HttpClient学习
HttpClient学习
(1)下面列举几个主要的Http相关概念的类
| 类名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| HttpClient | 建立请求客户端 |
| HttpGet | 代表请求方法,类似的还有HttpHead, HttpPost, HttpPut, HttpDelete, HttpTrace, HttpOptions等 |
| HttpResponse | 表示请求的响应(包括响应状态、协议等头信息,Header封装各种头信息,头信息又包括HeaderElement,都可以采用迭代器的方式进行迭代读取) |
| HttpEntity | 表示相应的实体,用于存放传送的内容,也就是body体,存在于request和response中,request只有post和put方法有,response中都有Entity,除了一些特殊情况不包含内容。Entity根据来源分为三种:streamed,一次读取;wrapping,从其他entity封装;self-contained,从内存中读取,可反复读。 |
| URIBuilder | 工具类用来生成url,主要是设置协议、域名和路径,还有各种参数等 |
(2)HttpEntity的几个主要函数
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| getContentType | 获取内容类型 |
| getContentLength | 获取内容长度 |
| getContent | 获取内容的输入流InputStream |
- HttpEntity entity=response.getEntity();
- System.out.println(entity.getContentType());
- System.out.println(entity.getContentLength());
- InputStream in=entity.getContent();//直接获取输入流,一次读取
(3)HttpEntity直接获取的streamed流
- 只能读取一次,如果想读取多次,就要进行缓存,利用wrapping方式将streamed进行包装BufferedHttpEntity
- BufferedHttpEntity bufEntity=new BufferedHttpEntity(entity);//通过构造形式封装进缓存,可多次读取
(4)HttpEntity也可放在post和put方法的请求中
- 作为请求传递的内容。内容可以是文件,也可以提交form参数
- File file=new File("out.txt");
- FileEntity fileEntity=new FileEntity(file, ContentType.create("text/plain", "UTF-8"));//文件内容输入
- List<NameValuePair> formparams = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>();
- formparams.add(new BasicNameValuePair("param1", "value1"));
- formparams.add(new BasicNameValuePair("param2", "value2"));
- UrlEncodedFormEntity formEntity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(formparams, "UTF-8");//form表单内容输入
- HttpPost post=new HttpPost("http://www.baidu.com");
- post.setEntity(fileEntity);
(5)response处理类最方便的是ResponseHandler类,它的功能是将entity转化为不同的内容格式
- ResponseHandler<byte[]> handler = new ResponseHandler<byte[]>() {
- public byte[] handleResponse(
- HttpResponse response) throws ClientProtocolException, IOException {
- HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
- if (entity != null) {
- return EntityUtils.toByteArray(entity);
- } else {
- return null;
- }
- }
- };
- byte[] response = httpclient.execute(httpget, handler);
- ResponseHandler<String> handler1=new BasicResponseHandler();
- String response1= httpclient.execute(httpget,handler1);
(6)request请求时可以设置一些http参数httpparam
和httpcontext相似,httpclient可以设置客户端范围的,httprequest也可以设置,但是请求范围的。
| 参数名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| CoreProtocolPNames.PROTOCOL_VERSION='http.protocol.version' | 协议版本 |
| CoreProtocolPNames.HTTP_ELEMENT_CHARSET='http.protocol.element-charset' | 协议元素编码 |
| CoreProtocolPNames.HTTP_CONTENT_CHARSET='http.protocol.content-charset' | 协议内容编码 |
| CoreProtocolPNames.USER_AGENT='http.useragent' | 用户端,写爬虫的时候有用 |
| CoreProtocolPNames.STRICT_TRANSFER_ENCODING='http.protocol.strict-transfer-encoding' | (... |
| CoreProtocolPNames.USE_EXPECT_CONTINUE='http.protocol.expect-continue' | ... |
| CoreProtocolPNames.WAIT_FOR_CONTINUE='http.protocol.wait-for-continue' | ... |
- httpclient.getParams().setParameter(CoreProtocolPNames.PROTOCOL_VERSION,
- HttpVersion.HTTP_1_0); // Default to HTTP 1.0
