JDK源码分析 NIO实现
总列表:http://hg.openjdk.java.net/
小版本:http://hg.openjdk.java.net/jdk8u
jdk:http://hg.openjdk.java.net/jdk8u/jdk8u60/file/d8f4022fe0cd
hotspot:http://hg.openjdk.java.net/jdk8u/jdk8u60/hotspot/file/37240c1019fd
调用本地native方法
package sun.nio.ch;
public class IOUtil {
...
public static native void configureBlocking(FileDescriptor var0, boolean var1) throws IOException;对应jdk文件位置:
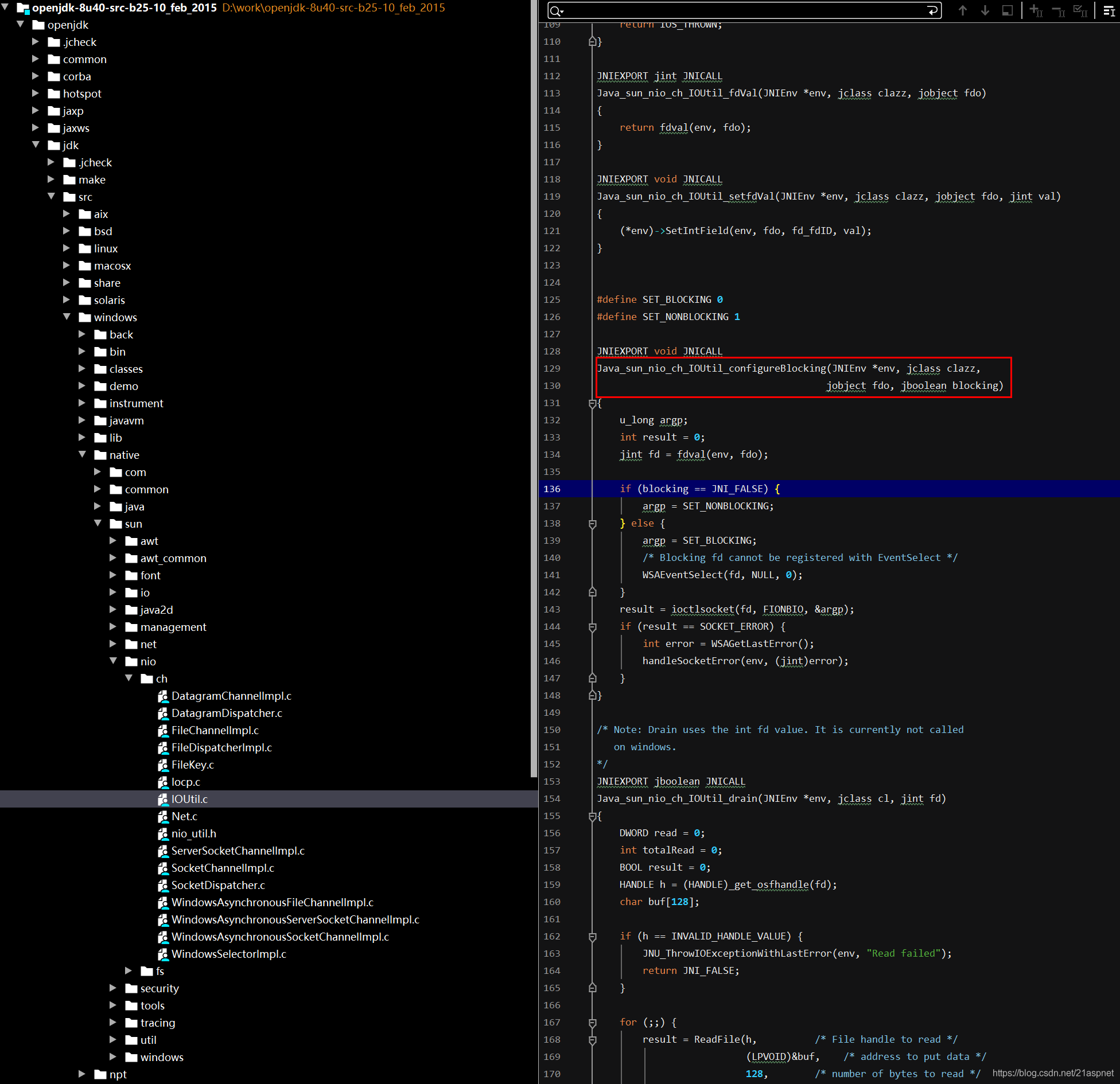
https://blog.csdn.net/wangyangzhizhou/article/details/42613273
https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/11142083.html
EPoll.c
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_sun_nio_ch_EPoll_epollWait(JNIEnv *env, jclass c,jint epfd, jlong address, jint numfds)
{struct epoll_event *events = jlong_to_ptr(address);int res;RESTARTABLE(epoll_wait(epfd, events, numfds, -1), res);if (res < 0) {JNU_ThrowIOExceptionWithLastError(env, "epoll_wait failed");}return res;
}这种情况在同一层可以省略EPoll,否则是找不到的
package sun.nio.ch
class EPollArrayWrapper{private native int epollCreate();private native void epollCtl(int epfd, int opcode, int fd, int events);private native int epollWait(long pollAddress, int numfds, long timeout,int epfd) throws IOException;private static native int sizeofEPollEvent();private static native int offsetofData();private static native void interrupt(int fd);private static native void init();}void initInterrupt(int fd0, int fd1) {outgoingInterruptFD = fd1;incomingInterruptFD = fd0;epollCtl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd0, EPOLLIN);}int poll(long timeout) throws IOException {updateRegistrations();updated = epollWait(pollArrayAddress, NUM_EPOLLEVENTS, timeout, epfd);for (int i=0; i<updated; i++) {if (getDescriptor(i) == incomingInterruptFD) {interruptedIndex = i;interrupted = true;break;}}return updated;}调用方
package sun.nio.ch;
class EPollSelectorImpl{/*** Package private constructor called by factory method in* the abstract superclass Selector.*/EPollSelectorImpl(SelectorProvider sp) throws IOException {super(sp);long pipeFds = IOUtil.makePipe(false);fd0 = (int) (pipeFds >>> 32);fd1 = (int) pipeFds;pollWrapper = new EPollArrayWrapper();pollWrapper.initInterrupt(fd0, fd1);fdToKey = new HashMap<>();}protected int doSelect(long timeout) throws IOException {if (closed)throw new ClosedSelectorException();processDeregisterQueue();try {begin();pollWrapper.poll(timeout);} finally {end();}processDeregisterQueue();int numKeysUpdated = updateSelectedKeys();if (pollWrapper.interrupted()) {// Clear the wakeup pipepollWrapper.putEventOps(pollWrapper.interruptedIndex(), 0);synchronized (interruptLock) {pollWrapper.clearInterrupted();IOUtil.drain(fd0);interruptTriggered = false;}}return numKeysUpdated;}
}https://www.cnblogs.com/Jack-Blog/p/12394487.html
注意:epoll_wait在 \glibc-2.31\sysdeps\unix\sysv\linux\sys\epoll.h
glibc是gnu发布的libc库,也即c运行库。glibc是linux 系统中最底层的api(应用程序开发接口),几乎其它任何的运行库都会倚赖于glibc。
/* Copyright (C) 2002-2020 Free Software Foundation, Inc.This file is part of the GNU C Library.The GNU C Library is free software; you can redistribute it and/ormodify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General PublicLicense as published by the Free Software Foundation; eitherversion 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.The GNU C Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty ofMERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNULesser General Public License for more details.You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General PublicLicense along with the GNU C Library; if not, see<https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. */#ifndef _SYS_EPOLL_H
#define _SYS_EPOLL_H 1#include <stdint.h>
#include <sys/types.h>#include <bits/types/sigset_t.h>/* Get the platform-dependent flags. */
#include <bits/epoll.h>#ifndef __EPOLL_PACKED
# define __EPOLL_PACKED
#endifenum EPOLL_EVENTS{EPOLLIN = 0x001,
#define EPOLLIN EPOLLINEPOLLPRI = 0x002,
#define EPOLLPRI EPOLLPRIEPOLLOUT = 0x004,
#define EPOLLOUT EPOLLOUTEPOLLRDNORM = 0x040,
#define EPOLLRDNORM EPOLLRDNORMEPOLLRDBAND = 0x080,
#define EPOLLRDBAND EPOLLRDBANDEPOLLWRNORM = 0x100,
#define EPOLLWRNORM EPOLLWRNORMEPOLLWRBAND = 0x200,
#define EPOLLWRBAND EPOLLWRBANDEPOLLMSG = 0x400,
#define EPOLLMSG EPOLLMSGEPOLLERR = 0x008,
#define EPOLLERR EPOLLERREPOLLHUP = 0x010,
#define EPOLLHUP EPOLLHUPEPOLLRDHUP = 0x2000,
#define EPOLLRDHUP EPOLLRDHUPEPOLLEXCLUSIVE = 1u << 28,
#define EPOLLEXCLUSIVE EPOLLEXCLUSIVEEPOLLWAKEUP = 1u << 29,
#define EPOLLWAKEUP EPOLLWAKEUPEPOLLONESHOT = 1u << 30,
#define EPOLLONESHOT EPOLLONESHOTEPOLLET = 1u << 31
#define EPOLLET EPOLLET};/* Valid opcodes ( "op" parameter ) to issue to epoll_ctl(). */
#define EPOLL_CTL_ADD 1 /* Add a file descriptor to the interface. */
#define EPOLL_CTL_DEL 2 /* Remove a file descriptor from the interface. */
#define EPOLL_CTL_MOD 3 /* Change file descriptor epoll_event structure. */typedef union epoll_data
{void *ptr;int fd;uint32_t u32;uint64_t u64;
} epoll_data_t;struct epoll_event
{uint32_t events; /* Epoll events */epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */
} __EPOLL_PACKED;__BEGIN_DECLS/* Creates an epoll instance. Returns an fd for the new instance.The "size" parameter is a hint specifying the number of filedescriptors to be associated with the new instance. The fdreturned by epoll_create() should be closed with close(). */
extern int epoll_create (int __size) __THROW;/* Same as epoll_create but with an FLAGS parameter. The unused SIZEparameter has been dropped. */
extern int epoll_create1 (int __flags) __THROW;/* Manipulate an epoll instance "epfd". Returns 0 in case of success,-1 in case of error ( the "errno" variable will contain thespecific error code ) The "op" parameter is one of the EPOLL_CTL_*constants defined above. The "fd" parameter is the target of theoperation. The "event" parameter describes which events the calleris interested in and any associated user data. */
extern int epoll_ctl (int __epfd, int __op, int __fd,struct epoll_event *__event) __THROW;/* Wait for events on an epoll instance "epfd". Returns the number oftriggered events returned in "events" buffer. Or -1 in case oferror with the "errno" variable set to the specific error code. The"events" parameter is a buffer that will contain triggeredevents. The "maxevents" is the maximum number of events to bereturned ( usually size of "events" ). The "timeout" parameterspecifies the maximum wait time in milliseconds (-1 == infinite).This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with__THROW. */
extern int epoll_wait (int __epfd, struct epoll_event *__events,int __maxevents, int __timeout);/* Same as epoll_wait, but the thread's signal mask is temporarilyand atomically replaced with the one provided as parameter.This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with__THROW. */
extern int epoll_pwait (int __epfd, struct epoll_event *__events,int __maxevents, int __timeout,const __sigset_t *__ss);__END_DECLS#endif /* sys/epoll.h */
Epoll实现机制:
epoll fd有一个私有的struct eventpoll,它记录哪一个fd注册到了epfd上。
eventpoll 同样有一个等待队列,记录所有等待的线程。还有一个预备好的fd列表,这些fd可以进行读或写。
相关内核实现代码在fs/eventpoll.c
https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/fs/eventpoll.c
判断是否tcp有激活事件:net/ipv4/tcp.c:tcp_poll函数
/** fs/eventpoll.c (Efficient event retrieval implementation)* Copyright (C) 2001,...,2009 Davide Libenzi** This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or* (at your option) any later version.** Davide Libenzi <davidel@xmailserver.org>**/#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/file.h>
#include <linux/signal.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/list.h>
#include <linux/hash.h>
#include <linux/spinlock.h>
#include <linux/syscalls.h>
#include <linux/rbtree.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/eventpoll.h>
#include <linux/mount.h>
#include <linux/bitops.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/anon_inodes.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <asm/mman.h>
#include <linux/atomic.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/compat.h>/** LOCKING:* There are three level of locking required by epoll :** 1) epmutex (mutex)* 2) ep->mtx (mutex)* 3) ep->lock (spinlock)** The acquire order is the one listed above, from 1 to 3.* We need a spinlock (ep->lock) because we manipulate objects* from inside the poll callback, that might be triggered from* a wake_up() that in turn might be called from IRQ context.* So we can't sleep inside the poll callback and hence we need* a spinlock. During the event transfer loop (from kernel to* user space) we could end up sleeping due a copy_to_user(), so* we need a lock that will allow us to sleep. This lock is a* mutex (ep->mtx). It is acquired during the event transfer loop,* during epoll_ctl(EPOLL_CTL_DEL) and during eventpoll_release_file().* Then we also need a global mutex to serialize eventpoll_release_file()* and ep_free().* This mutex is acquired by ep_free() during the epoll file* cleanup path and it is also acquired by eventpoll_release_file()* if a file has been pushed inside an epoll set and it is then* close()d without a previous call to epoll_ctl(EPOLL_CTL_DEL).* It is also acquired when inserting an epoll fd onto another epoll* fd. We do this so that we walk the epoll tree and ensure that this* insertion does not create a cycle of epoll file descriptors, which* could lead to deadlock. We need a global mutex to prevent two* simultaneous inserts (A into B and B into A) from racing and* constructing a cycle without either insert observing that it is* going to.* It is necessary to acquire multiple "ep->mtx"es at once in the* case when one epoll fd is added to another. In this case, we* always acquire the locks in the order of nesting (i.e. after* epoll_ctl(e1, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, e2), e1->mtx will always be acquired* before e2->mtx). Since we disallow cycles of epoll file* descriptors, this ensures that the mutexes are well-ordered. In* order to communicate this nesting to lockdep, when walking a tree* of epoll file descriptors, we use the current recursion depth as* the lockdep subkey.* It is possible to drop the "ep->mtx" and to use the global* mutex "epmutex" (together with "ep->lock") to have it working,* but having "ep->mtx" will make the interface more scalable.* Events that require holding "epmutex" are very rare, while for* normal operations the epoll private "ep->mtx" will guarantee* a better scalability.*//* Epoll private bits inside the event mask */
#define EP_PRIVATE_BITS (EPOLLWAKEUP | EPOLLONESHOT | EPOLLET)/* Maximum number of nesting allowed inside epoll sets */
#define EP_MAX_NESTS 4#define EP_MAX_EVENTS (INT_MAX / sizeof(struct epoll_event))#define EP_UNACTIVE_PTR ((void *) -1L)#define EP_ITEM_COST (sizeof(struct epitem) + sizeof(struct eppoll_entry))struct epoll_filefd {struct file *file;int fd;
} __packed;/** Structure used to track possible nested calls, for too deep recursions* and loop cycles.*/
struct nested_call_node {struct list_head llink;void *cookie;void *ctx;
};/** This structure is used as collector for nested calls, to check for* maximum recursion dept and loop cycles.*/
struct nested_calls {struct list_head tasks_call_list;spinlock_t lock;
};/** Each file descriptor added to the eventpoll interface will* have an entry of this type linked to the "rbr" RB tree.* Avoid increasing the size of this struct, there can be many thousands* of these on a server and we do not want this to take another cache line.*/
struct epitem {/* RB tree node used to link this structure to the eventpoll RB tree */struct rb_node rbn;/* List header used to link this structure to the eventpoll ready list */struct list_head rdllink;/** Works together "struct eventpoll"->ovflist in keeping the* single linked chain of items.*/struct epitem *next;/* The file descriptor information this item refers to */struct epoll_filefd ffd;/* Number of active wait queue attached to poll operations */int nwait;/* List containing poll wait queues */struct list_head pwqlist;/* The "container" of this item */struct eventpoll *ep;/* List header used to link this item to the "struct file" items list */struct list_head fllink;/* wakeup_source used when EPOLLWAKEUP is set */struct wakeup_source __rcu *ws;/* The structure that describe the interested events and the source fd */struct epoll_event event;
};/** This structure is stored inside the "private_data" member of the file* structure and represents the main data structure for the eventpoll* interface.*/
