C++中函数指针的使用
A function pointer is a variable that stores the address of a function that can later be called through that function pointer. This is useful because functions encapsulate behavior.
函数指针是一个指向函数的指针,函数指针表示一个函数的入口地址。指针是变量,所以函数指针也是变量,因此可以使用变量定义的方式来定义函数指针。只是这个指针它不像普通的指针指向一个变量,而它指向的是一个函数,也就是它存储的是一个函数的地址。
在C中,一个函数指针可以多次赋值。取地址符号是可选的,却是推荐使用的。在C++中,对于赋值必须要加”&”,而且还必须在此之前已经定义好了一个类实例,取地址符号要操作于这个类实例的对应的函数成员上。在使用成员函数的指针调用成员函数时,必须要加类实例的名称,然后再使用.*或者->*来使用成员函数指针。
函数指针没有普通变量指针的算术操作,但是可以进行比较操作。
C语言函数指针的定义形式:返回类型 (*函数指针名称)(参数类型, 参数类型, …);
C++函数指针的定义形式:返回类型 (类名称::*函数成员名称)(参数类型,参数类型, …);
C++中,类的静态成员函数指针和C的指针用法相同,不需要加类名。普通成员函数,一定要加类名。
函数指针一般有两个用途:调用函数和做函数的参数。
下面是从其他文章中copy的测试代码,详细内容介绍可以参考对应的reference:
#include <stdio.h> // for printf
#include <string.h> // for strchr
#include <math.h>
#include <functional>
#include <algorithm> // for std::swap, use <utility> instead if C++11
#include <iostream>
#include "function_pointers.hpp"// reference: http://www.newty.de/fpt/intro.html// reference: http://www.cprogramming.com/tutorial/function-pointers.html
void my_int_func(int x)
{printf("%d\n", x);
}int test_function_pointers1()
{void (*foo)(int);// Initializing Function Pointers:// To initialize a function pointer, you must give it the address of a function in your program.// the ampersand is actually optionalfoo = &my_int_func;// call my_int_func (note that you do not need to write (*foo)(2) )foo(2); // 2// but if you want to, you may (*foo)(2); // 2return 0;
}int int_sorter(const void *first_arg, const void *second_arg)
{int first = *(int*)first_arg;int second = *(int*)second_arg;if (first < second) {return -1;} else if (first == second) {return 0;} else {return 1;}
}int test_function_pointers2()
{int array[10];for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {array[i] = 10 - i;}// void qsort(void *base, size_t nmemb, size_t size, int(*compar)(const void *, const void *));qsort(array, 10, sizeof(int), int_sorter);for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {printf("%d\n", array[i]); // 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10}return 0;
}// Note our user-defined comparison is the third parameter
void selectionSort(int *array, int size, bool(*comparisonFcn)(int, int))
{// Step through each element of the arrayfor (int startIndex = 0; startIndex < size; ++startIndex) {// smallestIndex is the index of the smallest element we've encountered so far.int smallestIndex = startIndex;// Look for smallest element remaining in the array (starting at startIndex+1)for (int currentIndex = startIndex + 1; currentIndex < size; ++currentIndex) {// If the current element is smaller than our previously found smallestif (comparisonFcn(array[smallestIndex], array[currentIndex])) // COMPARISON DONE HERE// This is the new smallest number for this iterationsmallestIndex = currentIndex;}// Swap our start element with our smallest elementstd::swap(array[startIndex], array[smallestIndex]);}
}// Here is a comparison function that sorts in ascending order
// (Note: it's exactly the same as the previous ascending() function)
bool ascending(int x, int y)
{return x > y; // swap if the first element is greater than the second
}// Here is a comparison function that sorts in descending order
bool descending(int x, int y)
{return x < y; // swap if the second element is greater than the first
}// This function prints out the values in the array
void printArray(int *array, int size)
{for (int index = 0; index < size; ++index)std::cout << array[index] << " ";std::cout << '\n';
}// reference: http://www.learncpp.com/cpp-tutorial/78-function-pointers/
int test_function_pointers3()
{int array[9] = { 3, 7, 9, 5, 6, 1, 8, 2, 4 };// Sort the array in descending order using the descending() functionselectionSort(array, 9, descending);printArray(array, 9); // 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1// Sort the array in ascending order using the ascending() functionselectionSort(array, 9, ascending);printArray(array, 9); // 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9return 0;
}bool evensFirst(int x, int y)
{// if x is even and y is odd, x goes first (no swap needed)if ((x % 2 == 0) && !(y % 2 == 0))return false;// if x is odd and y is even, y goes first (swap needed)if (!(x % 2 == 0) && (y % 2 == 0))return true;// otherwise sort in ascending orderreturn ascending(x, y);
