C++11中shared_ptr的使用
在C++中,动态内存的管理是通过一对运算符来完成的:new,在动态内存中为对象分配空间并返回一个指向该对象的指针,可以选择对对象进行初始化;delete,接受一个动态对象的指针,销毁该对象,并释放与之关联的内存。
动态内存的使用很容易出问题,因为确保在正确的时间释放内存是极其困难的。有时会忘记释放内存,在这种情况下会产生内存泄露;有时在尚有指针引用内存的情况下就释放了它,在这种情况下就会产生引用非法内存的指针。
为了更容易(同时也更安全)地使用动态内存,C++11标准库提供了两种智能指针(smart pointer)类型来管理动态对象。智能指针的行为类似常规指针,重要的区别是它负责自动释放所指的对象。C++11标准库提供的这两种智能指针的区别在于管理底层指针的方式:shared_ptr允许多个指针指向同一个对象;unique_ptr则"独占"所指向的对象。C++11标准库还定义了一个名为weak_ptr的辅助类,它是一种弱引用,指向shared_ptr所管理的对象。这三种类型都定义在memory头文件中。智能指针是模板类而不是指针。类似vector,智能指针也是模板,当创建一个智能指针时,必须提供额外的信息即指针可以指向的类型。默认初始化的智能指针中保存着一个空指针。智能指针的使用方式与普通指针类似。解引用一个智能指针返回它指向的对象。如果在一个条件判断中使用智能指针,效果就是检测它是否为空。
std::shared_ptris a smart pointer that retains shared ownership of an object through a pointer. Several shared_ptr objects may own the same object. The object is destroyed and its memory deallocated when either of the following happens: (1)、the last remaining shared_ptr owning the object is destroyed; (2)、the last remaining shared_ptr owning the object is assigned another pointer via operator= or reset().
A shared_ptr can share ownership of an object while storing a pointer to another object. This feature can be used to point to member objects while owning the object they belong to. The stored pointer is the one accessed by get(), the dereference and the comparison operators. The managed pointer is the one passed to the deleter when use count reaches zero.
A shared_ptr may also own no objects, in which case it is called empty (an empty shared_ptr may have a non-null stored pointer if the aliasing constructor was used to create it).
All member functions (including copy constructor and copy assignment) can be called by multiple threads on different instances of shared_ptr without additional synchronization even if these instances are copies and share ownership of the same object. If multiple threads of execution access the same shared_ptr without synchronization and any of those accesses uses a non-const member function of shared_ptr then a data race will occur; the shared_ptr overloads of atomic functions can be used to prevent the data race.
The ownership of an object can only be shared with another shared_ptr by copy constructing or copy assigning its value to another shared_ptr. Constructing a new shared_ptr using the raw underlying pointer owned by another shared_ptr leads to undefined behavior.
The shared_ptr type is a smart pointer in the C++ standard library that is designed for scenarios in which more than one owner might have to manage the lifetime of the object in memory. After you initialize a shared_ptr you can copy it, pass it by value in function arguments, and assign it to other shared_ptr instances. All the instances point to the same object, and share access to one "control block" that increments and decrements the reference count whenever a new shared_ptr is added, goes out of scope, or is reset. When the reference count reaches zero, the control block deletes the memory resource and itself.
Whenever possible, use the make_shared (<memory>) function to create a shared_ptr when the memory resource is created for the first time. make_shared is exception-safe. It uses the same call to allocate the memory for the control block and the resource, and thereby reduces the construction overhead. If you do not use make_shared, then you have to use an explicit new expression to create the object before you pass it to the shared_ptr constructor.
