尺度空间理论与图像金字塔
我们之所以决定使用卷积后的特征是因为图像具有一种“静态性”的属性。也就是说使用卷积就是为了提取显著特征,减少特征维数,减少计算量。
在对图像进行卷积操作后的只管现象:图像变得模糊了,可是我们依然能够分辨出是什么!所以卷积就是提取显著特征!
1尺度空间理论
- 尺度不变性:人类在识别一个物体时,不管这个物体或远或近,都能对它进行正确的辨认,这就是所谓的尺度不变性。尺度空间理论经常与生物视觉关联, 有人也称图像局部不变性特征为基于生物视觉的不变性方法。
旋转不变性:当这个物体发生旋转时,我们照样可以正确地辨认它,这就是所谓的旋转不变性。全局特征:从整个图像中抽取的特征。较多的运用在图像检索领域,如图像颜色直方图。
局部特征:从图像的局部区域中抽取的特征(这个局部区域往往是图像中的一个像素及它周围的邻域)。
一种好的局部特征应该具有下面的特性:
- 可重复性:同一个物体在不同时间,不同角度拍到图像中,检测到的特征对应的越多越好。
- 独特性:特征在该物体上表现为独特性,能与场景下其他物体区分。
- 局部性:特征往往是物体某个局部的特点,这样才可以避免遮挡时不能匹配的问题。
- 数量性:检测到的特征数目一定要多,密集度最好能在一定程度上反映图像的内容。
- 准确性:得到的特征应该能被精确定位,能够精确到像素。
- 高效性:特征检测算法运算要快。
- 2 具体实施过程
$$G_l(i,j)=\sum^{2}_{m=-2}\sum_{n=-2}^2\omega(m,n)G_{l-1}(2i+m,2j+n)$$
$$(1\le l \le N,0 \le i \le R_l,0 \le j \le C_l)$$
式中,$N$为高斯金字塔顶层 拨动号;$R_l$和$G_l$分别为高斯金字塔第$l$层的行数和列数;$\omega(m,n)$是一个二维可分离的$5 \times 5$窗口函数,表达式为: $$\omega=\frac{1}{256} \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 4 & 6 & 4 & 1\\ 4 & 16 & 24 & 16 & 4\\ 6 & 24 &36 & 24 & 6\\ 4 & 16 & 24 & 16 & 4\\ 1 & 4 & 6 & 4 & 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} =\frac{1}{16}\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 4 & 6 & 4 &1 \end{bmatrix}\times\frac{1}{16}\begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 4 \\ 6 \\ 4 \\1 \end{bmatrix} $$
void genPyr(const Mat& imgSrc, vector<Mat>& outPutArray, int TYPE, int level) {outPutArray.assign(level + 1, Mat());outPutArray[0] = imgSrc.clone(); // the 0 level is the image. for (int i = 0; i != level; i++){pyrDown(outPutArray[i], outPutArray[i + 1]);}if (PYR_GUASS == TYPE){return;}for (int i = 0; i != level; i++){Mat UpSampleImg;pyrUp(outPutArray[i + 1], UpSampleImg, outPutArray[i].size());outPutArray[i] -= UpSampleImg;} }
$$ G_l^{\ast}(i,j)=4\sum_{m=-2}^2\sum_{n=-2}^2\omega(m,n)G_l(\frac{i+m}{2},\frac{j+n}{2}) \\ (0 \le l \le N,0 \le i \le R_l,0 \le j \le G_l) $$
上面的系数4,是因为每次能参与加权的项,的权值和为4/256,这个与我们用的$\omega$的值有关。 式中,
$$ G_l(\frac{i+m}{2},\frac{j+n}{2})=\begin{cases} G_l(\frac{i+m}{2},\frac{j+n}{2}), & 当\frac{i+m}{2},\frac{j+n}{2}为整数时 \\ 0, & 其他 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} LP_l=G_l-G_{l+1}^{\ast}, & 当0 \le l \le N时 \\ LP_N=G_N, & 当l=N时 \end{cases} $$