struct eventpoll {/* Protect the access to this structure */spinlock_t lock;/** This mutex is used to ensure that files are not removed* while epoll is using them. This is held during the event* collection loop, the file cleanup path, the epoll file exit* code and the ctl operations.*/struct mutex mtx;/* Wait queue used by sys_epoll_wait() */wait_queue_head_t wq;/* Wait queue used by file->poll() */wait_queue_head_t poll_wait;/* List of ready file descriptors */struct list_head rdllist;/* RB tree root used to store monitored fd structs */struct rb_root rbr;/** This is a single linked list that chains all the "struct epitem" that* happened while transferring ready events to userspace w/out* holding ->lock.*/struct epitem *ovflist;/* wakeup_source used when ep_scan_ready_list is running */struct wakeup_source *ws;/* The user that created the eventpoll descriptor */struct user_struct *user;struct file *file;/* used to optimize loop detection check */int visited;struct list_head visited_list_link;
};/* Wait structure used by the poll hooks */
struct eppoll_entry {/* List header used to link this structure to the "struct epitem" */struct list_head llink;/* The "base" pointer is set to the container "struct epitem" */struct epitem *base;/** Wait queue item that will be linked to the target file wait* queue head.*/wait_queue_t wait;/* The wait queue head that linked the "wait" wait queue item */wait_queue_head_t *whead;
};/* Wrapper struct used by poll queueing */
struct ep_pqueue {poll_table pt;struct epitem *epi;
};/* Used by the ep_send_events() function as callback private data */
struct ep_send_events_data {int maxevents;struct epoll_event __user *events;
};/** Configuration options available inside /proc/sys/fs/epoll/*/
/* Maximum number of epoll watched descriptors, per user */
static long max_user_watches __read_mostly;/** This mutex is used to serialize ep_free() and eventpoll_release_file().*/
static DEFINE_MUTEX(epmutex);/* Used to check for epoll file descriptor inclusion loops */
static struct nested_calls poll_loop_ncalls;/* Used for safe wake up implementation */
static struct nested_calls poll_safewake_ncalls;/* Used to call file's f_op->poll() under the nested calls boundaries */
static struct nested_calls poll_readywalk_ncalls;/* Slab cache used to allocate "struct epitem" */
static struct kmem_cache *epi_cache __read_mostly;/* Slab cache used to allocate "struct eppoll_entry" */
static struct kmem_cache *pwq_cache __read_mostly;/* Visited nodes during ep_loop_check(), so we can unset them when we finish */
static LIST_HEAD(visited_list);/** List of files with newly added links, where we may need to limit the number* of emanating paths. Protected by the epmutex.*/
static LIST_HEAD(tfile_check_list);#ifdef CONFIG_SYSCTL#include <linux/sysctl.h>static long zero;
static long long_max = LONG_MAX;ctl_table epoll_table[] = {{.procname = "max_user_watches",.data = &max_user_watches,.maxlen = sizeof(max_user_watches),.mode = 0644,.proc_handler = proc_doulongvec_minmax,.extra1 = &zero,.extra2 = &long_max,},{ }
};
#endif /* CONFIG_SYSCTL */static const struct file_operations eventpoll_fops;static inline int is_file_epoll(struct file *f)
{return f->f_op == &eventpoll_fops;
}/* Setup the structure that is used as key for the RB tree */
static inline void ep_set_ffd(struct epoll_filefd *ffd,struct file *file, int fd)
{ffd->file = file;ffd->fd = fd;
}/* Compare RB tree keys */
static inline int ep_cmp_ffd(struct epoll_filefd *p1,struct epoll_filefd *p2)
{return (p1->file > p2->file ? +1:(p1->file < p2->file ? -1 : p1->fd - p2->fd));
}/* Tells us if the item is currently linked */
static inline int ep_is_linked(struct list_head *p)
{return !list_empty(p);
}static inline struct eppoll_entry *ep_pwq_from_wait(wait_queue_t *p)
{return container_of(p, struct eppoll_entry, wait);
}/* Get the "struct epitem" from a wait queue pointer */
static inline struct epitem *ep_item_from_wait(wait_queue_t *p)
{return container_of(p, struct eppoll_entry, wait)->base;
}/* Get the "struct epitem" from an epoll queue wrapper */
static inline struct epitem *ep_item_from_epqueue(poll_table *p)
{return container_of(p, struct ep_pqueue, pt)->epi;
}/* Tells if the epoll_ctl(2) operation needs an event copy from userspace */
static inline int ep_op_has_event(int op)
{return op != EPOLL_CTL_DEL;
}/* Initialize the poll safe wake up structure */
static void ep_nested_calls_init(struct nested_calls *ncalls)
{INIT_LIST_HEAD(&ncalls->tasks_call_list);spin_lock_init(&ncalls->lock);
}/*** ep_events_available - Checks if ready events might be available.** @ep: Pointer to the eventpoll context.** Returns: Returns a value different than zero if ready events are available,* or zero otherwise.*/
static inline int ep_events_available(struct eventpoll *ep)
{return !list_empty(&ep->rdllist) || ep->ovflist != EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;
}/*** ep_call_nested - Perform a bound (possibly) nested call, by checking* that the recursion limit is not exceeded, and that* the same nested call (by the meaning of same cookie) is* no re-entered.** @ncalls: Pointer to the nested_calls structure to be used for this call.* @max_nests: Maximum number of allowed nesting calls.* @nproc: Nested call core function pointer.* @priv: Opaque data to be passed to the @nproc callback.* @cookie: Cookie to be used to identify this nested call.* @ctx: This instance context.** Returns: Returns the code returned by the @nproc callback, or -1 if* the maximum recursion limit has been exceeded.*/
static int ep_call_nested(struct nested_calls *ncalls, int max_nests,int (*nproc)(void *, void *, int), void *priv,void *cookie, void *ctx)
{int error, call_nests = 0;unsigned long flags;struct list_head *lsthead = &ncalls->tasks_call_list;struct nested_call_node *tncur;struct nested_call_node tnode;spin_lock_irqsave(&ncalls->lock, flags);/** Try to see if the current task is already inside this wakeup call.* We use a list here, since the population inside this set is always* very much limited.*/list_for_each_entry(tncur, lsthead, llink) {if (tncur->ctx == ctx &&(tncur->cookie == cookie || ++call_nests > max_nests)) {/** Ops ... loop detected or maximum nest level reached.* We abort this wake by breaking the cycle itself.*/error = -1;goto out_unlock;}}/* Add the current task and cookie to the list */tnode.ctx = ctx;tnode.cookie = cookie;list_add(&tnode.llink, lsthead);spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ncalls->lock, flags);/* Call the nested function */error = (*nproc)(priv, cookie, call_nests);/* Remove the current task from the list */spin_lock_irqsave(&ncalls->lock, flags);list_del(&tnode.llink);
out_unlock:spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ncalls->lock, flags);return error;
}/** As described in commit 0ccf831cb lockdep: annotate epoll* the use of wait queues used by epoll is done in a very controlled* manner. Wake ups can nest inside each other, but are never done* with the same locking. For example:** dfd = socket(...);* efd1 = epoll_create();* efd2 = epoll_create();* epoll_ctl(efd1, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, dfd, ...);* epoll_ctl(efd2, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, efd1, ...);** When a packet arrives to the device underneath "dfd", the net code will* issue a wake_up() on its poll wake list. Epoll (efd1) has installed a* callback wakeup entry on that queue, and the wake_up() performed by the* "dfd" net code will end up in ep_poll_callback(). At this point epoll* (efd1) notices that it may have some event ready, so it needs to wake up* the waiters on its poll wait list (efd2). So it calls ep_poll_safewake()* that ends up in another wake_up(), after having checked about the* recursion constraints. That are, no more than EP_MAX_POLLWAKE_NESTS, to* avoid stack blasting.** When CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC is enabled, make sure lockdep can handle* this special case of epoll.*/
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC
static inline void ep_wake_up_nested(wait_queue_head_t *wqueue,unsigned long events, int subclass)
{unsigned long flags;spin_lock_irqsave_nested(&wqueue->lock, flags, subclass);wake_up_locked_poll(wqueue, events);spin_unlock_irqrestore(&wqueue->lock, flags);
}
#else
static inline void ep_wake_up_nested(wait_queue_head_t *wqueue,unsigned long events, int subclass)
{wake_up_poll(wqueue, events);
}
#endifstatic int ep_poll_wakeup_proc(void *priv, void *cookie, int call_nests)
{ep_wake_up_nested((wait_queue_head_t *) cookie, POLLIN,1 + call_nests);return 0;
}/** Perform a safe wake up of the poll wait list. The problem is that* with the new callback'd wake up system, it is possible that the* poll callback is reentered from inside the call to wake_up() done* on the poll wait queue head. The rule is that we cannot reenter the* wake up code from the same task more than EP_MAX_NESTS times,* and we cannot reenter the same wait queue head at all. This will* enable to have a hierarchy of epoll file descriptor of no more than* EP_MAX_NESTS deep.*/
static void ep_poll_safewake(wait_queue_head_t *wq)
{int this_cpu = get_cpu();ep_call_nested(&poll_safewake_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS,ep_poll_wakeup_proc, NULL, wq, (void *) (long) this_cpu);put_cpu();
}static void ep_remove_wait_queue(struct eppoll_entry *pwq)
{wait_queue_head_t *whead;rcu_read_lock();/* If it is cleared by POLLFREE, it should be rcu-safe */whead = rcu_dereference(pwq->whead);if (whead)remove_wait_queue(whead, &pwq->wait);rcu_read_unlock();
}/** This function unregisters poll callbacks from the associated file* descriptor. Must be called with "mtx" held (or "epmutex" if called from* ep_free).*/
static void ep_unregister_pollwait(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epitem *epi)
{struct list_head *lsthead = &epi->pwqlist;struct eppoll_entry *pwq;while (!list_empty(lsthead)) {pwq = list_first_entry(lsthead, struct eppoll_entry, llink);list_del(&pwq->llink);ep_remove_wait_queue(pwq);kmem_cache_free(pwq_cache, pwq);}
}/* call only when ep->mtx is held */
static inline struct wakeup_source *ep_wakeup_source(struct epitem *epi)
{return rcu_dereference_check(epi->ws, lockdep_is_held(&epi->ep->mtx));
}/* call only when ep->mtx is held */
static inline void ep_pm_stay_awake(struct epitem *epi)
{struct wakeup_source *ws = ep_wakeup_source(epi);if (ws)__pm_stay_awake(ws);
}static inline bool ep_has_wakeup_source(struct epitem *epi)
{return rcu_access_pointer(epi->ws) ? true : false;
}/* call when ep->mtx cannot be held (ep_poll_callback) */
static inline void ep_pm_stay_awake_rcu(struct epitem *epi)
{struct wakeup_source *ws;rcu_read_lock();ws = rcu_dereference(epi->ws);if (ws)__pm_stay_awake(ws);rcu_read_unlock();
}/*** ep_scan_ready_list - Scans the ready list in a way that makes possible for* the scan code, to call f_op->poll(). Also allows for* O(NumReady) performance.** @ep: Pointer to the epoll private data structure.* @sproc: Pointer to the scan callback.* @priv: Private opaque data passed to the @sproc callback.* @depth: The current depth of recursive f_op->poll calls.** Returns: The same integer error code returned by the @sproc callback.*/
static int ep_scan_ready_list(struct eventpoll *ep,int (*sproc)(struct eventpoll *,struct list_head *, void *),void *priv,int depth)
{int error, pwake = 0;unsigned long flags;struct epitem *epi, *nepi;LIST_HEAD(txlist);/** We need to lock this because we could be hit by* eventpoll_release_file() and epoll_ctl().*/mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, depth);/** Steal the ready list, and re-init the original one to the* empty list. Also, set ep->ovflist to NULL so that events* happening while looping w/out locks, are not lost. We cannot* have the poll callback to queue directly on ep->rdllist,* because we want the "sproc" callback to be able to do it* in a lockless way.*/spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);list_splice_init(&ep->rdllist, &txlist);ep->ovflist = NULL;spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);/** Now call the callback function.*/error = (*sproc)(ep, &txlist, priv);spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);/** During the time we spent inside the "sproc" callback, some* other events might have been queued by the poll callback.* We re-insert them inside the main ready-list here.*/for (nepi = ep->ovflist; (epi = nepi) != NULL;nepi = epi->next, epi->next = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR) {/** We need to check if the item is already in the list.* During the "sproc" callback execution time, items are* queued into ->ovflist but the "txlist" might already* contain them, and the list_splice() below takes care of them.*/if (!ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) {list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);}}/** We need to set back ep->ovflist to EP_UNACTIVE_PTR, so that after* releasing the lock, events will be queued in the normal way inside* ep->rdllist.*/ep->ovflist = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;/** Quickly re-inject items left on "txlist".*/list_splice(&txlist, &ep->rdllist);__pm_relax(ep->ws);if (!list_empty(&ep->rdllist)) {/** Wake up (if active) both the eventpoll wait list and* the ->poll() wait list (delayed after we release the lock).*/if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))pwake++;}spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);/* We have to call this outside the lock */if (pwake)ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);return error;
