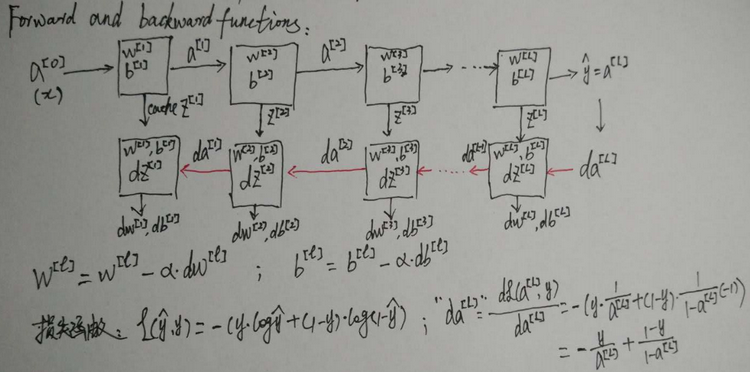
吴恩达老师深度学习视频课笔记:多隐含层神经网络公式推导(二分类)
多隐含层神经网络的推导步骤非常类似于单隐含层神经网络的步骤,只不过是多重复几遍。关于单隐含层神经网络公式的推导可以参考: http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/79370310 逻辑回归是一个浅层模型(shadow model),或称单层…

Python中的元编程:一个关于修饰器和元类的简单教程
作者 | Saurabh Kukade译者 | 刘畅出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)最近,作者遇到一个非常有趣的概念,它就是用 Python 进行元编程。我想在本文中分享我对该主题的见解。作者希望它可以帮助解决这个问题,因为很多人说…

获取用户电脑的上网IP地址
在项目中经常要获取用户的上网的IP地址,如何获取用户的IP地址,方法很多,现在介绍以下2种。 /// <summary> /// 获取本机在局域网的IP地址 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> …
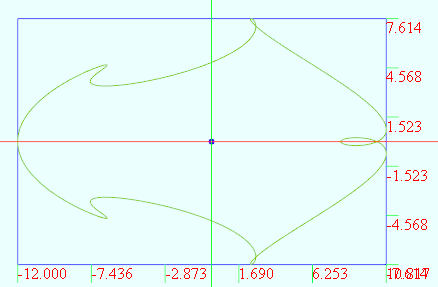
数学图形(1.40)T_parameter
不记得在哪搞了个数学公式生成的图形. vertices 1000t from 0 to (2*PI) r 2.0 x r*(5*cos(t) - cos(6*t)) y r*(3*sin(t) - sin(4*t)) 给线加上一维变量的变化,使之变成面: vertices D1:360 D2:21u from 0 to (2*PI) D1 v from 0 to 20 D2x (v2)*cos(u) - cos((v3)*u…

K-均值聚类(K-Means) C++代码实现
K-均值聚类(K-Means)简介可以参考: http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/79276668 以下是K-Means的C实现,code参考OpenCV 3.3中的cv::kmeans函数,均值点初始化的方法仅支持KMEANS_RANDOM_CENTERS。以下是从数据集MNIST中提取…

让学生网络相互学习,为什么深度相互学习优于传统蒸馏模型?| 论文精读
作者 | Ying Zhang,Tao Xiang等译者 | 李杰出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)蒸馏模型是一种将知识从教师网络(teacher)传递到学生网络(student)的有效且广泛使用的技术。通常来说,…

mac apache 配置
mac系统自带apache这无疑给广大的开发朋友提供了便利,接下来是针对其中的一些说明 一、自带apache相关命令 1. sudo apachectl start 启动服务,需要权限,就是你计算机的password 2. sudo apachectl stop 终止服务 ####3. sudo apachectl rest…

jQuery学习---------认识事件处理
3种事件模型:原始事件模型DOM事件模型IE事件模型原始事件模型(0级事件模型)1、事件处理程序被定义为函数实例,然后绑定到DOM元素事件对象上,实现事件的注册。例子:var btn document.getElementsByTagName(…
C++中的虚函数表介绍
在C语言中,当我们使用基类的引用或指针调用一个虚成员函数时会执行动态绑定。因为我们直到运行时才能知道到底调用了哪个版本的虚函数,所以所有虚函数都必须有定义。通常情况下,如果我们不使用某个函数,则无须为该函数提供定义。但是我们必须…

AI如何赋能金融行业?百度、图灵深视等同台分享技术实践
近日,由BTCMEX举办的金融技术创新研讨会在北京举办。BTCMEX投资人李笑来,AI技术公司TuringPass、百度、美国Apache基金会项目Pulsar、区块链安全公司SlowMist等相关专家参加了此次会议,共同探讨了金融技术在创新方面的现状。 图灵深视副总裁许…

【Win32 API学习]打开可执行文件
在MFC中打开其他可执行文件常用到的方法有:WinExec、ShellExecute、CreatProcess。 1.WinExec WinExec 主要运行EXE文件,用法简单,只有两个参数,前一个指定命令路径,后一个指定窗口显示方式: UINT WinExec(…

支付宝接口使用文档说明 支付宝异步通知
支付宝接口使用文档说明 支付宝异步通知(notify_url)与return_url. 现支付宝的通知有两类。 A服务器通知,对应的参数为notify_url,支付宝通知使用POST方式 B页面跳转通知,对应的参数为return_url,支付宝通知使用GET方式 ÿ…

完全隐藏Master Page Site Actions菜单只有管理员才可以看见
1. 在Master Page Head 增加下面的Style <style type"text/css"> .ms-cui-tt{visibility:hidden;} </style> 2. 增加SPSecurityTrimmedControl <SharePoint:SPRibbonPeripheralContent runat"server" Location"TabRowLeft&qu…
深度学习中的随机梯度下降(SGD)简介
随机梯度下降(Stochastic Gradient Descent, SGD)是梯度下降算法的一个扩展。机器学习中反复出现的一个问题是好的泛化需要大的训练集,但大的训练集的计算代价也更大。机器学习算法中的代价函数通常可以分解成每个样本的代价函数的总和。随着训练集规模增长为数十亿…

推荐系统中的前沿技术研究与落地:深度学习、AutoML与强化学习 | AI ProCon 2019...
整理 | 夕颜出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)个性化推荐算法滥觞于互联网的急速发展,随着国内外互联网公司,如 Netflix 在电影领域,亚马逊、淘宝、京东等在电商领域,今日头条在内容领域的采用和推动&…

运维日志管理系统
因公司数据安全和分析的需要,故调研了一下 GlusterFS lagstash elasticsearch kibana 3 redis 整合在一起的日志管理应用:安装,配置过程,使用情况等续一,glusterfs分布式文件系统部署:说明…