}int test_function_pointers4()
{int array[9] = { 3, 7, 9, 5, 6, 1, 8, 2, 4 };selectionSort(array, 9, evensFirst);printArray(array, 9); // 2 4 6 8 1 3 5 7 9return 0;
}int getInteger()
{std::cout << "Enter an integer: ";int x;std::cin >> x;return x;
}char getOperation()
{char op;do {std::cout << "Enter an operation ('+', '-', '*', '/'): ";std::cin >> op;} while (op != '+' && op != '-' && op != '*' && op != '/');return op;
}int add(int x, int y)
{return x + y;
}int subtract(int x, int y)
{return x - y;
}int multiply(int x, int y)
{return x * y;
}int divide(int x, int y)
{return x / y;
}typedef int(*arithmeticFcn)(int, int);arithmeticFcn getArithmeticFcn(char op)
{switch (op) {default: // default will be to addcase '+': return add;case '-': return subtract;case '*': return multiply;case '/': return divide;}
}int test_function_pointers5()
{int x = getInteger(); // 5char op = getOperation(); // *int y = getInteger(); // 6arithmeticFcn fcn = getArithmeticFcn(op);std::cout << x << ' ' << op << ' ' << y << " = " << fcn(x, y) << '\n'; // 5 * 6 = 30return 0;
}struct arithmeticStruct
{char op;arithmeticFcn fcn;
};static arithmeticStruct arithmeticArray[] {{ '+', add },{ '-', subtract },{ '*', multiply },{ '/', divide }
};arithmeticFcn getArithmeticFcn_(char op)
{for (auto &arith : arithmeticArray) {if (arith.op == op)return arith.fcn;}return add; // default will be to add
}int test_function_pointers6()
{int x = getInteger();char op = getOperation();int y = getInteger();arithmeticFcn fcn = getArithmeticFcn_(op);std::cout << x << ' ' << op << ' ' << y << " = " << fcn(x, y) << '\n'; // 5 * 6 = 30return 0;
}double cm_to_inches(double cm)
{return cm / 2.54;
}// reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Function_pointer
int test_function_pointers7()
{double(*func1)(double) = cm_to_inches;printf("%f\n", func1(15.0)); // 5.905512return 0;
}// Function taking a function pointer as an argument
double compute_sum(double(*funcp)(double), double lo, double hi)
{double sum = 0.0;// Add values returned by the pointed-to function '*funcp'for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {double x, y;// Use the function pointer 'funcp' to invoke the functionx = i / 100.0 * (hi - lo) + lo;y = (*funcp)(x);sum += y;}return sum / 101.0;
}int test_function_pointers8()
{double(*fp)(double); // Function pointerdouble sum;// Use 'sin()' as the pointed-to functionfp = sin;sum = compute_sum(fp, 0.0, 1.0);printf("sum(sin): %f\n", sum); // sum(sin): 0.459308// Use 'cos()' as the pointed-to functionfp = cos;sum = compute_sum(fp, 0.0, 1.0);printf("sum(cos): %f\n", sum); // sum(cos): 0.840758return 0;
}int add_(int first, int second)
{return first + second;
}int subtract_(int first, int second)
{return first - second;
}int operation(int first, int second, int(*functocall)(int, int))
{return (*functocall)(first, second);
}int test_function_pointers9()
{int a, b;int(*plus)(int, int) = add_;int(*minus)(int, int) = subtract_;a = operation(7, 5, plus);b = operation(20, a, minus);std::cout << "a = " << a << " and b = " << b << std::endl; // a = 12 and b = 8return 0;
}static double derivative(const std::function<double(double)> &f, double x0, double eps)
{double eps2 = eps / 2;double lo = x0 - eps2;double hi = x0 + eps2;return (f(hi) - f(lo)) / eps;
}static double f(double x)
{return x * x;
}int test_function_pointers10()
{double x = 1;std::cout << "d/dx(x ^ 2) [@ x = " << x << "] = " << derivative(f, x, 1e-5) << std::endl; // d/dx(x ^ 2) [@ x = 1] = 2return 0;
}class Foo {public:int add(int i, int j){return i + j;}int mult(int i, int j){return i*j;}static int negate(int i){return -i;}
};int bar1(int i, int j, Foo* pFoo, int(Foo::*pfn)(int, int))
{return (pFoo->*pfn)(i, j);
}typedef int(Foo::*Foo_pfn)(int, int);int bar2(int i, int j, Foo* pFoo, Foo_pfn pfn)
{return (pFoo->*pfn)(i, j);
}typedef int(*PFN)(int);int bar3(int i, PFN pfn)
{return pfn(i);
}int test_function_pointers11()
{Foo foo;std::cout << "Foo::add(2,4) = " << bar1(2, 4, &foo, &Foo::add) << std::endl; // Foo::add(2,3) = 6std::cout << "Foo::mult(3,5) = " << bar2(3, 5, &foo, &Foo::mult) << std::endl; // Foo::mult(3,5) = 15std::cout << "Foo::negate(6) = " << bar3(6, &Foo::negate) << std::endl; // Foo::negate(6) = -6return 0;