后来Koenerink、Lindeberg[Scale-space theory in computer vision]、Florack等人用精确的数学形式通过不同的途径都证明了高斯核是实现尺度变换的唯一变换核。
虽然很多研究者从可分性、旋转不变性、因果性等特性推出高斯滤波器是建立线性尺度空间的最优滤波器。然后在数字图像处理中,需要对核函数进行采样,离散的高斯函数并不满足连续高斯函数的的一些优良的性质。所以后来出现了一些非线性的滤波器组来建立尺度空间,如B样条核函数。
使用高斯滤波器对图像进行尺度空间金塔塔图的构建,让这个尺度空间具有下面的性质:
信号在尺度t上的表达可以看成是原信号在空间上的一系列加权平均,权重就是具有不同尺度参数的高斯核。
信号在尺度t上的表达也对应于用一个无方向性的孔径函数(特征长度为$\sigma=\sqrt{t}$)来观测信号的结果。这时候信号中特征长度小于$\sigma$的精细结构会被抑制[理解为一维信号上小于$\sigma$的波动会被平滑掉。
也叫高斯核族的半群(Semi-Group)性质:两个高斯核的卷积等同于另外一个不同核参数的高斯核卷积。
$$g(\mu,\sigma_1)\ast g(\mu,\sigma_2)=g(\mu,\sqrt{\sigma_1^2+\sigma_2^2})$$
这个性质的意思就是说不同的高斯核对图像的平滑是连续的。
这个特征可以从人眼的视觉原理去理解,人在看一件 物体时,离得越远,物体的细节看到的越少,细节特征是在减少的。
高斯核对图像进行滤波具有压制局部细节的性质。
这里只是一个公式推导的问题,对原来的信号加一个变换函数,对变换后的信号再进行高斯核的尺度空间生成,新的信号的极值点等特征是不变的。
Young对经生理学的研究中发现,哺乳动物的视网膜和视觉皮层的感受区域可以很好地用4阶以内的高斯微分来建模。
3 为什么用高斯核
图像的金字塔化能高效地(计算效率也较高)对图像进行多尺度的表达,但它缺乏坚实的理论基础,不能分析图像中物体的各种尺度(虽然我们有小猫的金字塔图像,我们还是不知道原图像内小猫的大小)。
信号的尺度空间刚提出是就是通过一系列单参数、宽度递增的高斯滤波器将原始信号滤波得到到组低频信号。那么一个很明显的疑问是:除了高斯滤波之外,其他带有参数t的低通滤波器是否也可以用来生成一个尺度空间。
后来Koenerink、Lindeberg[Scale-space theory in computer vision]、Florack等人用精确的数学形式通过不同的途径都证明了高斯核是实现尺度变换的唯一变换核。
虽然很多研究者从可分性、旋转不变性、因果性等特性推出高斯滤波器是建立线性尺度空间的最优滤波器。然后在数字图像处理中,需要对核函数进行采样,离散的高斯函数并不满足连续高斯函数的的一些优良的性质。所以后来出现了一些非线性的滤波器组来建立尺度空间,如B样条核函数。
使用高斯滤波器对图像进行尺度空间金塔塔图的构建,让这个尺度空间具有下面的性质:
1)加权平均和有限孔径效应
信号在尺度t上的表达可以看成是原信号在空间上的一系列加权平均,权重就是具有不同尺度参数的高斯核。
信号在尺度t上的表达也对应于用一个无方向性的孔径函数(特征长度为σ=t√)来观测信号的结果。这时候信号中特征长度小于σ的精细结构会被抑制[理解为一维信号上小于σ的波动会被平滑掉。]。
2)层叠平滑
也叫高斯核族的半群(Semi-Group)性质:两个高斯核的卷积等同于另外一个不同核参数的高斯核卷积。
这个性质的意思就是说不同的高斯核对图像的平滑是连续的。
3)局部极值递性
这个特征可以从人眼的视觉原理去理解,人在看一件物体时,离得越远,物体的细节看到的越少,细节特征是在减少的。
高斯核对图像进行滤波具有压制局部细节的性质。
4)尺度伸缩不变性。
这里只是一个公式推导的问题,对原来的信号加一个变换函数,对变换后的信号再进行高斯核的尺度空间生成,新的信号的极值点等特征是不变的。
Young对经生理学的研究中发现,哺乳动物的视网膜和视觉皮层的感受区域可以很好地用4阶以内的高斯微分来建模。
4 尺度的选择
一般我们采集到的图像中,我们并不知道我们感兴趣的目标在图像中的尺度,在这样的情况下,我们对图像进行分析时就无法选择合适的参数,比如边缘检测,可能由于参数不当,而造成过多的局部细节。
如下图所示:红色圆圈内的斑点的大小(直径)比例对应着两幅图像之间尺度比例(scale ratio)。如果对两幅图像采用相同的固定尺度的LoG检测器检测,很难将这两个斑点检测出来。LoG检测器相当于一个匹配滤波器,只有当LoG的尺度与图片中斑点结构尺度相当时才会有较强的响应。如果用与左图中斑点结构相当大小尺度LoG算子,在中的大斑点的对应的LoG响应很小不能被检测出来,反之亦然。因此固定尺度的LoG斑点检测器不具有尺度不变性。使用尺度空间进行多尺度检测可以将两幅图像中不同尺度的斑点检测出来。但是由于斑点结构是在一定尺度范围之内存在的,比如用5~8尺度的LoG可能都能检测出来右边图像中的斑点结构,所以在尺度空间中进行斑点检测会有重复检测的缺点。
在实际操作中,我们需要定义一个特征响应函数,在不同的尺度空间上寻找一个极值点。比如小猫的金字塔图像分析时,我们定义了一个大小为[w,h]的小猫的模板,用这个模板去与金字塔系列图像匹配,一定有匹配度最佳(即特征响应最强)。
需要注意的是,图像结构往往是在粗糙的尺度上被检测到,此时位置信息未必是最准确的,因此通常图像的尺度分析包含两个阶段:首先在粗尺度上进行特征(结构)检测,然后再在细尺度上进行精确定位。
5.高斯金字塔
Gaussian Pyramid
Imagine the pyramid as a set of layers in which the higher the layer, the smaller the size.