}/** Removes a "struct epitem" from the eventpoll RB tree and deallocates* all the associated resources. Must be called with "mtx" held.*/
static int ep_remove(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epitem *epi)
{unsigned long flags;struct file *file = epi->ffd.file;/** Removes poll wait queue hooks. We _have_ to do this without holding* the "ep->lock" otherwise a deadlock might occur. This because of the* sequence of the lock acquisition. Here we do "ep->lock" then the wait* queue head lock when unregistering the wait queue. The wakeup callback* will run by holding the wait queue head lock and will call our callback* that will try to get "ep->lock".*/ep_unregister_pollwait(ep, epi);/* Remove the current item from the list of epoll hooks */spin_lock(&file->f_lock);if (ep_is_linked(&epi->fllink))list_del_init(&epi->fllink);spin_unlock(&file->f_lock);rb_erase(&epi->rbn, &ep->rbr);spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);if (ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink))list_del_init(&epi->rdllink);spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);wakeup_source_unregister(ep_wakeup_source(epi));/* At this point it is safe to free the eventpoll item */kmem_cache_free(epi_cache, epi);atomic_long_dec(&ep->user->epoll_watches);return 0;
}static void ep_free(struct eventpoll *ep)
{struct rb_node *rbp;struct epitem *epi;/* We need to release all tasks waiting for these file */if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);/** We need to lock this because we could be hit by* eventpoll_release_file() while we're freeing the "struct eventpoll".* We do not need to hold "ep->mtx" here because the epoll file* is on the way to be removed and no one has references to it* anymore. The only hit might come from eventpoll_release_file() but* holding "epmutex" is sufficient here.*/mutex_lock(&epmutex);/** Walks through the whole tree by unregistering poll callbacks.*/for (rbp = rb_first(&ep->rbr); rbp; rbp = rb_next(rbp)) {epi = rb_entry(rbp, struct epitem, rbn);ep_unregister_pollwait(ep, epi);}/** Walks through the whole tree by freeing each "struct epitem". At this* point we are sure no poll callbacks will be lingering around, and also by* holding "epmutex" we can be sure that no file cleanup code will hit* us during this operation. So we can avoid the lock on "ep->lock".* We do not need to lock ep->mtx, either, we only do it to prevent* a lockdep warning.*/mutex_lock(&ep->mtx);while ((rbp = rb_first(&ep->rbr)) != NULL) {epi = rb_entry(rbp, struct epitem, rbn);ep_remove(ep, epi);}mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);mutex_unlock(&epmutex);mutex_destroy(&ep->mtx);free_uid(ep->user);wakeup_source_unregister(ep->ws);kfree(ep);
}static int ep_eventpoll_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{struct eventpoll *ep = file->private_data;if (ep)ep_free(ep);return 0;
}static inline unsigned int ep_item_poll(struct epitem *epi, poll_table *pt)
{pt->_key = epi->event.events;return epi->ffd.file->f_op->poll(epi->ffd.file, pt) & epi->event.events;
}static int ep_read_events_proc(struct eventpoll *ep, struct list_head *head,void *priv)
{struct epitem *epi, *tmp;poll_table pt;init_poll_funcptr(&pt, NULL);list_for_each_entry_safe(epi, tmp, head, rdllink) {if (ep_item_poll(epi, &pt))return POLLIN | POLLRDNORM;else {/** Item has been dropped into the ready list by the poll* callback, but it's not actually ready, as far as* caller requested events goes. We can remove it here.*/__pm_relax(ep_wakeup_source(epi));list_del_init(&epi->rdllink);}}return 0;
}static int ep_poll_readyevents_proc(void *priv, void *cookie, int call_nests)
{return ep_scan_ready_list(priv, ep_read_events_proc, NULL, call_nests + 1);
}static unsigned int ep_eventpoll_poll(struct file *file, poll_table *wait)
{int pollflags;struct eventpoll *ep = file->private_data;/* Insert inside our poll wait queue */poll_wait(file, &ep->poll_wait, wait);/** Proceed to find out if wanted events are really available inside* the ready list. This need to be done under ep_call_nested()* supervision, since the call to f_op->poll() done on listed files* could re-enter here.*/pollflags = ep_call_nested(&poll_readywalk_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS,ep_poll_readyevents_proc, ep, ep, current);return pollflags != -1 ? pollflags : 0;
}#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
static int ep_show_fdinfo(struct seq_file *m, struct file *f)
{struct eventpoll *ep = f->private_data;struct rb_node *rbp;int ret = 0;mutex_lock(&ep->mtx);for (rbp = rb_first(&ep->rbr); rbp; rbp = rb_next(rbp)) {struct epitem *epi = rb_entry(rbp, struct epitem, rbn);ret = seq_printf(m, "tfd: %8d events: %8x data: %16llx\n",epi->ffd.fd, epi->event.events,(long long)epi->event.data);if (ret)break;}mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);return ret;
}
#endif/* File callbacks that implement the eventpoll file behaviour */
static const struct file_operations eventpoll_fops = {
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS.show_fdinfo = ep_show_fdinfo,
#endif.release = ep_eventpoll_release,.poll = ep_eventpoll_poll,.llseek = noop_llseek,
};/** This is called from eventpoll_release() to unlink files from the eventpoll* interface. We need to have this facility to cleanup correctly files that are* closed without being removed from the eventpoll interface.*/
void eventpoll_release_file(struct file *file)
{struct list_head *lsthead = &file->f_ep_links;struct eventpoll *ep;struct epitem *epi;/** We don't want to get "file->f_lock" because it is not* necessary. It is not necessary because we're in the "struct file"* cleanup path, and this means that no one is using this file anymore.* So, for example, epoll_ctl() cannot hit here since if we reach this* point, the file counter already went to zero and fget() would fail.* The only hit might come from ep_free() but by holding the mutex* will correctly serialize the operation. We do need to acquire* "ep->mtx" after "epmutex" because ep_remove() requires it when called* from anywhere but ep_free().** Besides, ep_remove() acquires the lock, so we can't hold it here.*/mutex_lock(&epmutex);while (!list_empty(lsthead)) {epi = list_first_entry(lsthead, struct epitem, fllink);ep = epi->ep;list_del_init(&epi->fllink);mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, 0);ep_remove(ep, epi);mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);}mutex_unlock(&epmutex);
}static int ep_alloc(struct eventpoll **pep)
{int error;struct user_struct *user;struct eventpoll *ep;user = get_current_user();error = -ENOMEM;ep = kzalloc(sizeof(*ep), GFP_KERNEL);if (unlikely(!ep))goto free_uid;spin_lock_init(&ep->lock);mutex_init(&ep->mtx);init_waitqueue_head(&ep->wq);init_waitqueue_head(&ep->poll_wait);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&ep->rdllist);ep->rbr = RB_ROOT;ep->ovflist = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;ep->user = user;*pep = ep;return 0;free_uid:free_uid(user);return error;
}/** Search the file inside the eventpoll tree. The RB tree operations* are protected by the "mtx" mutex, and ep_find() must be called with* "mtx" held.*/
static struct epitem *ep_find(struct eventpoll *ep, struct file *file, int fd)
{int kcmp;struct rb_node *rbp;struct epitem *epi, *epir = NULL;struct epoll_filefd ffd;ep_set_ffd(&ffd, file, fd);for (rbp = ep->rbr.rb_node; rbp; ) {epi = rb_entry(rbp, struct epitem, rbn);kcmp = ep_cmp_ffd(&ffd, &epi->ffd);if (kcmp > 0)rbp = rbp->rb_right;else if (kcmp < 0)rbp = rbp->rb_left;else {epir = epi;break;}}return epir;
}/** This is the callback that is passed to the wait queue wakeup* mechanism. It is called by the stored file descriptors when they* have events to report.*/
static int ep_poll_callback(wait_queue_t *wait, unsigned mode, int sync, void *key)
{int pwake = 0;unsigned long flags;struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_wait(wait);struct eventpoll *ep = epi->ep;if ((unsigned long)key & POLLFREE) {ep_pwq_from_wait(wait)->whead = NULL;/** whead = NULL above can race with ep_remove_wait_queue()* which can do another remove_wait_queue() after us, so we* can't use __remove_wait_queue(). whead->lock is held by* the caller.*/list_del_init(&wait->task_list);}spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);/** If the event mask does not contain any poll(2) event, we consider the* descriptor to be disabled. This condition is likely the effect of the* EPOLLONESHOT bit that disables the descriptor when an event is received,* until the next EPOLL_CTL_MOD will be issued.*/if (!(epi->event.events & ~EP_PRIVATE_BITS))goto out_unlock;/** Check the events coming with the callback. At this stage, not* every device reports the events in the "key" parameter of the* callback. We need to be able to handle both cases here, hence the* test for "key" != NULL before the event match test.*/if (key && !((unsigned long) key & epi->event.events))goto out_unlock;/** If we are transferring events to userspace, we can hold no locks* (because we're accessing user memory, and because of linux f_op->poll()* semantics). All the events that happen during that period of time are* chained in ep->ovflist and requeued later on.*/if (unlikely(ep->ovflist != EP_UNACTIVE_PTR)) {if (epi->next == EP_UNACTIVE_PTR) {epi->next = ep->ovflist;ep->ovflist = epi;if (epi->ws) {/** Activate ep->ws since epi->ws may get* deactivated at any time.*/__pm_stay_awake(ep->ws);}}goto out_unlock;}/* If this file is already in the ready list we exit soon */if (!ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) {list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);ep_pm_stay_awake_rcu(epi);}/** Wake up ( if active ) both the eventpoll wait list and the ->poll()* wait list.*/if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))pwake++;out_unlock:spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);/* We have to call this outside the lock */if (pwake)ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);return 1;
}/** This is the callback that is used to add our wait queue to the* target file wakeup lists.*/
static void ep_ptable_queue_proc(struct file *file, wait_queue_head_t *whead,poll_table *pt)
{struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_epqueue(pt);struct eppoll_entry *pwq;if (epi->nwait >= 0 && (pwq = kmem_cache_alloc(pwq_cache, GFP_KERNEL))) {init_waitqueue_func_entry(&pwq->wait, ep_poll_callback);pwq->whead = whead;pwq->base = epi;add_wait_queue(whead, &pwq->wait);list_add_tail(&pwq->llink, &epi->pwqlist);epi->nwait++;} else {/* We have to signal that an error occurred */epi->nwait = -1;}
}static void ep_rbtree_insert(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epitem *epi)
{int kcmp;struct rb_node **p = &ep->rbr.rb_node, *parent = NULL;struct epitem *epic;while (*p) {parent = *p;epic = rb_entry(parent, struct epitem, rbn);kcmp = ep_cmp_ffd(&epi->ffd, &epic->ffd);if (kcmp > 0)p = &parent->rb_right;elsep = &parent->rb_left;}rb_link_node(&epi->rbn, parent, p);rb_insert_color(&epi->rbn, &ep->rbr);
}#define PATH_ARR_SIZE 5
/** These are the number paths of length 1 to 5, that we are allowing to emanate* from a single file of interest. For example, we allow 1000 paths of length* 1, to emanate from each file of interest. This essentially represents the* potential wakeup paths, which need to be limited in order to avoid massive* uncontrolled wakeup storms. The common use case should be a single ep which* is connected to n file sources. In this case each file source has 1 path* of length 1. Thus, the numbers below should be more than sufficient. These* path limits are enforced during an EPOLL_CTL_ADD operation, since a modify* and delete can't add additional paths. Protected by the epmutex.*/
static const int path_limits[PATH_ARR_SIZE] = { 1000, 500, 100, 50, 10 };
static int path_count[PATH_ARR_SIZE];static int path_count_inc(int nests)
{/* Allow an arbitrary number of depth 1 paths */if (nests == 0)return 0;if (++path_count[nests] > path_limits[nests])return -1;return 0;