}void one(int a, int b) { std::cout << a + b << "\n"; }
void two(int a, int b) { std::cout << a*b << "\n"; }// reference: http://www.dev-hq.net/c++/20--function-pointers
int test_function_pointers12()
{//void(*fptr)(int, int); // Declare a function pointer to voids with two int params//fptr = one; // fptr -> one//fptr(12, 3); // => one(12, 3)//fptr = two; // fptr -> two//fptr(5, 4); // => two(5, 3)void(*fptr[2])(int, int);fptr[0] = one;fptr[1] = two;fptr[0](12, 3); // one(12, 3) // 15fptr[1](5, 4); // two(5, 3) // 20return 0;
}class Number
{
public:int i;Number() { i = 0; }int one() { return i + 1; }int two() { return i + 2; }
};int test_function_pointers13()
{Number object; // Create a new 'Number' object named 'object'// Declare a pointer array with two elements which are pointers to member functions in "Number" of type 'int' with takes no paramsint (Number::*NumberPtr[2])();NumberPtr[0] = &Number::one;NumberPtr[1] = &Number::two;std::cout << (object.*NumberPtr[0])() << std::endl; // 1std::cout << (object.*NumberPtr[1])() << std::endl; // 2return 0;
}class Employee
{
public:Employee(){wageCalc = &Employee::CalculateWage; // wageCalc -> CalculateWage}void UpgradeToExperienced(){wageCalc = &Employee::CalculateExperiencedWage; // wageCalc -> CalculateExperiencedWage}double Pay(double hours){return (this->*wageCalc)(hours); // => object.*wageCalc(hours)}private:double (Employee::*wageCalc)(double hours); // The member function ptrdouble CalculateWage(double hours){return 10 * hours;}double CalculateExperiencedWage(double hours){return 20 * hours;}
};int test_function_pointers14()
{Employee one;std::cout << one.Pay(10) << std::endl; // 100one.UpgradeToExperienced();std::cout << one.Pay(10) << std::endl; // 200return 0;
}void add_1(int a, int b)
{printf("Addition is %d\n", a + b);
}
void subtract_1(int a, int b)
{printf("Subtraction is %d\n", a - b);
}
void multiply_1(int a, int b)
{printf("Multiplication is %d\n", a*b);
}// reference: http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/function-pointer-in-c/
int test_function_pointers15()
{// fun_ptr_arr is an array of function pointersvoid(*fun_ptr_arr[])(int, int) = { add_1, subtract_1, multiply_1 };unsigned int ch, a = 15, b = 10;printf("Enter Choice: 0 for add, 1 for subtract and 2 for multiply\n");scanf("%d", &ch); // 1if (ch > 2) return 0;(*fun_ptr_arr[ch])(a, b); // Subtraction is 5return 0;
}class Foo_{
public:int f(std::string str){std::cout << "Foo_::f()" << std::endl;return 1;}
};// reference: http://www.codeguru.com/cpp/cpp/article.php/c17401/C-Tutorial-PointertoMember-Function.htm
int test_function_pointers16()
{int (Foo_::*fptr) (std::string) = &Foo_::f;Foo_ obj;(obj.*fptr)("str");//call: Foo::f() through an object // Foo_::f()Foo_* p = &obj;(p->*fptr)("str");//call: Foo::f() through a pointer // Foo_::f()return 0;
}class Foo_1{
public:// A "static" member function has no "this" pointerstatic int f(std::string str){std::cout << "Foo::f()" << std::endl;return 1;}
};int test_function_pointers17()
{//int (Foo_1::*fptr) (string) = &Foo_1::f; // error int(*fptr) (std::string) = &Foo_1::f; // correct(*fptr)("str"); // call Foo_1::f() // Foo::f()return 0;
}class Foo_2{
public:int f(char* c = 0){std::cout << "Foo_2::f()" << std::endl;return 1;}
};class Bar{
public:void b(int i = 0){std::cout << "Bar::b()" << std::endl;}
};class FooDerived :public Foo_2{
public:int f(char* c = 0){std::cout << "FooDerived::f()" << std::endl;return 1;}
};int test_function_pointers18()
{typedef int (Foo_2::*FPTR) (char*);typedef void (Bar::*BPTR) (int);typedef int (FooDerived::*FDPTR) (char*);FPTR fptr = &Foo_2::f;BPTR bptr = &Bar::b;FDPTR fdptr = &FooDerived::f;// Bptr = static_cast<void (Bar::*) (int)> (fptr); // errorfdptr = static_cast<int (Foo_2::*) (char*)> (fptr); // OK: contravarianceBar obj;(obj.*(BPTR)fptr)(1); // call: Foo_2::f() // Foo_2::f()return 0;
}class Foo_3{
public:virtual int f(char* c = 0){std::cout << "Foo_3::f()" << std::endl;return 1;}
};class Bar_3{
public:virtual void b(int i = 0){std::cout << "Bar_3::b()" << std::endl;}
};class FooDerived_3 :public Foo_3{