In order to hide the operator new and to provide an optimization while allocating the object to be shared, the variadic template function make_shared was created. It is a template function that performs three tasks:
(1)、Allocates contiguous memory for the object and for the reference counter. This makes the creation and destruction of objects faster because only one allocation and deallocation will be needed when creating the object to be shared and its reference counter.
(2)、Invokes to the constructor of the class being instantiated forwarding the arguments used when this function was invoked.
(3)、Returns a shared_ptr to the newly created object.
make_shared<T>is a variadic template function that receives as arguments, the arguments that the constructor of class T needs.
智能指针实质就是重载了->和*操作符的类,由类来实现对内存的管理,确保即使有异常产生,也可以通过智能指针类的析构函数完成内存的释放。
shared_ptr的类型转换不能使用一般的static_cast,这种方式进行的转换会导致转换后的指针无法再被shared_ptr对象正确的管理。应该使用专门用于shared_ptr类型转换的 static_pointer_cast<T>() , const_pointer_cast<T>() 和dynamic_pointer_cast<T>()。
使用shared_ptr避免了手动使用delete来释放由new申请的资源,标准库也引入了make_shared函数来创建一个shared_ptr对象,使用shared_ptr和make_shared,你的代码里就可以使new和delete消失,同时又不必担心内存的泄露。shared_ptr是一个模板类。
C++开发处理内存泄漏最有效的办法就是使用智能指针,使用智能指针就不会担心内存泄露的问题了,因为智能指针可以自动删除分配的内存。
智能指针是指向动态分配(堆)对象指针,用于生存期控制,能够确保自动正确的销毁动态分配的对象,防止内存泄露。它的一种通用实现技术是使用引用计数。每次使用它,内部的引用计数加1,每次析构一次,内部引用计数减1,减为0时,删除所指向的堆内存。
每一个shared_ptr的拷贝都指向相同的内存。在最后一个shared_ptr析构的时候, 内存才会被释放。
可以通过构造函数、赋值函数或者make_shared函数初始化智能指针。
shared_ptr基于”引用计数”模型实现,多个shared_ptr可指向同一个动态对象,并维护一个共享的引用计数器,记录了引用同一对象的shared_ptr实例的数量。当最后一个指向动态对象的shared_ptr销毁时,会自动销毁其所指对象(通过delete操作符)。
shared_ptr的默认能力是管理动态内存,但支持自定义的Deleter以实现个性化的资源释放动作。
最安全的分配和使用动态内存的方法是调用一个名为make_shared的标准库函数。此函数在动态内存中分配一个对象并初始化它,返回指向此对象的shared_ptr。当要用make_shared时,必须指定想要创建的对象的类型,定义方式与模板类相同。在函数名之后跟一个尖括号,在其中给出类型。例如,调用make_shared<string>时传递的参数必须与string的某个构造函数相匹配。如果不传递任何参数,对象就会进行值初始化。
通常用auto定义一个对象来保存make_shared的结果。
当进行拷贝或赋值操作时,每个shared_ptr都会记录有多少个其它shared_ptr指向相同的对象。
可以认为每个shared_ptr都有一个关联的计数器,通常称其为引用计数(reference count)。无论何时拷贝一个shared_ptr,计数器都会递增。例如,当用一个shared_ptr初始化另一个shared_ptr,或将它作为参数传递给一个函数以及作为函数的返回值时,它所关联的计数器就会递增。当给shared_ptr赋予一个新值或是shared_ptr被销毁(例如一个局部的shared_ptr离开其作用域)时,计数器就会递减。一旦一个shared_ptr的计数器变为0,它就会自动释放自己所管理的对象。
当指向一个对象的最后一个shared_ptr被销毁时,shared_ptr类会自动销毁此对象。它是通过另一个特殊的成员函数析构函数(destructor)来完成销毁工作的。类似于构造函数,每个类都有一个析构函数。就像构造函数控制初始化一样,析构函数控制此类型的对象销毁时做什么操作。shared_ptr的析构函数会递减它所指向的对象的引用计数。如果引用计数变为0,shared_ptr的析构函数就会销毁对象,并释放它占用的内存。
如果将shared_ptr存放于一个容器中,而后不再需要全部元素,而只使用其中一部分,要记得用erase删除不再需要的那些元素。
使用shared_ptr注意事项:
(1)、不要把一个原生指针给多个shared_ptr管理;
(2)、不要把this指针给shared_ptr;
(3)、不要在函数实参里创建shared_ptr;
(4)、不要不加思考地把指针替换为shared_ptr来防止内存泄漏,shared_ptr并不是万能的,而且使用它们的话也是需要一定的开销的;
(5)、环状的链式结构shared_ptr将会导致内存泄漏(可以结合weak_ptr来解决);
(6)、共享拥有权的对象一般比限定作用域的对象生存更久,从而将导致更高的平均资源使用时间;
(7)、在多线程环境中使用共享指针的代价非常大,这是因为你需要避免关于引用计数的数据竞争;
(8)、共享对象的析构器不会在预期的时间执行;
(9)、不使用相同的内置指针值初始化(或reset)多个智能指针;
(10)、不delete get()返回的指针;
(11)、不使用get()初始化或reset另一个智能指针;
(12)、如果使用get()返回的指针,记住当最后一个对应的智能指针销毁后,你的指针就变为无效了;
(13)、如果你使用智能指针管理的资源不是new分配的内存,记住传递给它一个删除器。
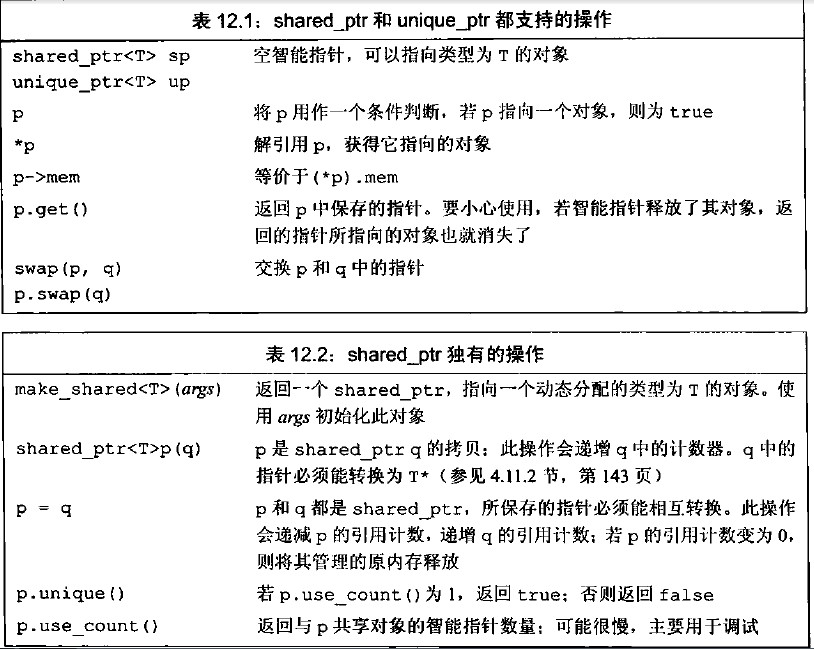
下图列出了shared_ptr支持的操作(来源于C++ Primer Fifth Edition 中文版):