Every layer is numbered from bottom to top, so layer
 (denoted as
(denoted as  is smaller than layer
is smaller than layer  (
( ).
).To produce layer
 in the Gaussian pyramid, we do the following:
in the Gaussian pyramid, we do the following:Convolve
 with a Gaussian kernel:
with a Gaussian kernel:
Remove every even-numbered row and column.
You can easily notice that the resulting image will be exactly one-quarter the area of its predecessor. Iterating this process on the input image
 (original image) produces the entire pyramid.
(original image) produces the entire pyramid.The procedure above was useful to downsample an image. What if we want to make it bigger?:
- First, upsize the image to twice the original in each dimension, wit the new even rows and columns filled with zeros (
 )
) - Perform a convolution with the same kernel shown above (multiplied by 4) to approximate the values of the “missing pixels”
- First, upsize the image to twice the original in each dimension, wit the new even rows and columns filled with zeros (
These two procedures (downsampling and upsampling as explained above) are implemented by the OpenCV functions pyrUp and pyrDown, as we will see in an example with the code below:
Note
When we reduce the size of an image, we are actually losing information of the image.
Code
This tutorial code’s is shown lines below. You can also download it from here
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>using namespace cv;/// Global variables
Mat src, dst, tmp;
char* window_name = "Pyramids Demo";/**
* @function main
*/
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{/// General instructionsprintf( "\n Zoom In-Out demo \n " );printf( "------------------ \n" );printf( " * [u] -> Zoom in \n" );printf( " * [d] -> Zoom out \n" );printf( " * [ESC] -> Close program \n \n" );/// Test image - Make sure it s divisible by 2^{n}src = imread( "../images/chicky_512.jpg" );if( !src.data ){ printf(" No data! -- Exiting the program \n");return -1; }tmp = src;dst = tmp;/// Create windownamedWindow( window_name, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );imshow( window_name, dst );/// Loopwhile( true ){int c;c = waitKey(10);if( (char)c == 27 ){ break; }if( (char)c == 'u' ){ pyrUp( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols*2, tmp.rows*2 ) );printf( "** Zoom In: Image x 2 \n" );}else if( (char)c == 'd' ){ pyrDown( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 ) );printf( "** Zoom Out: Image / 2 \n" );}imshow( window_name, dst );tmp = dst;}return 0;
}
Explanation
Let’s check the general structure of the program:
Load an image (in this case it is defined in the program, the user does not have to enter it as an argument)
/// Test image - Make sure it s divisible by 2^{n} src = imread( "../images/chicky_512.jpg" ); if( !src.data ){ printf(" No data! -- Exiting the program \n");return -1; }
Create a Mat object to store the result of the operations (dst) and one to save temporal results (tmp).
Mat src, dst, tmp; /* ... */ tmp = src; dst = tmp;
Create a window to display the result
namedWindow( window_name, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); imshow( window_name, dst );
Perform an infinite loop waiting for user input.
while( true ) {int c;c = waitKey(10);if( (char)c == 27 ){ break; }if( (char)c == 'u' ){ pyrUp( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols*2, tmp.rows*2 ) );printf( "** Zoom In: Image x 2 \n" );}else if( (char)c == 'd' ){ pyrDown( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 ) );printf( "** Zoom Out: Image / 2 \n" );}imshow( window_name, dst );tmp = dst; }
Our program exits if the user presses ESC. Besides, it has two options:
Perform upsampling (after pressing ‘u’)
pyrUp( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols*2, tmp.rows*2 )
We use the function pyrUp with 03 arguments:
- tmp: The current image, it is initialized with the src original image.
- dst: The destination image (to be shown on screen, supposedly the double of the input image)
- Size( tmp.cols*2, tmp.rows*2 ) : The destination size. Since we are upsampling, pyrUp expects a size double than the input image (in this case tmp).
Perform downsampling (after pressing ‘d’)
pyrDown( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 )
Similarly as with pyrUp, we use the function pyrDown with 03 arguments:
- tmp: The current image, it is initialized with the src original image.
- dst: The destination image (to be shown on screen, supposedly half the input image)
- Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 ) : The destination size. Since we are upsampling, pyrDown expects half the size the input image (in this case tmp).
Notice that it is important that the input image can be divided by a factor of two (in both dimensions). Otherwise, an error will be shown.
Finally, we update the input image tmp with the current image displayed, so the subsequent operations are performed on it.
tmp = dst;
Results
After compiling the code above we can test it. The program calls an image chicky_512.jpg that comes in the tutorial_code/image folder. Notice that this image is
 , hence a downsample won’t generate any error (
, hence a downsample won’t generate any error ( ). The original image is shown below:
). The original image is shown below:
First we apply two successive pyrDown operations by pressing ‘d’. Our output is:

Note that we should have lost some resolution due to the fact that we are diminishing the size of the image. This is evident after we apply pyrUp twice (by pressing ‘u’). Our output is now:
六:补充说明【OpenCV】SIFT原理与源码分析:DoG尺度空间构造
《SIFT原理与源码分析》系列文章索引:http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/8069548
尺度空间理论
尺度越大图像越模糊。
为什么要讨论尺度空间?
图像的尺度空间表达就是图像在所有尺度下的描述。
尺度空间表达与金字塔多分辨率表达
高斯模糊
高斯核是唯一可以产生多尺度空间的核(《Scale-space theory: A basic tool for analysing structures at different scales》)。一个图像的尺度空间L(x,y,σ) ,定义为原始图像I(x,y)与一个可变尺度的2维高斯函数G(x,y,σ)卷积运算。
二维空间高斯函数:
尺度空间:
尺度是自然客观存在的,不是主观创造的。高斯卷积只是表现尺度空间的一种形式。
二维空间高斯函数是等高线从中心成正太分布的同心圆:

分布不为零的点组成卷积阵与原始图像做变换,即每个像素值是周围相邻像素值的高斯平均。一个5*5的高斯模版如下所示:

高斯模版是圆对称的,且卷积的结果使原始像素值有最大的权重,距离中心越远的相邻像素值权重也越小。
在实际应用中,在计算高斯函数的离散近似时,在大概3σ距离之外的像素都可以看作不起作用,这些像素的计算也就可以忽略。所以,通常程序只计算(6σ+1)*(6σ+1)就可以保证相关像素影响。
高斯模糊另一个很厉害的性质就是线性可分:使用二维矩阵变换的高斯模糊可以通过在水平和竖直方向各进行一维高斯矩阵变换相加得到。

O(N^2*m*n)次乘法就缩减成了O(N*m*n)+O(N*m*n)次乘法。(N为高斯核大小,m,n为二维图像高和宽)
其实高斯这一部分只需要简单了解就可以了,在OpenCV也只需要一句代码:
- GaussianBlur(dbl, dbl, Size(), sig_diff, sig_diff);
金字塔多分辨率
金字塔是早期图像多尺度的表示形式。图像金字塔化一般包括两个步骤:使用低通滤波器平滑图像;对平滑图像进行降采样(通常是水平,竖直方向1/2),从而得到一系列尺寸缩小的图像。

上图中(a)是对原始信号进行低通滤波,(b)是降采样得到的信号。
而对于二维图像,一个传统的金字塔中,每一层图像由上一层分辨率的长、宽各一半,也就是四分之一的像素组成:

多尺度和多分辨率
尺度空间表达和金字塔多分辨率表达之间最大的不同是:
- 尺度空间表达是由不同高斯核平滑卷积得到,在所有尺度上有相同的分辨率;
- 而金字塔多分辨率表达每层分辨率减少固定比率。
DoG(Difference of Gaussian)
高斯拉普拉斯LoG金字塔

高斯差分DoG金字塔
 的近似。SIFT算法建议,在某一尺度上的特征检测可以通过对两个相邻高斯尺度空间的图像相减,得到DoG的响应值图像D(x,y,σ)。然后仿照LoG方法,通过对响应值图像D(x,y,σ)进行局部最大值搜索,在空间位置和尺度空间定位局部特征点。其中:
的近似。SIFT算法建议,在某一尺度上的特征检测可以通过对两个相邻高斯尺度空间的图像相减,得到DoG的响应值图像D(x,y,σ)。然后仿照LoG方法,通过对响应值图像D(x,y,σ)进行局部最大值搜索,在空间位置和尺度空间定位局部特征点。其中:


- // 构建nOctaves组(每组nOctaves+3层)高斯金字塔
- void SIFT::buildGaussianPyramid( const Mat& base, vector<Mat>& pyr, int nOctaves ) const
- {
- vector<double> sig(nOctaveLayers + 3);
- pyr.resize(nOctaves*(nOctaveLayers + 3));
- // precompute Gaussian sigmas using the following formula:
- // \sigma_{total}^2 = \sigma_{i}^2 + \sigma_{i-1}^2、
- // 计算对图像做不同尺度高斯模糊的尺度因子
- sig[0] = sigma;
- double k = pow( 2., 1. / nOctaveLayers );
- for( int i = 1; i < nOctaveLayers + 3; i++ )
- {
- double sig_prev = pow(k, (double)(i-1))*sigma;
- double sig_total = sig_prev*k;
- sig[i] = std::sqrt(sig_total*sig_total - sig_prev*sig_prev);
- }
- for( int o = 0; o < nOctaves; o++ )
- {
- // DoG金子塔需要nOctaveLayers+2层图像来检测nOctaves层尺度
- // 所以高斯金字塔需要nOctaveLayers+3层图像得到nOctaveLayers+2层DoG金字塔
- for( int i = 0; i < nOctaveLayers + 3; i++ )
- {
- // dst为第o组(Octave)金字塔
- Mat& dst = pyr[o*(nOctaveLayers + 3) + i];
- // 第0组第0层为原始图像
- if( o == 0 && i == 0 )
- dst = base;
- // base of new octave is halved image from end of previous octave
- // 每一组第0副图像时上一组倒数第三幅图像隔点采样得到
- else if( i == 0 )
- {
- const Mat& src = pyr[(o-1)*(nOctaveLayers + 3) + nOctaveLayers];
- resize(src, dst, Size(src.cols/2, src.rows/2),
- 0, 0, INTER_NEAREST);
- }
- // 每一组第i副图像是由第i-1副图像进行sig[i]的高斯模糊得到
- // 也就是本组图像在sig[i]的尺度空间下的图像
- else
- {
- const Mat& src = pyr[o*(nOctaveLayers + 3) + i-1];
- GaussianBlur(src, dst, Size(), sig[i], sig[i]);
- }
- }
- }
- }