public:int f(char* c = 0){std::cout << "FooDerived_3::f()" << std::endl;return 1;}
};int test_function_pointers19()
{typedef int (Foo_3::*FPTR) (char*);typedef void (Bar_3::*BPTR) (int);FPTR fptr = &Foo_3::f;BPTR bptr = &Bar_3::b;FooDerived_3 objDer;(objDer.*fptr)(0); // call: FooDerived::f(), not Foo::f() // FooDerived::f()Bar_3 obj;(obj.*(BPTR)fptr)(1); // call: Bar::b() , not Foo::f() // Bar_3::b()return 0;
}class Printer{ // An abstract printing machine
public:void Copy(char * buff, const char * source){ // copy the filestrcpy(buff, source);}void Append(char * buff, const char * source){ // extend the filestrcat(buff, source);}
};enum OPTIONS { COPY, APPEND }; // two possible commands in the menu.
typedef void(Printer::*PTR) (char*, const char*); // pointer-to-member function void working(OPTIONS option, Printer* machine, char* buff, const char* infostr)
{PTR pmf[2] = { &Printer::Copy, &Printer::Append }; // pointer array switch (option){case COPY:(machine->*pmf[COPY])(buff, infostr);break;case APPEND:(machine->*pmf[APPEND])(buff, infostr);break;}
}int test_function_pointers20()
{OPTIONS option;Printer machine;char buff[40]; // targetworking(COPY, &machine, buff, "Strings ");working(APPEND, &machine, buff, "are concatenated! ");std::cout << buff << std::endl; // Strings are concatenated!return 0;
}// reference: http://www.radmangames.com/programming/how-to-use-function-pointers-in-cplusplus
// 1. Declaring function pointer variables
// (1). Non member functions
// return_type (*varName)() = namespace::function; // no parameters
// return_type(*varName)(paramType1, paramTypeN) = namespace::function;
// (2). Member functions
// return_type (Class::*varName)(paramType1, paramTypeN) = &Class::method;
// (3). Typedefs for function pointer types
// typedef return_type (*TypeName)(paramType1, paramTypeN);
// typedef return_type(ExampleClass::*TypeName)(paramType1, paramTypeN);
// static_cast<void(Class::*)()>(&Class::method)
// 2. Using function pointer variables
// (1). Calling a non-member function pointer
/*
void (*funcPtr)(paramType1, paramTypeN) = namespace::function;
funcPtr(parameter1, parameterN);
*/
// (2). Calling a member function pointer
/*
void (Class::*memberFuncPtr)() = &Class::method;Class* ptrInstance = new Class();
(ptrInstance->*memberFuncPtr)();Class refInstance;
(refInstance.*memberFuncPtr)();
*/namespace
{int simple() { return 0; }float test1(int first, float second, char third) { return 0.0; }float test2(int first, float second, char third) { return 0.0; }template <typename T_Example>void templateExample(T_Example param) {}class Class{public: // interface void method(int var) {}void overload(int var) {}void overload(int first, float second) {}}; // class template <typename T_Example>class TemplateClass{public: // interface void templateDo(T_Example templateParam, int extraParam) {}}; // class } // namespace int test_function_pointers21()
{// non-member examples int(*simpleNonMember)() = simple;simpleNonMember();typedef float(*TestTypeFuncPtr)(int, float, char);TestTypeFuncPtr test1FuncPtr = test1;TestTypeFuncPtr test2FuncPtr = test2;test1(7, 12.5, 'c'); // directly test1FuncPtr(7, 12.5, 'c'); // through the function pointer test2FuncPtr(11, 857.2, 'r');// non-member template examples void(*templateExampleFuncPtr1)(int) = templateExample<int>;void(*templateExampleFuncPtr2)(float) = templateExample<float>;templateExampleFuncPtr1(7);templateExampleFuncPtr2(7.f);// member examples Class* classPtr = new Class();Class classRef;void (Class::*overload2FuncPtr)(int, float) = &Class::overload;(classRef.*overload2FuncPtr)(0, 2.f);typedef void (Class::*ClassIntParamTypeFuncPtr)(int);ClassIntParamTypeFuncPtr overload1AndMethodFuncPtr = nullptr;overload1AndMethodFuncPtr = &Class::method;overload1AndMethodFuncPtr = &Class::overload;(classPtr->*overload1AndMethodFuncPtr)(7);(classRef.*overload1AndMethodFuncPtr)(7);// template class member examples TemplateClass<float>* templateClassPtr = new TemplateClass<float>();typedef void (TemplateClass<float>::*TemplateDoTypeFloat)(float, int);TemplateDoTypeFloat templateDoFuncPtr = &TemplateClass<float>::templateDo;(templateClassPtr->*templateDoFuncPtr)(11.f, 5);return 0;
}相关文章:

只做好CTR预估远不够,淘宝融合CTR、GMV、收入等多目标有绝招
作者 | 吴海波转载自知乎用户吴海波【导读】一直以来,电商场景就存在 ctr、cvr、gmv、成交 uv 等多个目标,都是核心指标。理想情况下,提升 ctr 就能提升 gmv,但本文作者认为,在一定程度上, ctr 和 gmv 并不…

Android监听HOME按键
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> <!-- lang: java --> class HomeKeyEventBroadCastReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {static final String SYSTEM_REASON "reason";static final String SYSTEM_HOME_KEY "homekey";// …

OpenCV代码提取:merge/split函数的实现
对OpenCV中的merge/split函数进行了实现,经测试,与OpenCV3.1结果完全一致。merge实现代码merge.hpp:// fbc_cv is free software and uses the same licence as OpenCV // Email: fengbingchun163.com#ifndef FBC_CV_MERGE_HPP_ #define FBC_…

DeepMind提图像生成的递归神经网络DRAW,158行Python代码复现
作者 | Samuel Noriega译者 | Freesia编辑 | 夕颜出品 | AI科技大本营(ID: rgznai100)【导读】最近,谷歌 DeepMInd 发表论文( DRAW: A Recurrent Neural Network For Image Generation),提出了一个用于图像生成的递归神…