下面是从其他文章中copy的测试代码,详细内容介绍可以参考对应的reference:
#include "shared_ptr.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <memory> // shared_ptr
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <mutex>
#include <algorithm>//
// reference: http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/memory/shared_ptr
struct Base
{Base() { std::cout << " Base::Base()\n"; }// Note: non-virtual destructor is OK here~Base() { std::cout << " Base::~Base()\n"; }
};struct Derived : public Base
{Derived() { std::cout << " Derived::Derived()\n"; }~Derived() { std::cout << " Derived::~Derived()\n"; }
};void thr(std::shared_ptr<Base> p)
{std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));std::shared_ptr<Base> lp = p; // thread-safe, even though the shared use_count is incremented{static std::mutex io_mutex;std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(io_mutex);std::cout << "local pointer in a thread:\n"<< " lp.get() = " << lp.get()<< ", lp.use_count() = " << lp.use_count() << '\n';}
}int test_shared_ptr1()
{std::shared_ptr<Base> p = std::make_shared<Derived>();std::cout << "Created a shared Derived (as a pointer to Base)\n"<< " p.get() = " << p.get()<< ", p.use_count() = " << p.use_count() << '\n';std::thread t1(thr, p), t2(thr, p), t3(thr, p);p.reset(); // release ownership from mainstd::cout << "Shared ownership between 3 threads and released\n"<< "ownership from main:\n"<< " p.get() = " << p.get()<< ", p.use_count() = " << p.use_count() << '\n';t1.join(); t2.join(); t3.join();std::cout << "All threads completed, the last one deleted Derived\n";return 0;
}///
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/memory/shared_ptr/shared_ptr/
int test_shared_ptr2()
{struct C { int* data; };// shared_ptr constructor examplestd::shared_ptr<int> p1;std::shared_ptr<int> p2(nullptr);std::shared_ptr<int> p3(new int);std::shared_ptr<int> p4(new int, std::default_delete<int>());std::shared_ptr<int> p5(new int, [](int* p){delete p; }, std::allocator<int>());std::shared_ptr<int> p6(p5);std::shared_ptr<int> p7(std::move(p6));std::shared_ptr<int> p8(std::unique_ptr<int>(new int));std::shared_ptr<C> obj(new C);std::shared_ptr<int> p9(obj, obj->data);std::cout << "use_count:\n";std::cout << "p1: " << p1.use_count() << '\n'; // 0std::cout << "p2: " << p2.use_count() << '\n'; // 0std::cout << "p3: " << p3.use_count() << '\n'; // 1std::cout << "p4: " << p4.use_count() << '\n'; // 1std::cout << "p5: " << p5.use_count() << '\n'; // 2std::cout << "p6: " << p6.use_count() << '\n'; // 0std::cout << "p7: " << p7.use_count() << '\n'; // 2std::cout << "p8: " << p8.use_count() << '\n'; // 1std::cout << "p9: " << p9.use_count() << '\n'; // 2return 0;
}//
// reference: https://oopscenities.net/2013/10/06/smart-pointers-part-4-shared_ptr/
class Integer
{int n;
public:Integer(int n) : n(n) { }~Integer() { printf("Deleting %d\n", n); }int get() const { return n; }
};int test_shared_ptr3()
{auto a = std::make_shared<Integer>(10);auto b = std::make_shared<Integer>(20);auto c = a;auto d = std::make_shared<Integer>(30);auto e = b;a = d;b = std::make_shared<Integer>(40);auto f = c;b = f;printf("%d\n", a->get());printf("%d\n", b->get());printf("%d\n", c->get());printf("%d\n", d->get());printf("%d\n", e->get());printf("%d\n", f->get());return 0;
}//