- // 构建nOctaves组(每组nOctaves+2层)高斯差分金字塔
- void SIFT::buildDoGPyramid( const vector<Mat>& gpyr, vector<Mat>& dogpyr ) const
- {
- int nOctaves = (int)gpyr.size()/(nOctaveLayers + 3);
- dogpyr.resize( nOctaves*(nOctaveLayers + 2) );
- for( int o = 0; o < nOctaves; o++ )
- {
- for( int i = 0; i < nOctaveLayers + 2; i++ )
- {
- // 第o组第i副图像为高斯金字塔中第o组第i+1和i组图像相减得到
- const Mat& src1 = gpyr[o*(nOctaveLayers + 3) + i];
- const Mat& src2 = gpyr[o*(nOctaveLayers + 3) + i + 1];
- Mat& dst = dogpyr[o*(nOctaveLayers + 2) + i];
- subtract(src2, src1, dst, noArray(), CV_16S);
- }
- }
- }
SIFT简介
Scale Invariant Feature Transform,尺度不变特征变换匹配算法,是由David G. Lowe在1999年(《Object Recognition from Local Scale-Invariant Features》)提出的高效区域检测算法,在2004年(《Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints》)得以完善。
SIFT特征对旋转、尺度缩放、亮度变化等保持不变性,是非常稳定的局部特征,现在应用很广泛。而SIFT算法是将Blob检测,特征矢量生成,特征匹配搜索等步骤结合在一起优化。我会更新一系列文章,分析SIFT算法原理及OpenCV 2.4.2实现的SIFT源码:
- DoG尺度空间构造(Scale-space extrema detection)http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/8067881
- 关键点搜索与定位(Keypoint localization)http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/8087239
- 方向赋值(Orientation assignment)http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/8096072
- 关键点描述(Keypoint descriptor)http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/8113565
- OpenCV实现:特征检测器FeatureDetectorhttp://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/8652096
- SIFT中LoG和DoG的比较http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/27692123
SIFT in OpenCV
构造函数:
- SIFT::SIFT(int nfeatures=0, int nOctaveLayers=3, double contrastThreshold=0.04, double edgeThreshold=
- 10, double sigma=1.6)
nOctaveLayers:金字塔中每组的层数(算法中会自己计算这个值,后面会介绍)。
contrastThreshold:过滤掉较差的特征点的对阈值。contrastThreshold越大,返回的特征点越少。
edgeThreshold:过滤掉边缘效应的阈值。edgeThreshold越大,特征点越多(被多滤掉的越少)。
sigma:金字塔第0层图像高斯滤波系数,也就是σ。
重载操作符:
- void SIFT::operator()(InputArray img, InputArray mask, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, OutputArray
- descriptors, bool useProvidedKeypoints=false)
img:8bit灰度图像
mask:图像检测区域(可选)
keypoints:特征向量矩阵
descipotors:特征点描述的输出向量(如果不需要输出,需要传cv::noArray())。
useProvidedKeypoints:是否进行特征点检测。ture,则检测特征点;false,只计算图像特征描述。
函数源码
- SIFT::SIFT( int _nfeatures, int _nOctaveLayers,
- double _contrastThreshold, double _edgeThreshold, double _sigma )
- : nfeatures(_nfeatures), nOctaveLayers(_nOctaveLayers),
- contrastThreshold(_contrastThreshold), edgeThreshold(_edgeThreshold), sigma(_sigma)
- // sigma:对第0层进行高斯模糊的尺度空间因子。
- // 默认为1.6(如果是软镜摄像头捕获的图像,可以适当减小此值)
- {
- }
主要操作还是利用重载操作符()来执行:
- void SIFT::operator()(InputArray _image, InputArray _mask,
- vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints,
- OutputArray _descriptors,
- bool useProvidedKeypoints) const
- // mask :Optional input mask that marks the regions where we should detect features.
- // Boolean flag. If it is true, the keypoint detector is not run. Instead,
- // the provided vector of keypoints is used and the algorithm just computes their descriptors.
- // descriptors – The output matrix of descriptors.
- // Pass cv::noArray() if you do not need them.
- {
- Mat image = _image.getMat(), mask = _mask.getMat();
- if( image.empty() || image.depth() != CV_8U )
- CV_Error( CV_StsBadArg, "image is empty or has incorrect depth (!=CV_8U)" );
- if( !mask.empty() && mask.type() != CV_8UC1 )
- CV_Error( CV_StsBadArg, "mask has incorrect type (!=CV_8UC1)" );
- // 得到第1组(Octave)图像
- Mat base = createInitialImage(image, false, (float)sigma);
- vector<Mat> gpyr, dogpyr;
- // 每层金字塔图像的组数(Octave)
- int nOctaves = cvRound(log( (double)std::min( base.cols, base.rows ) ) / log(2.) - 2);
- // double t, tf = getTickFrequency();
- // t = (double)getTickCount();
- // 构建金字塔(金字塔层数和组数相等)
- buildGaussianPyramid(base, gpyr, nOctaves);
- // 构建高斯差分金字塔
- buildDoGPyramid(gpyr, dogpyr);
- //t = (double)getTickCount() - t;
- //printf("pyramid construction time: %g\n", t*1000./tf);
- // useProvidedKeypoints默认为false
- // 使用keypoints并计算特征点的描述符
- if( !useProvidedKeypoints )
- {
- //t = (double)getTickCount();
- findScaleSpaceExtrema(gpyr, dogpyr, keypoints);
- //除去重复特征点
- KeyPointsFilter::removeDuplicated( keypoints );
- // mask标记检测区域(可选)
- if( !mask.empty() )
- KeyPointsFilter::runByPixelsMask( keypoints, mask );
- // retainBest:根据相应保留指定数目的特征点(features2d.hpp)
- if( nfeatures > 0 )
- KeyPointsFilter::retainBest(keypoints, nfeatures);
- //t = (double)getTickCount() - t;
- //printf("keypoint detection time: %g\n", t*1000./tf);
- }
- else
- {
- // filter keypoints by mask
- // KeyPointsFilter::runByPixelsMask( keypoints, mask );
- }
- // 特征点输出数组
- if( _descriptors.needed() )
- {
- //t = (double)getTickCount();
- int dsize = descriptorSize();
- _descriptors.create((int)keypoints.size(), dsize, CV_32F);
- Mat descriptors = _descriptors.getMat();
- calcDescriptors(gpyr, keypoints, descriptors, nOctaveLayers);
- //t = (double)getTickCount() - t;
- //printf("descriptor extraction time: %g\n", t*1000./tf);
- }
- }
函数中用到的构造金字塔: buildGaussianPyramid(base, gpyr, nOctaves);等步骤请参见文章后续系列。
[1] opencv教程:图像金字塔
[2] 计算机视觉——算法与应用 3.5节 金字塔与小波
[3] 现代数字图像 1.1节 图像多分辨率真金字塔
[4] OpenCV的5种图像内插方法
[5] http://www.360doc.com/content/15/1115/12/25664332_513338038.shtml
[6] http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/8067881
[7] http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/8069548
[8]
相关文章:

【ACM】 multiset 的 一些应用
一、The kth great number 题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/HDU-4006 用set写超时 (在VJ里,用C显示Compilation Error,选择G,则是TLE) #include <iostream> #include <set> #include &…

apache2.2 做后端,增加真实ip到日志中
apache2.2使用mod_remoteip模块 一.安装 wget https://github.com/ttkzw/mod_remoteip-httpd22/raw/master/mod_remoteip.c/usr/local/apache/bin/apxs -i -c -n mod_remoteip.so mod_remoteip.c 二.添加Apache配置vi /usr/local/apache/conf/httpd.confInclude conf/extra/htt…