其他进制的数字
JS中如果需要表示16进制的数字,则需要以0X开头 0X10 八进制数字以0开头 070 070有些浏览器会以8进制解析,但是有些则用10进制解析,10进制为70,8进制为56 所以parseint() 第二个参数可以设定进制,比如 parseint(“070”,10)代表以10进制解析070 2进制以0b开头,但是不是所有浏览…

java中的移位运算符
移位运算符是在数字的二进制形式上进行平移。主要有左移(<<)、带符号右移(>>)以及无符号右移(>>>)。左移运算符(<<)的运算规则为:按二进制形…

C++11中nullptr的使用
在C语言中,NULL实际上是一个void* 的指针,然后把void* 指针赋值给其它类型的指针的时候,会隐式转换成相应的类型。而如果用一个C编译器来编译的时候是要出错的,因为C是强类型的,void* 是不能隐式转换成其它指针类型的。…

埃森哲、亚马逊和万事达卡抱团推出的区块链项目有何神通?
据外媒报道,今日埃森哲宣布了一项新的区块链项目,该项目为基于区块链的循环供应链,将与万事达卡和亚马逊共同合作。据官方介绍,这个基于区块链的循环供应链能够让客户识别供应链上的小规模供应商和种植者,例如…

小团队如何玩转物联网开发?
近几年来,物联网发展迅速:据中商产业研究院《2016——2021年中国物联网产业市场研究报告》显示,预计到2020年,中国物联网的整体规模将达2.2万亿元,产业规模比互联网大30倍。与之相反的是,物联网开发者在开发…

Build Boost C++ libraries for x32/x64 VC++ compilers on Windows
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> Boost is a set of libraries for the C programming language that provide support for tasks and structures such as linear algebra, pseudorandom number generation, multithreading, image processing, regular …

C++11中auto的使用
在C语言中,就有了auto关键字,它被当作是一个变量的存储类型修饰符,表示自动变量(局部变量)。它不能被单独使用,否则编译器会给出警告。在C11标准中,添加了新的类型推导特性。在C 11中,使用auto定义的变量不…

攻和防谁更厉害?AI技术在恶意软件检测中的应用和对抗
AI技术的发展为网络安全带来新机遇的同时,黑客也在逐渐利用AI漏洞建立对抗样本以躲避攻击,双方在各自领域的更多尝试也将是AI技术发展的一场新博弈。那么,在应用中,如何利用AI检测技术与恶意软件展开对抗? 腾讯安全技术…

一文看懂机器学习中的常用损失函数
作者丨stephenDC编辑丨zandy来源 | 大数据与人工智能(ID: ai-big-data)导语:损失函数虽然简单,却相当基础,可以看做是机器学习的一个组件。机器学习的其他组件,还包括激活函数、优化器、模型等。本文针对机…

Using Apache2 with JBoss AS7 on Ubuntu
大体思路同《Using Apache Web Server with Jboss AS 7》一致,但在Ubuntu上的操作与之前有些区别。 这里仍然演示mod_proxy的配置。 首先加载相应的模块。Ubuntu中加载模块和卸载模块均可以通过命令操作,与其对应的命令分别是a2enmod和a2dismod。 启用…

OpenCV代码提取:rotate函数的实现
OpenCV中并没有直接提供实现rotate的函数,这里通过getRotationMatrix2D和warpAffine函数实现rotate,并增加了一个crop参数,用来判断是否进行crop。目前支持uchar和float两种类型,经测试,与OpenCV3.1结果完全一致。公式…