// reference: http://www.linux-magazin.de/Ausgaben/2013/04/C-11
struct MyInt{MyInt(int v) :val(v){std::cout << " Hello: " << val << std::endl;}~MyInt(){std::cout << " Good Bye: " << val << std::endl;}int val;
};int test_shared_ptr4()
{std::shared_ptr<MyInt> sharPtr(new MyInt(1998));std::cout << " My value: " << sharPtr->val << std::endl;std::cout << "sharedPtr.use_count(): " << sharPtr.use_count() << std::endl;{std::shared_ptr<MyInt> locSharPtr(sharPtr);std::cout << "locSharPtr.use_count(): " << locSharPtr.use_count() << std::endl;}std::cout << "sharPtr.use_count(): " << sharPtr.use_count() << std::endl;std::shared_ptr<MyInt> globSharPtr = sharPtr;std::cout << "sharPtr.use_count(): " << sharPtr.use_count() << std::endl;globSharPtr.reset();std::cout << "sharPtr.use_count(): " << sharPtr.use_count() << std::endl;sharPtr = std::shared_ptr<MyInt>(new MyInt(2011));return 0;
}// reference: http://www.linux-magazin.de/Ausgaben/2013/04/C-11
template <typename T>
struct Deleter{void operator()(T *ptr){++Deleter::count;delete ptr;}static int count;
};template <typename T>
int Deleter<T>::count = 0;typedef Deleter<int> IntDeleter;
typedef Deleter<double> DoubleDeleter;
typedef Deleter<MyInt> MyIntDeleter;int test_shared_ptr5()
{{std::shared_ptr<int> sharedPtr1(new int(1998), IntDeleter());std::shared_ptr<int> sharedPtr2(new int(2011), IntDeleter());std::shared_ptr<double> sharedPtr3(new double(3.17), DoubleDeleter());std::shared_ptr<MyInt> sharedPtr4(new MyInt(2017), MyIntDeleter());}std::cout << "Deleted " << IntDeleter().count << " int values." << std::endl;std::cout << "Deleted " << DoubleDeleter().count << " double value." << std::endl;std::cout << "Deleted " << MyIntDeleter().count << " MyInt value." << std::endl;return 0;
}// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/memory/shared_ptr/reset/
int test_shared_ptr_reset()
{std::shared_ptr<int> sp; // emptysp.reset(new int); // takes ownership of pointer*sp = 10;std::cout << *sp << '\n';sp.reset(new int); // deletes managed object, acquires new pointer*sp = 20;std::cout << *sp << '\n';sp.reset(); // deletes managed objectreturn 0;
}//
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/memory/shared_ptr/get/
int test_shared_ptr_get()
{int* p = new int(10);std::shared_ptr<int> a(p);if (a.get() == p)std::cout << "a and p point to the same location\n";// three ways of accessing the same address:std::cout << *a.get() << "\n";std::cout << *a << "\n";std::cout << *p << "\n";return 0;
}///
struct C { int a; int b; };int test_shared_ptr_operator()
{// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/memory/shared_ptr/operator%20bool/// std::shared_ptr::operator bool: The function returns the same as get()!=0.std::shared_ptr<int> foo;std::shared_ptr<int> bar(new int(34));if (foo) std::cout << "foo points to " << *foo << '\n';else std::cout << "foo is null\n";if (bar) std::cout << "bar points to " << *bar << '\n';else std::cout << "bar is null\n";// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/memory/shared_ptr/operator*/// std::shared_ptr::operator*: It is equivalent to: *get().std::shared_ptr<int> foo_2(new int);std::shared_ptr<int> bar_2(new int(100));*foo_2 = *bar_2 * 2;std::cout << "foo_2: " << *foo_2 << '\n';std::cout << "bar_2: " << *bar_2 << '\n';// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/memory/shared_ptr/operator-%3E/// std::shared_ptr::operator->: It returns the same value as get()std::shared_ptr<C> foo_3;std::shared_ptr<C> bar_3(new C);foo_3 = bar_3;foo_3->a = 10;bar_3->b = 20;if (foo_3) std::cout << "foo_3: " << foo_3->a << ' ' << foo_3->b << '\n';if (bar_3) std::cout << "bar_3: " << bar_3->a << ' ' << bar_3->b << '\n';// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/memory/shared_ptr/operator=/std::shared_ptr<int> foo_4;std::shared_ptr<int> bar_4(new int(10));foo_4 = bar_4; // copybar_4 = std::make_shared<int>(20); // movestd::unique_ptr<int> unique(new int(30));foo_4 = std::move(unique); // move from unique_ptrstd::cout << "*foo_4: " << *foo_4 << '\n';std::cout << "*bar_4: " << *bar_4 << '\n';return 0;
}//
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/memory/shared_ptr/owner_before/
int test_shared_ptr_owner_before()
{int * p = new int(10);std::shared_ptr<int> a(new int(20));std::shared_ptr<int> b(a, p); // alias constructor// owner_before: true if the object is considered to be different from x and// go before it in a strict weak order based on ownership. false otherwise.std::cout << "comparing a and b...\n" << std::boolalpha;std::cout << "value-based: " << (!(a<b) && !(b<a)) << '\n';std::cout << "owner-based: " << (!a.owner_before(b) && !b.owner_before(a)) << '\n';delete p;return 0;
}/
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/memory/shared_ptr/swap/
int test_shared_ptr_swap()
{std::shared_ptr<int> foo(new int(10));std::shared_ptr<int> bar(new int(20));foo.swap(bar);std::cout << "*foo: " << *foo << '\n';std::cout << "*bar: " << *bar << '\n';return 0;
}//
// reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/memory/shared_ptr/unique/
int test_shared_ptr_unique()
{// std::shared_ptr::unique: This function shall return the same as (use_count()==1),// although it may do so in a more efficient way.std::shared_ptr<int> foo;std::shared_ptr<int> bar(new int);std::cout << "foo unique?\n" << std::boolalpha;std::cout << "1: " << foo.unique() << '\n'; // false (empty)foo = bar;std::cout << "2: " << foo.unique() << '\n'; // false (shared with bar)bar = nullptr;std::cout << "3: " << foo.unique() << '\n'; // truereturn 0;
}/
int test_shared_ptr_reset_delete()
{// new int[], with shard_ptr'reset function deleteint* p1 = new int[10];
{std::for_each(p1, p1 + 10, [](int& v){v = 5; });std::shared_ptr<int> p2;// p2和p1指向同一个内存空间p2.reset(p1, [](int* p) {delete[] p; });for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {fprintf(stdout, "p1: %d \n", p1[i]);fprintf(stdout, "p2: %d \n", p2.get()[i]);}
}// 运行到大括号外,此时p1的空间已经被释放for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {fprintf(stdout, "p1: %d \n", p1[i]);}//delete[] p1; // p1已释放,不能再deleteint* pa = new int[10];
{std::for_each(pa, pa + 10, [](int& v){v = 8; });std::shared_ptr<int> pb;// pb和pa指向同一个内存空间pb.reset(pa, [](int*) { });for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {fprintf(stdout, "pa: %d \n", pa[i]);fprintf(stdout, "pb: %d \n", pb.get()[i]);}
}// 运行到大括号外,此时pa的空间没有被释放for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {fprintf(stdout, "pa: %d \n", pa[i]);}delete[] pa; // pa没有被释放,需要deletereturn 0;
}GitHub:https://github.com/fengbingchun/Messy_Test
相关文章:

colly源码学习
colly源码学习 colly是一个golang写的网络爬虫。它使用起来非常顺手。看了一下它的源码,质量也是非常好的。本文就阅读一下它的源码。 使用示例 func main() {c : colly.NewCollector()// Find and visit all linksc.OnHTML("a[href]", func(e *colly.HTM…

可惜了,你们只看到“双马会”大型尬聊
作者 | 夕颜出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)导读:2019 年 8 月 29 日,世界人工智能大会(WAIC)在上海正式拉开帷幕。开幕式上,最让人瞩目的莫过于阿里巴巴前 CEO 马云与特斯拉 CEO Elon Musk …

Java 过滤特殊字符的 正则表达式
Java正则表达式学习: 因为正则表达式是一个很庞杂的体系,此例仅举些入门的概念,更多的请参阅相关书籍及自行摸索。 \\ 反斜杠 \t 间隔 (\u0009) \n 换行 (\u000A) \r 回车 (\u000D) \d 数字 等价于[0-9] \D 非数字 等价于[^0-9] \s 空…
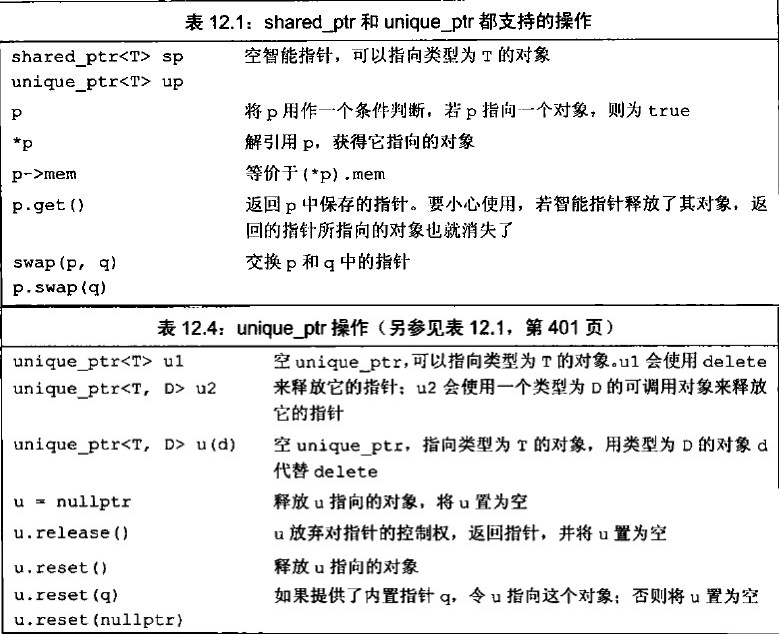
C++11中unique_ptr的使用
在C中,动态内存的管理是通过一对运算符来完成的:new,在动态内存中为对象分配空间并返回一个指向该对象的指针,可以选择对对象进行初始化;delete,接受一个动态对象的指针,销毁该对象,…