高可用方案系统架构
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 高可用方案 系统架构 转载于:https://my.oschina.net/qiongtaoli/blog/3007587

OpenCV3.2.0+VS2017在window10开发环境配置记录
本机环境:win10 64位 OpenCV3.2.0 Visual Studio 2017 最后结果,亲测可用OpenCV官方下载地址: http://opencv.org/releases.html#本人选择opencv3.2.0基于Windows平台。读者根据自己需要选择合适版本及平台下载。 选择window版本的opencv下载…
C++vector迭代器失效的问题
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/olanmomo/article/details/38420907 转载:http://blog.csdn.net/stpeace/article/details/46507451 转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/xkfz007/articles/2509433.html 转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/BeyondAnyTime/archive/2012/08/13/2636375.html 有这样…

【HDU】1251统计难题 (字典树:二维数组,结构体数组,链表,map)
使用二维数组或者结构体数组都可以,但是在计数的时候有一点点小区别 一、结构体数组 #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <string> typedef long long ll; using namespace…
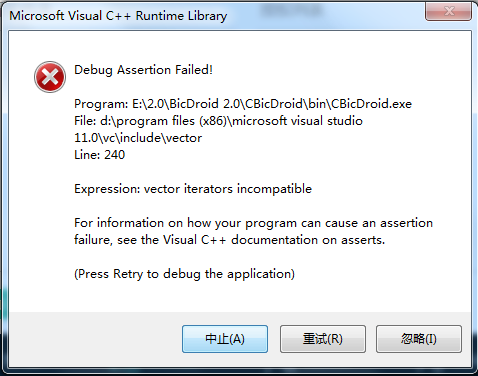
Jmeter干货 不常用却极其有用的几个地方
1. Jmeter测试计划下Run Thread Groups consecutively 表示序列化执行测试计划下所有线程组中的各个请求 如下图配置,新建的测试计划中,不默认勾选此项, 而享用Jmeter做接口自动化测试的同学们,会发现一个问题是,可能多…

图像滤波总结(面试经验总结)
目录 图像平滑处理,6种滤波总结的综合示例 【盒式滤波、均值滤波、高斯滤波、中值滤波、双边滤波导向滤波】 1-图像滤波 2-代码演示 3-显示结果 4-程序说明 5 角点检测(Harris,Fast,surf) 图像平滑处理,6种滤波总结的综合示…

【小贴士】DEV 多行注释
多行注释 Ctrl / 取消多行注释 Ctrl ,

JSP+Servlet基础一
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> JSP中的指令: 格式:<%指令的名称(page,taglib,include...) 属性属性值%> 指令中的page:用于整个页面,定义与页面相关的属性。page属性一共有13个。 1、常…

Chameleon跨端框架——壹个理想主义团队的开源作品
文章较长,信息量很大,请耐心阅读,必然有收获。下面正文开始~背景解决方案原理久经考验生产应用举例易用性好多态协议学习成本低渐进式接入业内对比后期规划理想主义历经近20个月打磨,滴滴跨端方案chameleon终于开源了github.com/d…

尺度空间理论与图像金字塔(二)
SIFT简介 整理一下方便阅读,作者写的东西摘自论文,在此感谢xiaowei等的贡献 DoG尺度空间构造(Scale-space extrema detection)http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/8067881关键点搜索与定位(Keypoint l…

仿桌面通知pnotify插件
在做网站的时候,alert弹出框是非常常见的情形。但是,有些情况下,弹框对用户来说是并不友好的。调研了几个其他的提示插件了,发现pnotify比较好用,可配置性也高。 使用示例: <!DOCTYPE html> <html…

【HDU】1305 Immediate Decodability(字典树:结构体数组,二维数组,链表/指针)
一、用的二维数组 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int maxn 100; int tr[maxn][2]; int mk[maxn]; int tot;void insert(string s) {int u 0;for(int i0;i<s.length();i){int x s[i]-0;if(tr…

Hyperledger Grid:一个用于分布式供应链解决方案的框架
Hyperledger在最近的一篇博文中发布了一个名为Hyperledger Grid的新项目。Grid是一个用于集成分布式账本技术(DLT)解决方案与供应链行业企业业务系统的框架。该项目提供了一个参考架构、通用数据模型和智能合约,所有这些都是基于开放标准和行…

尺度不变特征变换匹配算法详解
尺度不变特征变换匹配算法详解Scale Invariant Feature Transform(SIFT)Just For Fun对于初学者,从David G.Lowe的论文到实现,有许多鸿沟,本文帮你跨越。1、SIFT综述 尺度不变特征转换(Scale-invariant feature transform或SIFT)是一种电脑视…