}static void path_count_init(void)
{int i;for (i = 0; i < PATH_ARR_SIZE; i++)path_count[i] = 0;
}static int reverse_path_check_proc(void *priv, void *cookie, int call_nests)
{int error = 0;struct file *file = priv;struct file *child_file;struct epitem *epi;list_for_each_entry(epi, &file->f_ep_links, fllink) {child_file = epi->ep->file;if (is_file_epoll(child_file)) {if (list_empty(&child_file->f_ep_links)) {if (path_count_inc(call_nests)) {error = -1;break;}} else {error = ep_call_nested(&poll_loop_ncalls,EP_MAX_NESTS,reverse_path_check_proc,child_file, child_file,current);}if (error != 0)break;} else {printk(KERN_ERR "reverse_path_check_proc: ""file is not an ep!\n");}}return error;
}/*** reverse_path_check - The tfile_check_list is list of file *, which have* links that are proposed to be newly added. We need to* make sure that those added links don't add too many* paths such that we will spend all our time waking up* eventpoll objects.** Returns: Returns zero if the proposed links don't create too many paths,* -1 otherwise.*/
static int reverse_path_check(void)
{int error = 0;struct file *current_file;/* let's call this for all tfiles */list_for_each_entry(current_file, &tfile_check_list, f_tfile_llink) {path_count_init();error = ep_call_nested(&poll_loop_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS,reverse_path_check_proc, current_file,current_file, current);if (error)break;}return error;
}static int ep_create_wakeup_source(struct epitem *epi)
{const char *name;struct wakeup_source *ws;if (!epi->ep->ws) {epi->ep->ws = wakeup_source_register("eventpoll");if (!epi->ep->ws)return -ENOMEM;}name = epi->ffd.file->f_path.dentry->d_name.name;ws = wakeup_source_register(name);if (!ws)return -ENOMEM;rcu_assign_pointer(epi->ws, ws);return 0;
}/* rare code path, only used when EPOLL_CTL_MOD removes a wakeup source */
static noinline void ep_destroy_wakeup_source(struct epitem *epi)
{struct wakeup_source *ws = ep_wakeup_source(epi);RCU_INIT_POINTER(epi->ws, NULL);/** wait for ep_pm_stay_awake_rcu to finish, synchronize_rcu is* used internally by wakeup_source_remove, too (called by* wakeup_source_unregister), so we cannot use call_rcu*/synchronize_rcu();wakeup_source_unregister(ws);
}/** Must be called with "mtx" held.*/
static int ep_insert(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event *event,struct file *tfile, int fd)
{int error, revents, pwake = 0;unsigned long flags;long user_watches;struct epitem *epi;struct ep_pqueue epq;user_watches = atomic_long_read(&ep->user->epoll_watches);if (unlikely(user_watches >= max_user_watches))return -ENOSPC;if (!(epi = kmem_cache_alloc(epi_cache, GFP_KERNEL)))return -ENOMEM;/* Item initialization follow here ... */INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->rdllink);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->fllink);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->pwqlist);epi->ep = ep;ep_set_ffd(&epi->ffd, tfile, fd);epi->event = *event;epi->nwait = 0;epi->next = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;if (epi->event.events & EPOLLWAKEUP) {error = ep_create_wakeup_source(epi);if (error)goto error_create_wakeup_source;} else {RCU_INIT_POINTER(epi->ws, NULL);}/* Initialize the poll table using the queue callback */epq.epi = epi;init_poll_funcptr(&epq.pt, ep_ptable_queue_proc);/** Attach the item to the poll hooks and get current event bits.* We can safely use the file* here because its usage count has* been increased by the caller of this function. Note that after* this operation completes, the poll callback can start hitting* the new item.*/revents = ep_item_poll(epi, &epq.pt);/** We have to check if something went wrong during the poll wait queue* install process. Namely an allocation for a wait queue failed due* high memory pressure.*/error = -ENOMEM;if (epi->nwait < 0)goto error_unregister;/* Add the current item to the list of active epoll hook for this file */spin_lock(&tfile->f_lock);list_add_tail(&epi->fllink, &tfile->f_ep_links);spin_unlock(&tfile->f_lock);/** Add the current item to the RB tree. All RB tree operations are* protected by "mtx", and ep_insert() is called with "mtx" held.*/ep_rbtree_insert(ep, epi);/* now check if we've created too many backpaths */error = -EINVAL;if (reverse_path_check())goto error_remove_epi;/* We have to drop the new item inside our item list to keep track of it */spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);/* If the file is already "ready" we drop it inside the ready list */if ((revents & event->events) && !ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) {list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);/* Notify waiting tasks that events are available */if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))pwake++;}spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);atomic_long_inc(&ep->user->epoll_watches);/* We have to call this outside the lock */if (pwake)ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);return 0;error_remove_epi:spin_lock(&tfile->f_lock);if (ep_is_linked(&epi->fllink))list_del_init(&epi->fllink);spin_unlock(&tfile->f_lock);rb_erase(&epi->rbn, &ep->rbr);error_unregister:ep_unregister_pollwait(ep, epi);/** We need to do this because an event could have been arrived on some* allocated wait queue. Note that we don't care about the ep->ovflist* list, since that is used/cleaned only inside a section bound by "mtx".* And ep_insert() is called with "mtx" held.*/spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);if (ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink))list_del_init(&epi->rdllink);spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);wakeup_source_unregister(ep_wakeup_source(epi));error_create_wakeup_source:kmem_cache_free(epi_cache, epi);return error;
}/** Modify the interest event mask by dropping an event if the new mask* has a match in the current file status. Must be called with "mtx" held.*/
static int ep_modify(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epitem *epi, struct epoll_event *event)
{int pwake = 0;unsigned int revents;poll_table pt;init_poll_funcptr(&pt, NULL);/** Set the new event interest mask before calling f_op->poll();* otherwise we might miss an event that happens between the* f_op->poll() call and the new event set registering.*/epi->event.events = event->events; /* need barrier below */epi->event.data = event->data; /* protected by mtx */if (epi->event.events & EPOLLWAKEUP) {if (!ep_has_wakeup_source(epi))ep_create_wakeup_source(epi);} else if (ep_has_wakeup_source(epi)) {ep_destroy_wakeup_source(epi);}/** The following barrier has two effects:** 1) Flush epi changes above to other CPUs. This ensures* we do not miss events from ep_poll_callback if an* event occurs immediately after we call f_op->poll().* We need this because we did not take ep->lock while* changing epi above (but ep_poll_callback does take* ep->lock).** 2) We also need to ensure we do not miss _past_ events* when calling f_op->poll(). This barrier also* pairs with the barrier in wq_has_sleeper (see* comments for wq_has_sleeper).** This barrier will now guarantee ep_poll_callback or f_op->poll* (or both) will notice the readiness of an item.*/smp_mb();/** Get current event bits. We can safely use the file* here because* its usage count has been increased by the caller of this function.*/revents = ep_item_poll(epi, &pt);/** If the item is "hot" and it is not registered inside the ready* list, push it inside.*/if (revents & event->events) {spin_lock_irq(&ep->lock);if (!ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) {list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);/* Notify waiting tasks that events are available */if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))pwake++;}spin_unlock_irq(&ep->lock);}/* We have to call this outside the lock */if (pwake)ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);return 0;
}static int ep_send_events_proc(struct eventpoll *ep, struct list_head *head,void *priv)
{struct ep_send_events_data *esed = priv;int eventcnt;unsigned int revents;struct epitem *epi;struct epoll_event __user *uevent;struct wakeup_source *ws;poll_table pt;init_poll_funcptr(&pt, NULL);/** We can loop without lock because we are passed a task private list.* Items cannot vanish during the loop because ep_scan_ready_list() is* holding "mtx" during this call.*/for (eventcnt = 0, uevent = esed->events;!list_empty(head) && eventcnt < esed->maxevents;) {epi = list_first_entry(head, struct epitem, rdllink);/** Activate ep->ws before deactivating epi->ws to prevent* triggering auto-suspend here (in case we reactive epi->ws* below).** This could be rearranged to delay the deactivation of epi->ws* instead, but then epi->ws would temporarily be out of sync* with ep_is_linked().*/ws = ep_wakeup_source(epi);if (ws) {if (ws->active)__pm_stay_awake(ep->ws);__pm_relax(ws);}list_del_init(&epi->rdllink);revents = ep_item_poll(epi, &pt);/** If the event mask intersect the caller-requested one,* deliver the event to userspace. Again, ep_scan_ready_list()* is holding "mtx", so no operations coming from userspace* can change the item.*/if (revents) {if (__put_user(revents, &uevent->events) ||__put_user(epi->event.data, &uevent->data)) {list_add(&epi->rdllink, head);ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);return eventcnt ? eventcnt : -EFAULT;}eventcnt++;uevent++;if (epi->event.events & EPOLLONESHOT)epi->event.events &= EP_PRIVATE_BITS;else if (!(epi->event.events & EPOLLET)) {/** If this file has been added with Level* Trigger mode, we need to insert back inside* the ready list, so that the next call to* epoll_wait() will check again the events* availability. At this point, no one can insert* into ep->rdllist besides us. The epoll_ctl()* callers are locked out by* ep_scan_ready_list() holding "mtx" and the* poll callback will queue them in ep->ovflist.*/list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);}}}return eventcnt;
}static int ep_send_events(struct eventpoll *ep,struct epoll_event __user *events, int maxevents)
{struct ep_send_events_data esed;esed.maxevents = maxevents;esed.events = events;return ep_scan_ready_list(ep, ep_send_events_proc, &esed, 0);
}static inline struct timespec ep_set_mstimeout(long ms)
{struct timespec now, ts = {.tv_sec = ms / MSEC_PER_SEC,.tv_nsec = NSEC_PER_MSEC * (ms % MSEC_PER_SEC),};ktime_get_ts(&now);return timespec_add_safe(now, ts);
}/*** ep_poll - Retrieves ready events, and delivers them to the caller supplied* event buffer.** @ep: Pointer to the eventpoll context.* @events: Pointer to the userspace buffer where the ready events should be* stored.* @maxevents: Size (in terms of number of events) of the caller event buffer.* @timeout: Maximum timeout for the ready events fetch operation, in* milliseconds. If the @timeout is zero, the function will not block,* while if the @timeout is less than zero, the function will block* until at least one event has been retrieved (or an error* occurred).** Returns: Returns the number of ready events which have been fetched, or an* error code, in case of error.*/
static int ep_poll(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event __user *events,int maxevents, long timeout)
{int res = 0, eavail, timed_out = 0;unsigned long flags;long slack = 0;wait_queue_t wait;ktime_t expires, *to = NULL;if (timeout > 0) {struct timespec end_time = ep_set_mstimeout(timeout);slack = select_estimate_accuracy(&end_time);to = &expires;*to = timespec_to_ktime(end_time);} else if (timeout == 0) {/** Avoid the unnecessary trip to the wait queue loop, if the* caller specified a non blocking operation.*/timed_out = 1;spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);goto check_events;}fetch_events:spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);if (!ep_events_available(ep)) {/** We don't have any available event to return to the caller.* We need to sleep here, and we will be wake up by* ep_poll_callback() when events will become available.*/init_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current);__add_wait_queue_exclusive(&ep->wq, &wait);for (;;) {/** We don't want to sleep if the ep_poll_callback() sends us* a wakeup in between. That's why we set the task state* to TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE before doing the checks.*/set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);if (ep_events_available(ep) || timed_out)break;if (signal_pending(current)) {res = -EINTR;break;}spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);if (!schedule_hrtimeout_range(to, slack, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS))timed_out = 1;spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);}__remove_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);}