从这篇YouTube论文,剖析强化学习在工业级场景推荐系统中的应用
作者 | 吴海波转载自知乎用户吴海波【导读】本文作者根据两篇工业界背景的论文解答了 RL 在推荐场景需要解决的问题与困难,以及入门需要学习得相关知识点。2 个月前,业界开始流传 youtube 成功将 RL 应用在了推荐场景,并且演讲者在视频中说是…

java中两个Integer类型的值相比较的问题
转载自: https://www.cnblogs.com/xh0102/p/5280032.html 两个Integer类型整数进行比较时,一定要先用intValue()方法将其转换为int数之后再进行比较,因为直接使用比较两个Integer会出现问题。 总结: 当给Integer直接赋值时&#x…

C#共享内存实例 附源码
原文 C#共享内存实例 附源码 网上有C#共享内存类,不过功能太简单了,并且写内存每次都从开头写。故对此进行了改进,并做了个小例子,供需要的人参考。 主要改进点: 通过利用共享内存的一部分空间(以下称为“数据信息区”…

C++11中weak_ptr的使用
在C中,动态内存的管理是通过一对运算符来完成的:new,在动态内存中为对象分配空间并返回一个指向该对象的指针,可以选择对对象进行初始化;delete,接受一个动态对象的指针,销毁该对象,…

经典不过时,回顾DeepCompression神经网络压缩
作者 | 薰风初入弦转载自知乎导读:本文作者为我们详细讲述了 ICLR 2016 的最佳论文 Deep Compression 中介绍的神经网络压缩方法。神经网络压缩一直是一个重要的研究方向,而目前业界最认可的压缩方法莫过于 ICLR 2016 的最佳论文 Deep Compression&#…

区块链技术特点之去中心化特性
想知道更多关于区块链技术知识,请百度【链客区块链技术问答社区】 链客,有问必答!! 由于区块链技术去中心化的特性,其在我们生活中的很多重要领域(如金融、管理)等方面具有重要的意义。例如&…

Android APK反编译
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/ithomer/article/details/6727581 一、Apk反编译得到Java源代码 下载上述反编译工具包,打开apk2java目录下的dex2jar-0.0.9.9文件夹,内含apk反编译成java源码工具,以及源码查看工具。 apk反编译工具dex…

Java泛型进阶 - 如何取出泛型类型参数
在JDK5引入了泛型特性之后,她迅速地成为Java编程中不可或缺的元素。然而,就跟泛型乍一看似乎非常容易一样,许多开发者也非常容易就迷失在这项特性里。多数Java开发者都会注意到Java编译器的类型擦除实现方式,Type Erasure会导致关…

C++11中override的使用
override是C11中的一个继承控制关键字。override确保在派生类中声明的重载函数跟基类的虚函数有相同的声明。 override明确地表示一个函数是对基类中一个虚函数的重载。更重要的是,它会检查基类虚函数和派生类中重载函数的签名不匹配问题。如果签名不匹配ÿ…

平头哥发布一站式芯片设计平台“无剑”,芯片设计成本降低50%
导读:8 月 29 日,在上海举行的世界人工智能大会上,阿里巴巴旗下半导体公司平头哥发布 SoC 芯片平台“无剑”。无剑是面向 AIoT 时代的一站式芯片设计平台,提供集芯片架构、基础软件、算法与开发工具于一体的整体解决方案ÿ…

Windows XP下,JDK环境变量配置
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 1.安装JDK,安装过程中可以自定义安装目录等信息,例如我们选择安装目录为D:\java\jdk1.5.0_08; 2.安装完成后,右击“我的电脑”,点击“属性”; 3.选择…

Markdown语法简介
Markdown是一种方便记忆、书写的纯文本标记语言,用户可以使用这些标记符号以最小的输入代价生成极富表现力的文档。它目标是实现易读易写。Markdown的语法全由一些符号所组成。Markdown语法的目标是成为一种适用于网络的书写语言。 Markdown优点:纯文本…

吴恩达:AI未来将呈现四大发展趋势
作者 | 夕颜出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)导读:8 月 30 日,世界人工智能大会精彩继续。在今天的全球工业智能峰会上,Landing.AI 创始人及首席执行官吴恩达来到现场,做了题为《人工智能是新电力》的演讲…

嵌入式课程安排 嵌入式培训课程大纲参考
嵌入式是一门综合性的学科,现在学习嵌入式开发不是单纯局限于单片机或者Linux,嵌入式课程中包含着非常多的内容。以粤嵌嵌入式课程进行参考,看看我们要学习嵌入式的话,要掌握哪些必备的技能。嵌入式课程安排包含:1、入…