【POJ】2503 Babelfish(字典树,map,指针)
一、map 输入时候的格式有点难想,还有一种想法是用gets读取,然后用sscanf分开,分别存到两个数组中去,再加入map中,但是这一种方法目前还没有实现。。 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include …

ndk-build: CreateProcess error=193
为什么80%的码农都做不了架构师?>>> 问题:ndk-build": CreateProcess error193 解决:该问题表明,调用了非windows程序,在build.xml中将ndk-build修改为ndk-build.cmd即可ant编译 转载于:https://my.o…
AI芯片初创公司单纯卖芯片还是捆绑算法的商业模式更好?...
雷锋网在《资本寒冬,这样的AI芯片公司2019年危矣》一文中已经提到,2019年的资本寒冬以及整个半导体行业的低迷,将会让那些没有技术独特性以及缺乏商业落地能力,且现金流控制不好的AI芯片公司面临巨大的挑战,甚至大概率…
VS2017配置OpenCV3.2+contrib3.2
VS2017配置OpenCV3.2contrib3.2前言opecv3.2opencv_contrib3.2模块都编译配置了在配置contrib之前,尝试直接配置OpeCV3.2-vc14,发现可以正常使用,也就是说官方包虽然只有vc14,但vs2017(vc15)也支持的很好。操作环境:WIN10 64bit &…
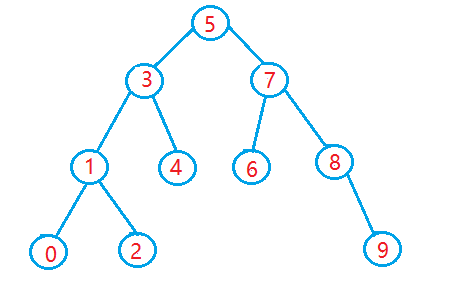
【ACM】二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree /BS Tree) 小结
动态管理集合的数据结构——二叉搜索树 搜索树是一种可以进行插入,搜索,删除等操作的数据结构,可以用字典或者优先队列。 二叉排序树又称为二叉查找树,他或者为空树,或者是满足如下性质的二叉树。 (1&…

android安卓动态设置控件宽高
LayoutParams layoutParamsp_w_picpathView.getLayoutParams();layoutParams.width100;layoutParams.height200;p_w_picpathView.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/11020803/1860242

《深入java虚拟机》读书笔记类加载
概述 类加载机制是指虚拟机将描述类的数据从Class文件中加载到内存,并进行数据验证、解析、初始化等过程,最后形成可以直接被虚拟机使用的java类型。在java语言中类的加载、链接、初始化等过程并不是在编译时期完成,而是在运行时期才进行的&a…

SLAM之特征匹配(一)————RANSAC-------OpenCV中findFundamentalMat函数使用的模型
目录 1.RANSAC原理 2. RANSAC算法步骤: 3. RANSAC源码解析 step one niters最初的值为2000,这就是初始时的RANSAC算法的循环次数,getSubset()函数是从一组对应的序列中随机的选出4组(因为要想计算出一…

I hope so 2016-Oct-10
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> <I hope so> - A joke A: Do you think your son will forget all he learned at college? B: I hopse so. He certainly cant make a living by kissing girls! 转载于:https://my.oschina.net/u/553266/blog/75…

【Codeforces】158B-Taxi(贪心,怎么贪咧)
贪心 emmmm http://codeforces.com/contest/158/problem/B 题目大意:有四种旅客,四人一组,三人一组,两人一组,一人一组,一辆出租车最多可以坐四个人,并且一组里的人必须坐一辆车,…

90 后 CTO 创业 6 年,做了一件改变互联网的“小事”
TGO 鲲鹏会在武汉举行了一场线下分享活动 —— 冲破壁垒,打造精英的技术团队 。来自极验的 90 后 CTO 黄胜蓝分享了他的团队故事,以及在他看来一个创新团队应该具备的特征。极验 CTO \u0026 TGO 鲲鹏会会员黄胜蓝在现场进行分享 1. 创新:非典…
ORB特征(二)
为了满足实时性的要求,前面文章中介绍过(具体链接如下)快速提取特征点算法Fast,以及特征描述子Brief。本篇文章介绍的ORB算法结合了Fast和Brief的速度优势,并做了改进,且ORB是免费Ethan Rublee等人2011年在《ORB&#…

【POJ】2377 Bad Cowtractors(最大生成树)
简单题,模板题 求解最大生成树,提交一直WA,感觉没有什么问题啊,就是在求解最小生成树的模板基础上稍加修改即可,后来发现在输出a,b,c给map二维数组的时候还必须有判断条件,略为有点…

使用let替换var实现块级作用域的小发现
在讲述javascript没有块级作用域的时候都会提到一个非常经典的例子: var obj{name:helo,age:15 }; var arr[];for(var i0;i<5;i){arr[i]i;console.log(i);} console.log(arr); console.log(i);因为javascript没有块级作用域,所以控制台打印出来的结果…