在 Node.js 中用子进程操作标准输入/输出
翻译:疯狂的技术宅原文:http://2ality.com/2018/05/chi... 本文首发微信公众号:jingchengyideng欢迎关注,每天都给你推送新鲜的前端技术文章 在本中,我们在 Node.js 中把 shell 命令作为子进程运行。然后异步读取这些进…

再见,Python 2.x
整理 | 屠敏来源 | CSDN(ID:CSDNnews)在技术的长河中,软件、工具、系统等版本的迭代本是常事,但由于使用习惯、版本的兼容性、易用性等因素,很多用户及开发者在使用或做开发的过程中,并不愿意及…

Android UI系列-----CheckBox和RadioButton(1)
主要记录一下CheckBox多选框和RadioGroup、RadioButton单选框的设置以及注册监听器 1.CheckBox 布局文件: <LinearLayout xmlns:android"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:tools"http://schemas.android.com/tools"android…

C++中struct的使用
C语言继承了C语言的struct,并且加以扩充。在C语言中struct是只能定义数据成员,而不能定义成员函数的。而在C中,struct类似于class,在其中既可以定义数据成员,又可以定义成员函数。结构类型是用户定义的复合类型&#x…

填报表中也可以添加 html 事件
在实际的项目开发中,填报表的应用十分广泛。 多数情况下,填报表会作为整个项目的一部分配合需求灵活使用,但有时也会受大项目环境的影响,产生一些特别的要求。比如,通常报表单元格的数据类型大多是文本,有时…

60+业内技术专家,9大核心技术专题,AI ProCon倒计时一周!
2018 年,由 CSDN 举办的第一届 AI 开发者大会喊出“只讲技术,拒绝空谈”,两天会议时间,国内外几十家顶尖科技企业讲述了其主流技术及其应用案例,真正引领国内开发者紧跟技术浪潮。一年过去,在你还未有所觉察…

密码学研究-数字签名
引入:提到签名,大家都不陌生,大家知道,重大的文件一般都要领导签名,来确保这个文件的真实有效。而一些比较重要的合同,比如买房的购房合同,都要盖“骑缝章”,这个骑缝章,…
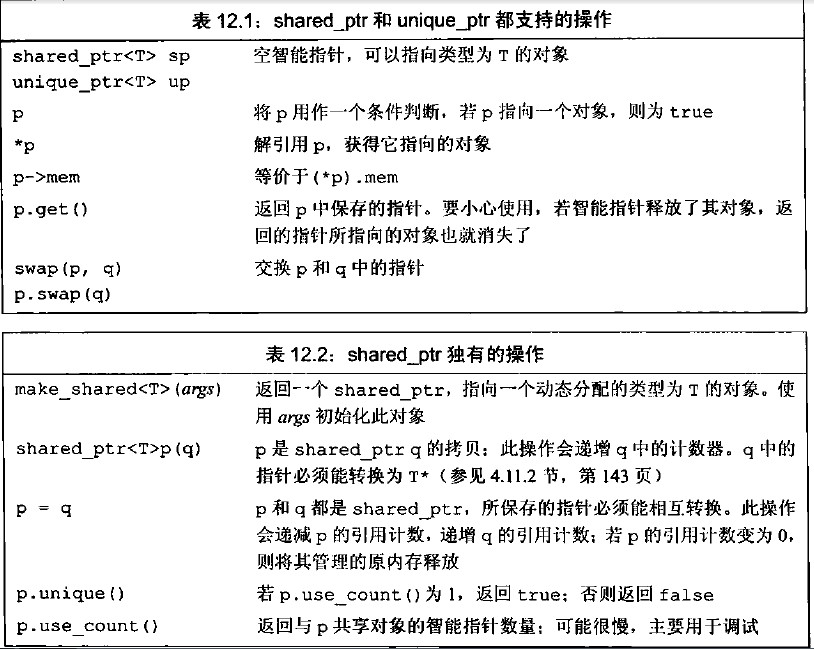
C++11中shared_ptr的使用
在C中,动态内存的管理是通过一对运算符来完成的:new,在动态内存中为对象分配空间并返回一个指向该对象的指针,可以选择对对象进行初始化;delete,接受一个动态对象的指针,销毁该对象,…

colly源码学习
colly源码学习 colly是一个golang写的网络爬虫。它使用起来非常顺手。看了一下它的源码,质量也是非常好的。本文就阅读一下它的源码。 使用示例 func main() {c : colly.NewCollector()// Find and visit all linksc.OnHTML("a[href]", func(e *colly.HTM…