Linux网站架构系列之Apache----进阶篇
本篇博文为Linux网站架构系列之apache的第二篇,我将带大家一起学习apache的编译参数,目录结构和配置文件等方面的知识,实现对apache服务的进一步掌握,并使之能更好的应用到生产实战中去。一、编译参数在上篇的apache部署中&#x…

仅用10天设计的JavaScript,凭什么成为程序员最受欢迎的编程语言?
导语:在这个世纪之交诞生的 JavaScript,没人想到会发展为当今世界上最流行的语言之一。它不够成熟,不够严肃,甚至连名字都是模仿的 Java。那么,JavaScript 的成功是依靠运气和完美时机的侥幸吗?其实不然——…

C++11中= delete;的使用
C11中,对于deleted函数,编译器会对其禁用,从而避免某些非法的函数调用或者类型转换,从而提高代码的安全性。 对于 C 的类,如果程序员没有为其定义特殊成员函数,那么在需要用到某个特殊成员函数的时候&…
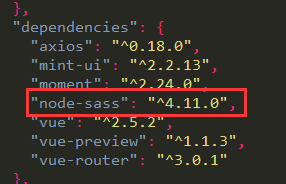
vue 使用scss
使用vue-cli模板创建的项目中,使用scss步骤 1. cmd命令: cnpm install sass-loader --save-devcnpm install node-sass --sava-dev2.查看package.json文件中是否已自动添加以下信息 3. 转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/duanzhenzhen/p/10453495.html

EBS form日历可选范围设置(calendar.setup )介绍
Calendar是Template提供给我们的standard object.可以使我们方便的为日期型字段提供日期的选择列表.form中设置日历方法:1. 为日期型字段指定LOV(ENABLE_LIST_LAMP)2. 在字段的KEY–LISTVAL事件中编写代码:Calendar.showCalendar Package包含如下几个Procedure:1. Calendar.sho…

人工智能对地球环境科学的推进
一项德国耶拿[1]和汉堡[2]科学家在《自然》杂志发起的研究表明,人工智能可以有效地推进我们对于地球气候系统的理解。特别是在当前深度学习的潜力还未被完全开发的情况下。在人工智能的帮助下一些复杂的动态环境,如飓风,森林火灾,…

从概念到应用,终于有人把数据挖掘讲明白了
作者:陈封能(Pang-Ning Tan)、迈克尔斯坦巴赫(Michael Steinbach)等来源 | 大数据(ID: hzdashuju)【导语】数据采集和存储技术的迅速发展,加之数据生成与传播的便捷性&am…

C++11中default的使用
在C11中,对于defaulted函数,编译器会为其自动生成默认的函数定义体,从而获得更高的代码执行效率,也可免除程序员手动定义该函数的工作量。 C的类有四类特殊成员函数,它们分别是:默认构造函数、析构函数、拷…

Android开发:setAlpha()方法和常用RGB颜色表----颜色, r g b分量数值(int), 16进制表示 一一对应...
杂家前文Android颜色对照表只有颜色和十六进制,有时候需要设置r g b分量的int值,如paint.setARGB(255, 127, 255, 212);就需要自己计算下分量的各个值。这里提供一个带有r g b分量的int型的颜色表。注意paint.setAlpha()及paint.setARGB(&…

【redis】c/c++操作redis(对于hiredis的封装)
前言 最近一直在学习redis,通过c/cpp来执行redis命令,使用的是hiredis客户端来实现的。 先简单贴一下代码 头文件 #include <vector> #include <string> #include <hiredis/hiredis.h> typedef enum en_redisResultType {redis_reply_…

OpenCV代码提取:transpose函数的实现
OpenCV中的transpose函数实现图像转置,公式为:目前fbc_cv库中也实现了transpose函数,支持多通道,uchar和float两种数据类型,经测试,与OpenCV3.1结果完全一致。实现代码transpose.hpp:// fbc_cv …

只给测试集不给训练集,要怎么做自己的物体检测器?
9 月5 日,下周四,大家期待已久的由《动手学深度学习》作者,亚马逊首席科学家亲自带领的「深度学习实训营」就要在北京开营了。今天,李沐已经把这次深度学习实训营白天的教学内容和代码上传到 Gituhub 和 D2L.ai 网站了,…