check_events:/* Is it worth to try to dig for events ? */eavail = ep_events_available(ep);spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);/** Try to transfer events to user space. In case we get 0 events and* there's still timeout left over, we go trying again in search of* more luck.*/if (!res && eavail &&!(res = ep_send_events(ep, events, maxevents)) && !timed_out)goto fetch_events;return res;
}/*** ep_loop_check_proc - Callback function to be passed to the @ep_call_nested()* API, to verify that adding an epoll file inside another* epoll structure, does not violate the constraints, in* terms of closed loops, or too deep chains (which can* result in excessive stack usage).** @priv: Pointer to the epoll file to be currently checked.* @cookie: Original cookie for this call. This is the top-of-the-chain epoll* data structure pointer.* @call_nests: Current dept of the @ep_call_nested() call stack.** Returns: Returns zero if adding the epoll @file inside current epoll* structure @ep does not violate the constraints, or -1 otherwise.*/
static int ep_loop_check_proc(void *priv, void *cookie, int call_nests)
{int error = 0;struct file *file = priv;struct eventpoll *ep = file->private_data;struct eventpoll *ep_tovisit;struct rb_node *rbp;struct epitem *epi;mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, call_nests + 1);ep->visited = 1;list_add(&ep->visited_list_link, &visited_list);for (rbp = rb_first(&ep->rbr); rbp; rbp = rb_next(rbp)) {epi = rb_entry(rbp, struct epitem, rbn);if (unlikely(is_file_epoll(epi->ffd.file))) {ep_tovisit = epi->ffd.file->private_data;if (ep_tovisit->visited)continue;error = ep_call_nested(&poll_loop_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS,ep_loop_check_proc, epi->ffd.file,ep_tovisit, current);if (error != 0)break;} else {/** If we've reached a file that is not associated with* an ep, then we need to check if the newly added* links are going to add too many wakeup paths. We do* this by adding it to the tfile_check_list, if it's* not already there, and calling reverse_path_check()* during ep_insert().*/if (list_empty(&epi->ffd.file->f_tfile_llink))list_add(&epi->ffd.file->f_tfile_llink,&tfile_check_list);}}mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);return error;
}/*** ep_loop_check - Performs a check to verify that adding an epoll file (@file)* another epoll file (represented by @ep) does not create* closed loops or too deep chains.** @ep: Pointer to the epoll private data structure.* @file: Pointer to the epoll file to be checked.** Returns: Returns zero if adding the epoll @file inside current epoll* structure @ep does not violate the constraints, or -1 otherwise.*/
static int ep_loop_check(struct eventpoll *ep, struct file *file)
{int ret;struct eventpoll *ep_cur, *ep_next;ret = ep_call_nested(&poll_loop_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS,ep_loop_check_proc, file, ep, current);/* clear visited list */list_for_each_entry_safe(ep_cur, ep_next, &visited_list,visited_list_link) {ep_cur->visited = 0;list_del(&ep_cur->visited_list_link);}return ret;
}static void clear_tfile_check_list(void)
{struct file *file;/* first clear the tfile_check_list */while (!list_empty(&tfile_check_list)) {file = list_first_entry(&tfile_check_list, struct file,f_tfile_llink);list_del_init(&file->f_tfile_llink);}INIT_LIST_HEAD(&tfile_check_list);
}/** Open an eventpoll file descriptor.*/
SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create1, int, flags)
{int error, fd;struct eventpoll *ep = NULL;struct file *file;/* Check the EPOLL_* constant for consistency. */BUILD_BUG_ON(EPOLL_CLOEXEC != O_CLOEXEC);if (flags & ~EPOLL_CLOEXEC)return -EINVAL;/** Create the internal data structure ("struct eventpoll").*/error = ep_alloc(&ep);if (error < 0)return error;/** Creates all the items needed to setup an eventpoll file. That is,* a file structure and a free file descriptor.*/fd = get_unused_fd_flags(O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC));if (fd < 0) {error = fd;goto out_free_ep;}file = anon_inode_getfile("[eventpoll]", &eventpoll_fops, ep,O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC));if (IS_ERR(file)) {error = PTR_ERR(file);goto out_free_fd;}ep->file = file;fd_install(fd, file);return fd;out_free_fd:put_unused_fd(fd);
out_free_ep:ep_free(ep);return error;
}SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create, int, size)
{if (size <= 0)return -EINVAL;return sys_epoll_create1(0);
}/** The following function implements the controller interface for* the eventpoll file that enables the insertion/removal/change of* file descriptors inside the interest set.*/
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_ctl, int, epfd, int, op, int, fd,struct epoll_event __user *, event)
{int error;int did_lock_epmutex = 0;struct file *file, *tfile;struct eventpoll *ep;struct epitem *epi;struct epoll_event epds;error = -EFAULT;if (ep_op_has_event(op) &©_from_user(&epds, event, sizeof(struct epoll_event)))goto error_return;/* Get the "struct file *" for the eventpoll file */error = -EBADF;file = fget(epfd);if (!file)goto error_return;/* Get the "struct file *" for the target file */tfile = fget(fd);if (!tfile)goto error_fput;/* The target file descriptor must support poll */error = -EPERM;if (!tfile->f_op || !tfile->f_op->poll)goto error_tgt_fput;/* Check if EPOLLWAKEUP is allowed */if ((epds.events & EPOLLWAKEUP) && !capable(CAP_BLOCK_SUSPEND))epds.events &= ~EPOLLWAKEUP;/** We have to check that the file structure underneath the file descriptor* the user passed to us _is_ an eventpoll file. And also we do not permit* adding an epoll file descriptor inside itself.*/error = -EINVAL;if (file == tfile || !is_file_epoll(file))goto error_tgt_fput;/** At this point it is safe to assume that the "private_data" contains* our own data structure.*/ep = file->private_data;/** When we insert an epoll file descriptor, inside another epoll file* descriptor, there is the change of creating closed loops, which are* better be handled here, than in more critical paths. While we are* checking for loops we also determine the list of files reachable* and hang them on the tfile_check_list, so we can check that we* haven't created too many possible wakeup paths.** We need to hold the epmutex across both ep_insert and ep_remove* b/c we want to make sure we are looking at a coherent view of* epoll network.*/if (op == EPOLL_CTL_ADD || op == EPOLL_CTL_DEL) {mutex_lock(&epmutex);did_lock_epmutex = 1;}if (op == EPOLL_CTL_ADD) {if (is_file_epoll(tfile)) {error = -ELOOP;if (ep_loop_check(ep, tfile) != 0) {clear_tfile_check_list();goto error_tgt_fput;}} elselist_add(&tfile->f_tfile_llink, &tfile_check_list);}mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, 0);/** Try to lookup the file inside our RB tree, Since we grabbed "mtx"* above, we can be sure to be able to use the item looked up by* ep_find() till we release the mutex.*/epi = ep_find(ep, tfile, fd);error = -EINVAL;switch (op) {case EPOLL_CTL_ADD:if (!epi) {epds.events |= POLLERR | POLLHUP;error = ep_insert(ep, &epds, tfile, fd);} elseerror = -EEXIST;clear_tfile_check_list();break;case EPOLL_CTL_DEL:if (epi)error = ep_remove(ep, epi);elseerror = -ENOENT;break;case EPOLL_CTL_MOD:if (epi) {epds.events |= POLLERR | POLLHUP;error = ep_modify(ep, epi, &epds);} elseerror = -ENOENT;break;}mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);error_tgt_fput:if (did_lock_epmutex)mutex_unlock(&epmutex);fput(tfile);
error_fput:fput(file);
error_return:return error;
}/** Implement the event wait interface for the eventpoll file. It is the kernel* part of the user space epoll_wait(2).*/
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_wait, int, epfd, struct epoll_event __user *, events,int, maxevents, int, timeout)
{int error;struct fd f;struct eventpoll *ep;/* The maximum number of event must be greater than zero */if (maxevents <= 0 || maxevents > EP_MAX_EVENTS)return -EINVAL;/* Verify that the area passed by the user is writeable */if (!access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE, events, maxevents * sizeof(struct epoll_event)))return -EFAULT;/* Get the "struct file *" for the eventpoll file */f = fdget(epfd);if (!f.file)return -EBADF;/** We have to check that the file structure underneath the fd* the user passed to us _is_ an eventpoll file.*/error = -EINVAL;if (!is_file_epoll(f.file))goto error_fput;/** At this point it is safe to assume that the "private_data" contains* our own data structure.*/ep = f.file->private_data;/* Time to fish for events ... */error = ep_poll(ep, events, maxevents, timeout);error_fput:fdput(f);return error;
}/** Implement the event wait interface for the eventpoll file. It is the kernel* part of the user space epoll_pwait(2).*/
SYSCALL_DEFINE6(epoll_pwait, int, epfd, struct epoll_event __user *, events,int, maxevents, int, timeout, const sigset_t __user *, sigmask,size_t, sigsetsize)
{int error;sigset_t ksigmask, sigsaved;/** If the caller wants a certain signal mask to be set during the wait,* we apply it here.*/if (sigmask) {if (sigsetsize != sizeof(sigset_t))return -EINVAL;if (copy_from_user(&ksigmask, sigmask, sizeof(ksigmask)))return -EFAULT;sigdelsetmask(&ksigmask, sigmask(SIGKILL) | sigmask(SIGSTOP));sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &ksigmask, &sigsaved);}error = sys_epoll_wait(epfd, events, maxevents, timeout);/** If we changed the signal mask, we need to restore the original one.* In case we've got a signal while waiting, we do not restore the* signal mask yet, and we allow do_signal() to deliver the signal on* the way back to userspace, before the signal mask is restored.*/if (sigmask) {if (error == -EINTR) {memcpy(¤t->saved_sigmask, &sigsaved,sizeof(sigsaved));set_restore_sigmask();} elsesigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &sigsaved, NULL);}return error;
}#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
COMPAT_SYSCALL_DEFINE6(epoll_pwait, int, epfd,struct epoll_event __user *, events,int, maxevents, int, timeout,const compat_sigset_t __user *, sigmask,compat_size_t, sigsetsize)
{long err;compat_sigset_t csigmask;sigset_t ksigmask, sigsaved;/** If the caller wants a certain signal mask to be set during the wait,* we apply it here.*/if (sigmask) {if (sigsetsize != sizeof(compat_sigset_t))return -EINVAL;if (copy_from_user(&csigmask, sigmask, sizeof(csigmask)))return -EFAULT;sigset_from_compat(&ksigmask, &csigmask);sigdelsetmask(&ksigmask, sigmask(SIGKILL) | sigmask(SIGSTOP));sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &ksigmask, &sigsaved);}err = sys_epoll_wait(epfd, events, maxevents, timeout);/** If we changed the signal mask, we need to restore the original one.* In case we've got a signal while waiting, we do not restore the* signal mask yet, and we allow do_signal() to deliver the signal on* the way back to userspace, before the signal mask is restored.*/if (sigmask) {if (err == -EINTR) {memcpy(¤t->saved_sigmask, &sigsaved,sizeof(sigsaved));set_restore_sigmask();} elsesigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &sigsaved, NULL);}return err;
}
#endifstatic int __init eventpoll_init(void)
{struct sysinfo si;si_meminfo(&si);/** Allows top 4% of lomem to be allocated for epoll watches (per user).*/max_user_watches = (((si.totalram - si.totalhigh) / 25) << PAGE_SHIFT) /EP_ITEM_COST;BUG_ON(max_user_watches < 0);/** Initialize the structure used to perform epoll file descriptor* inclusion loops checks.*/ep_nested_calls_init(&poll_loop_ncalls);/* Initialize the structure used to perform safe poll wait head wake ups */ep_nested_calls_init(&poll_safewake_ncalls);/* Initialize the structure used to perform file's f_op->poll() calls */ep_nested_calls_init(&poll_readywalk_ncalls);/** We can have many thousands of epitems, so prevent this from* using an extra cache line on 64-bit (and smaller) CPUs*/BUILD_BUG_ON(sizeof(void *) <= 8 && sizeof(struct epitem) > 128);/* Allocates slab cache used to allocate "struct epitem" items */epi_cache = kmem_cache_create("eventpoll_epi", sizeof(struct epitem),0, SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN | SLAB_PANIC, NULL);/* Allocates slab cache used to allocate "struct eppoll_entry" */pwq_cache = kmem_cache_create("eventpoll_pwq",sizeof(struct eppoll_entry), 0, SLAB_PANIC, NULL);return 0;
}
fs_initcall(eventpoll_init);
https://linux.die.net/man/2/epoll_wait
http://www.man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/epoll_wait.2.html
扩展阅读:NIO 源码分析(02-1) BIO 源码分析
NIO-EPollSelectorIpml源码分析
epoll源码实现分析[整理]
epoll内核源码详解+自己总结的流程 这个是比较完整的注释。
epoll内核源码分析
一文看懂DPDK
内核是导致瓶颈的原因所在,要解决问题需要绕过内核。所以主流解决方案都是旁路网卡IO,绕过内核直接在用户态收发包来解决内核的瓶颈。