可惜了,你们只看到“双马会”大型尬聊
作者 | 夕颜出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)导读:2019 年 8 月 29 日,世界人工智能大会(WAIC)在上海正式拉开帷幕。开幕式上,最让人瞩目的莫过于阿里巴巴前 CEO 马云与特斯拉 CEO Elon Musk …

Java 过滤特殊字符的 正则表达式
Java正则表达式学习: 因为正则表达式是一个很庞杂的体系,此例仅举些入门的概念,更多的请参阅相关书籍及自行摸索。 \\ 反斜杠 \t 间隔 (\u0009) \n 换行 (\u000A) \r 回车 (\u000D) \d 数字 等价于[0-9] \D 非数字 等价于[^0-9] \s 空…
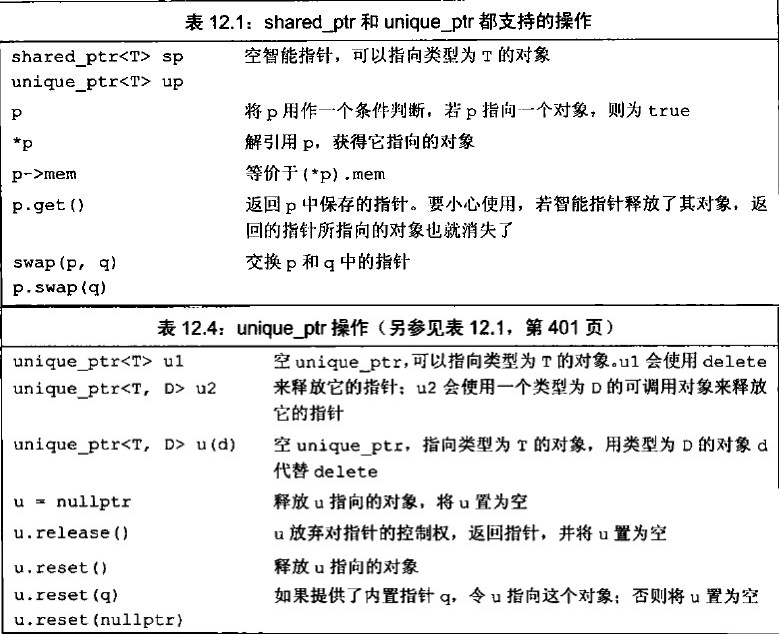
C++11中unique_ptr的使用
在C中,动态内存的管理是通过一对运算符来完成的:new,在动态内存中为对象分配空间并返回一个指向该对象的指针,可以选择对对象进行初始化;delete,接受一个动态对象的指针,销毁该对象,…

从这篇YouTube论文,剖析强化学习在工业级场景推荐系统中的应用
作者 | 吴海波转载自知乎用户吴海波【导读】本文作者根据两篇工业界背景的论文解答了 RL 在推荐场景需要解决的问题与困难,以及入门需要学习得相关知识点。2 个月前,业界开始流传 youtube 成功将 RL 应用在了推荐场景,并且演讲者在视频中说是…

java中两个Integer类型的值相比较的问题
转载自: https://www.cnblogs.com/xh0102/p/5280032.html 两个Integer类型整数进行比较时,一定要先用intValue()方法将其转换为int数之后再进行比较,因为直接使用比较两个Integer会出现问题。 总结: 当给Integer直接赋值时&#x…

C#共享内存实例 附源码
原文 C#共享内存实例 附源码 网上有C#共享内存类,不过功能太简单了,并且写内存每次都从开头写。故对此进行了改进,并做了个小例子,供需要的人参考。 主要改进点: 通过利用共享内存的一部分空间(以下称为“数据信息区”…