图片引自Jingjing Wu的文档《Flow Bifurcation on Intel® Ethernet Controller X710/XL710》
左边是原来的方式数据从 网卡 -> 驱动 -> 协议栈 -> Socket接口 -> 业务
右边是DPDK的方式,基于UIO(Userspace I/O)旁路数据。数据从 网卡 -> DPDK轮询模式-> DPDK基础库 -> 业务
用户态的好处是易用开发和维护,灵活性好。并且Crash也不影响内核运行,鲁棒性强。
相关文章:
Linux进程ID号--Linux进程的管理与调度(三)
进程ID概述 进程ID类型 要想了解内核如何来组织和管理进程ID,先要知道进程ID的类型: 内核中进程ID的类型用pid_type来描述,它被定义在include/linux/pid.h中 enum pid_type {PIDTYPE_PID,PIDTYPE_PGID,PIDTYPE_SID,PIDTYPE_MAX };12345671234567PID 内核…

【MATLAB】矩阵运算之矩阵分解
矩阵分解:把一个矩阵分解成为矩阵连乘的形式。矩阵的分解函数cholCholesky分解cholinc稀疏矩阵的不完全Cholesky分解lu矩阵LU分解luinc稀疏矩阵的不完全LU分解qr正交三角分解svd奇异值分解gsvd一般奇异值分解schur舒尔分解 在MATLAB中线性方程组的求解主要基于四种基…
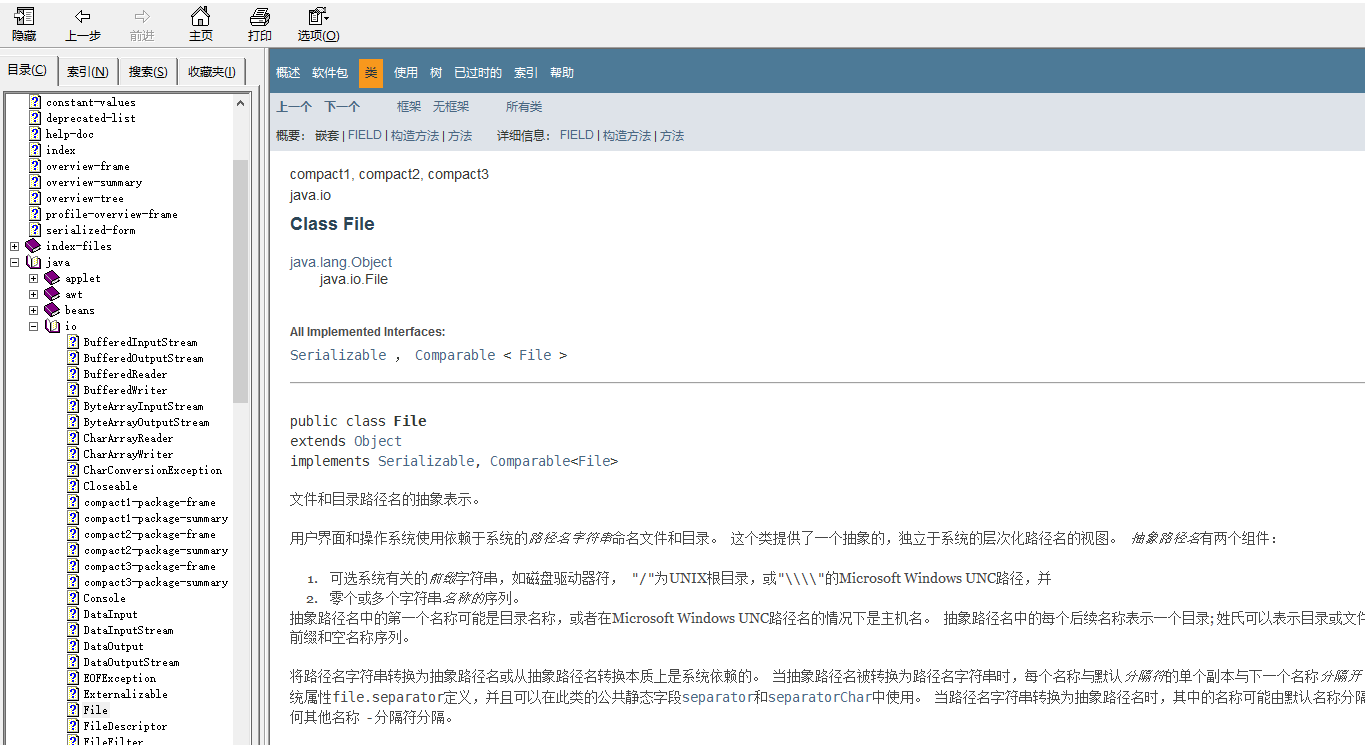
Java入门—输入输出流
File类的使用 文件是:文件可认为是相关记录或放在一起的数据的集合。 Java中,使用java.io.File类对文件进行操作 public class FileDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {String path "E:\\pdd";File f new File(path);//判断是文…
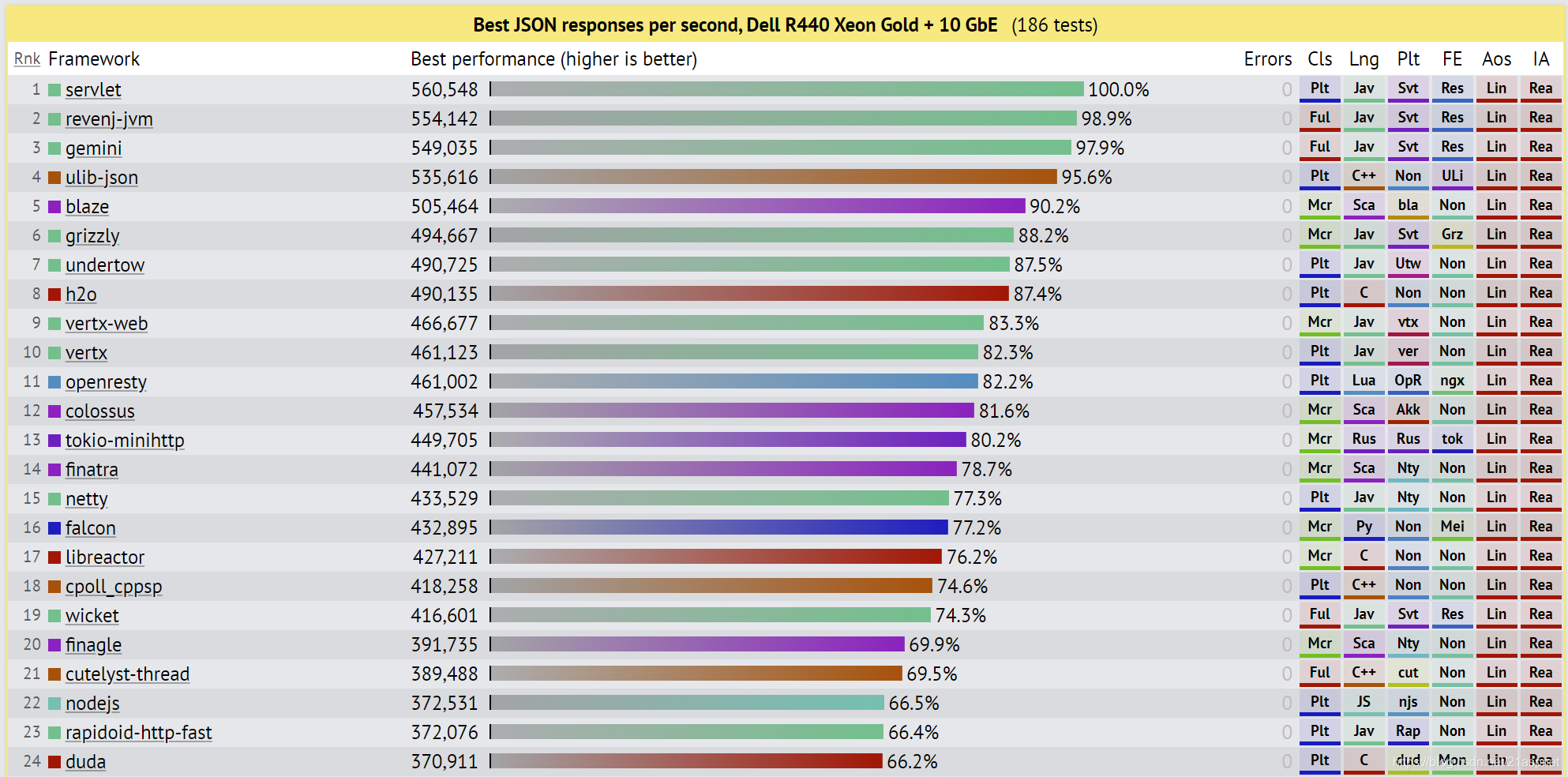
Web框架基准测试
Web Framework Benchmarks 这是许多执行基本任务(例如JSON序列化,数据库访问和服务器端模板组成)的Web应用程序框架的性能比较。每个框架都在实际的生产配置中运行。结果在云实例和物理硬件上捕获。测试实现主要是由社区贡献的,所…

vsftpd用户配置 No.2
在配置ftp虚拟用户的过程中,还有一种配置方式。yum -y install 安装vsftpdcp /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf.bak编辑vsftpd.conf开启下列选项:anonymous_enableNOlocal_enableYESwrite_enableYESlocal_umask022anon_mkdir_write_enab…

【MATLAB】稀疏矩阵(含有大量0元素的矩阵)
1、稀疏矩阵的储存方式 对于稀疏矩阵,MATLAB仅储存矩阵所有非零元素的值及其位置(行号和列号)。 2、稀疏矩阵的生成 1)利用sparse函数从满矩阵转换得到稀疏矩阵函数名称表示意义sparse(A)由非零元素和下标建立稀疏矩阵A。如果A已是…

httpTomcat
Tomcat是web应用服务器的一种 转载于:https://juejin.im/post/5beaf7e451882517165d91d1

memcached(二)事件模型源码分析
在memcachedd中,作者为了专注于缓存的设计,使用了libevent来开发事件模型。memcachedd的时间模型同nginx的类似,拥有一个主进行(master)以及多个工作者线程(woker)。 流程图 在memcached中&…

【MATLAB】MATLAB的控制流
1、if-else-end if expressioncommands1 elseif expression2commands2 ... else commandsn end 2、switch-case switch valuecase1 test1%如果value等于test1,执行command1,并结束此结构command1case2 test2command2...case3 testkcommandk otherw…

Linux查看本机端口
查看指定的端口 # lsof -i:port 查看所有端口 # netstat -aptn 安装telnet #yum install -y telnet.x86_64 #telnet ip 端口

Node.js安装
通过nvm安装 下载nvm并执行wget -qO- https://raw.github.com/creationix/nvm/v0.33.11/install.sh | sh将命令输出到终端命令中~/.bashrcexport NVM_DIR"$HOME/.nvm"更新文件source .bashrc通过nvm安装node.jsnvm install 10.13安装的版本是10.13的版本 通过命令查看…

mongodb常用语句以及SpringBoot中使用mongodb
普通查询 某个字段匹配数组内的元素数量的,假如region只有一个元素的 db.getCollection(map).find({region:{$size:1}}) 假如region只有0个元素的 db.getCollection(map).find({region:{$size:0}}) db.getCollection(map).find({region:{$size:1}}).count() db.get…

2002高教社杯---A车灯线光源的优化设计
A题 车灯线光源的优化设计 安装在汽车头部的车灯的形状为一旋转抛物面,车灯的对称轴水平地指向正前方, 其开口半径36毫米,深度21.6毫米。经过车灯的焦点,在与对称轴相垂直的水平方向,对称地放置一定长度的均匀分布的线光源。要求…

从Date类型转为中文字符串
//主方法public static String DateToCh(Date date) {Calendar cal Calendar.getInstance();cal.setTime(date);int year cal.get(Calendar.YEAR);int month cal.get(Calendar.MONTH) 1;int day cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);return getYear(year) getTenString(month…

第十四课 如何在DAPP应用实现自带钱包转账功能?
1,为什么DAPP生态需要自带钱包功能? 区块链是一个伟大的发明,它改变了生产关系。很多生态,有了区块链技术,可以由全公司员工的"全员合伙人"变成了全平台的”全体合伙人”了,是真正的共享经济模式…

为什么jdk源码推荐ThreadLocal使用static
ThreadLocal是线程私有变量,本身是解决多线程环境线程安全,可以说单线程实际上没必要使用。 既然多线程环境本身不使用static,那么又怎么会线程不安全。所以这个问题本身并不是问题,只是有人没有理解ThreadLocal的真正使用场景&a…

C与C++之间相互调用
1、导出C函数以用于C或C的项目 如果使用C语言编写的DLL,希望从中导出函数给C或C的模块访问,则应使用 __cplusplus 预处理器宏确定正在编译的语言。如果是从C语言模块使用,则用C链接声明这些函数。如果使用此技术并为DLL提供头文件,…
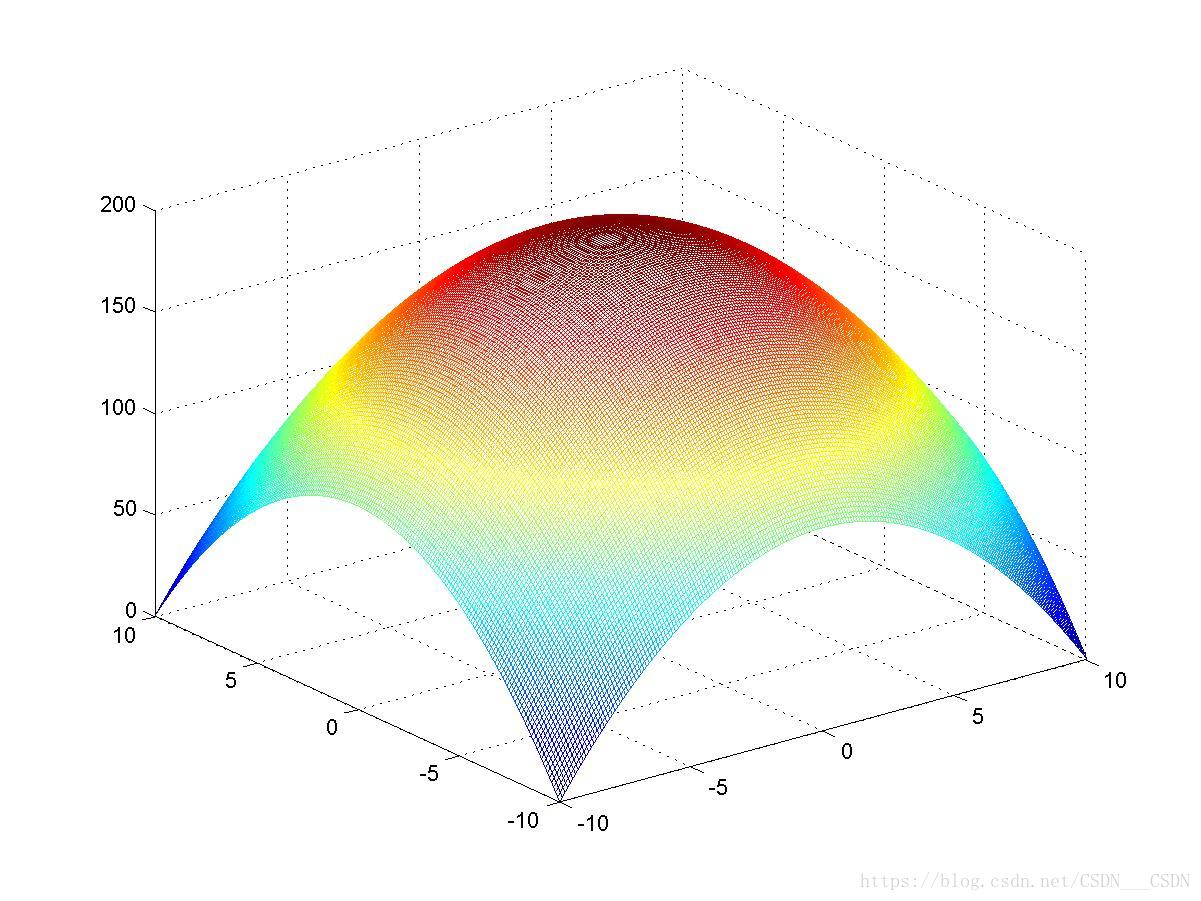
【MATLAB】三维图形的绘制mesh
步骤如下: (1)确定自变量x和y的取值范围和取值间隔 x x1 :dx :x2 , y y1 : dy : y2 (2)构成xoy平面上的自变量采样“格点”矩阵 ①利用格点矩阵的原理生成矩阵。 xx1:dx:x2; yy1:dy:y2; Xones(size(y))*x; Yy*o…

ORA-01919: role 'PLUSTRACE' does not exist
环境:Oracle 10g,11g.现象:在一次迁移测试中,发现有这样的角色赋权会报错不存在: SYSorcl> grant PLUSTRACE to jingyu; grant PLUSTRACE to jingyu* ERROR at line 1: ORA-01919: role PLUSTRACE does not exist 查询发现这个…
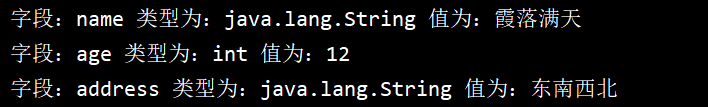
Java反射以及应用
需求:需要通过反射动态获取类的字段类型,然后做特殊处理 Java反射getDeclaredField和getField的区别 getDeclaredFiled 只能获取类本身的属性成员(包括私有、共有、保护) getField 仅能获取类(及其父类可以自己测试) public属性…

【MATLAB】雅可比矩阵jacobi matrix
参考页面: https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E9%9B%85%E5%8F%AF%E6%AF%94%E7%9F%A9%E9%98%B5/10753754?fraladdin#1 在向量微积分中,雅可比矩阵是一阶偏导数以一定方式排列成的矩阵,其行列式称为雅可比行列式。 由球坐标系到直角坐标系的转…

Laravel:使用Migrations
1、首先利用artisan创建一个可迁移的数据表模板,该命令运行后会在database/migrations目录下生成一个文件 php artisan make:migration create_fees_count_table --createfees_count 2、生成的文件包含up和down两个方法,其中up中是包含了添加表ÿ…

基于libevent和unix domain socket的本地server
https://www.pacificsimplicity.ca/blog/libevent-echo-server-tutorial 根据这一篇写一个最简单的demo。然后开始写client。 client调优 client最初的代码如下: 1 #include <sys/socket.h>2 #include <sys/un.h>3 #include <stdio.h>4 #include …
软件体系架构模式之一什么是软件架构模式
什么是软件架构模式 计划启动未开发的软件项目?然后选择正确的架构模式将对项目的结果起关键作用。选择市场上最流行或最新的技术并不总是意味着会带来最好的结果。但是,选择最合适的解决方案将为行之有效的问题和反复出现的问题提供可靠的解决方案。 …

HP 服务器 iLO 远程控制软件 介绍
iLO了解:iLO 是一组芯片,内部是vxworks的嵌入操作系统,在服务器的背后有一个标准RJ45口对外连接生产用交换机或者带外管理的交换机。iLO 全名是 Integrated Lights-out,它是惠普某些型号的服务器上集成的远程管理端口,它能够允许用…

【MATLAB】数据分析之数据插值
插值:求过已知有限个数据点的近似函数。 区别于拟合: 拟合:已知有限个数据点求近似函数,不要求过已知数据点,只要求在某种意义下它在这些点上的总偏差最小。 基本常用的插值方法:拉格朗日多项式插值&…

迈斯!啊呸~数学
1.数论 快速幂 int po(int x,int y) {int ans1;while(y){if(y%21)ans1ll*ans*x%p;x1ll*x*x%p;y/2;}return ans; } 乘法逆元(保证模域p与求逆元的数互质) po(a,p-2);//a为需要求逆元的数 扩展欧几里得(exgcd) #include<cstdio&g…
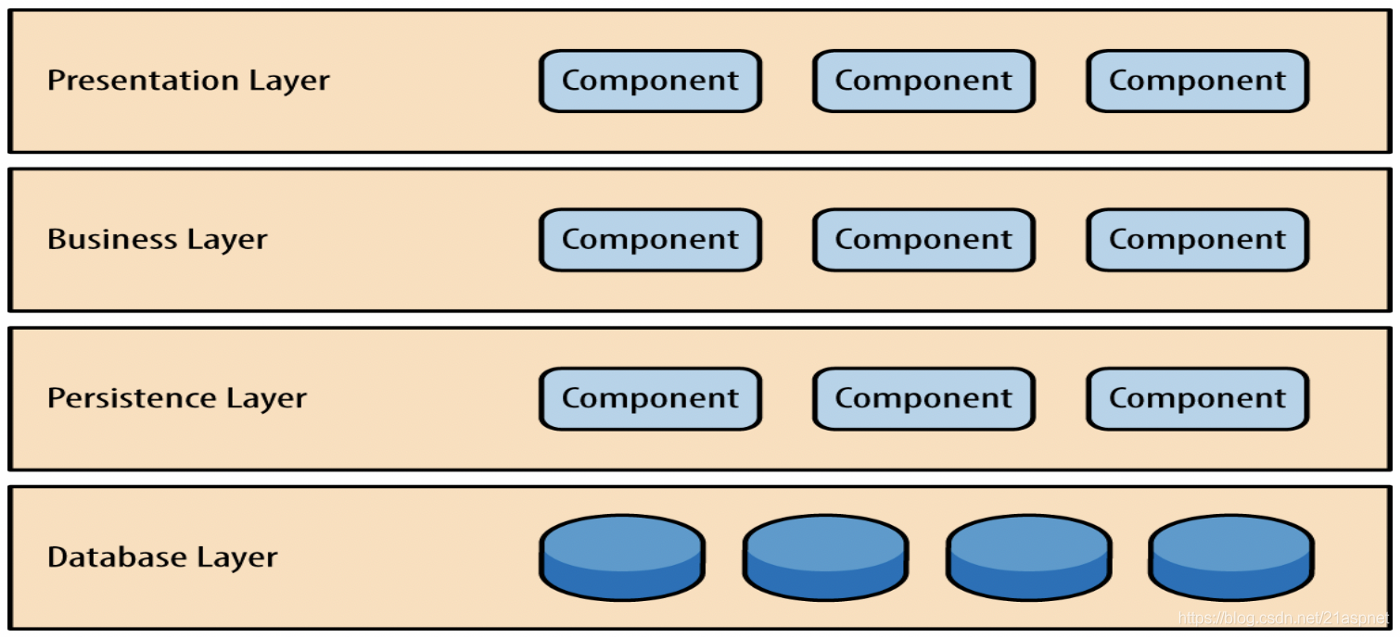
软件体系架构模式之二分层体系结构
分层体系结构模式是n层模式,其中组件被组织在水平层中。这是设计大多数软件的传统方法,并且具有独立性。这意味着所有组件都是互连的,但彼此之间不依赖。 图1:分层架构 在此体系结构中有四层,其中每一层在模块和其中的…

linux下mysql的root密码忘记解决方法
1.首先确认服务器出于安全的状态,最安全的状态是到服务器的Console上面操作,并且拔掉网线,或者可以使用--skip-networking限制只能从本地连接2.修改MySQL的登录设置: # vim /etc/my.cnf在[mysqld]的段中加上…
【Python】turtle库的小应用
心血来潮,哈哈哈,画的不好,请多见谅 大家如果想要尝试turtle库,可以借鉴: https://www.cnblogs.com/nowgood/p/turtle.html 导入库,我的pycharm里可以直接使用,哈哈哈,不行就pip…