- httpclient.getParams().setParameter(CoreProtocolPNames.HTTP_CONTENT_CHARSET,
- "UTF-8");
- HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet("http://www.google.com.hk/");
- httpget.getParams().setParameter(CoreProtocolPNames.PROTOCOL_VERSION,
- HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1); // Use HTTP 1.1 for this request only
- httpget.getParams().setParameter(CoreProtocolPNames.USE_EXPECT_CONTINUE,
- Boolean.FALSE);
(7)httpclient完成了对connection的控制
但是上面的方法都没有涉及连接的设置,这里提供一些参数可以进行设置通过HttpParam设置
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| CoreConnectionPNames.SO_TIMEOUT='http.socket.timeout' | 等待数据的最大时间,也就是两段连续数据读取之间的间隔 |
| CoreConnectionPNames.TCP_NODELAY='http.tcp.nodelay' | bool值,设置是否应用Naple算法,该算法最小化发送的包数,因此每个包很大,占带宽,有延迟 |
| CoreConnectionPNames.SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE='http.socket.buffer-size' | 设置接发数据的缓冲区大小 |
| CoreConnectionPNames.SO_LINGER='http.socket.linger' | ... |
| CoreConnectionPNames.CONNECTION_TIMEOUT='http.connection.timeout' | 设置连接超时 |
| CoreConnectionPNames.STALE_CONNECTION_CHECK='http.connection.stalecheck' | ... |
| CoreConnectionPNames.MAX_LINE_LENGTH='http.connection.max-line-length' | 设置每行最大长度 |
| CoreConnectionPNames.MAX_HEADER_COUNT='http.connection.max-header-count' | 设置头最大数量 |
| ConnConnectionPNames.MAX_STATUS_LINE_GARBAGE='http.connection.max-status-line-garbage' | ... |
(8)实际应用的中,从连接池里获取连接是比较好的方法,连接池负责管理连接。
- BasicClientConnectionManager man=new BasicClientConnectionManager();//最基本的连接池,一次只维护一个连接
- System.out.println(httpclient.getConnectionManager().getClass());//输出class org.apache.http.impl.conn.BasicClientConnectionManager
- //下面采用PoolingClientConnectionManager连接池管理,该连接池支持多线程操作
- if(httpConnManger==null)
- {
- SchemeRegistry schemeRegistry = new SchemeRegistry();
- schemeRegistry.register(
- new Scheme("http", 80, PlainSocketFactory.getSocketFactory()));
- httpConnManger=new PoolingClientConnectionManager(schemeRegistry);
- httpConnManger.setMaxTotal(10);
- httpConnManger.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(20);
- }
- HttpParams params=new BasicHttpParams();
- params.setParameter(CoreConnectionPNames.CONNECTION_TIMEOUT, CONNECTION_TIME);
- HttpClient httpClient=new DefaultHttpClient(httpConnManger,params);
- HttpGet httpGet=new HttpGet(urlAddr);
- HttpResponse response;
- try {
- response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
- } catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
- log.error(e.getMessage());
- return null;
- } catch (IOException e) {
- log.error(e.getMessage());
- return null;
- }
(9)需要代理的请求,设置HttpProxy
- HttpHost proxy = new HttpHost("127.0.0.1", 8080, "http");
- DefaultHttpClient httpclient = new DefaultHttpClient();
- httpclient.getParams().setParameter(ConnRoutePNames.DEFAULT_PROXY, proxy);
- HttpHost target = new HttpHost("issues.apache.org", 443, "https");
- HttpGet req = new HttpGet("/");
- System.out.println("executing request to " + target + " via " + proxy);
- HttpResponse rsp = httpclient.execute(target, req);
- HttpEntity entity = rsp.getEntity();
(10)需要登录验证的请求
- httpclient.getCredentialsProvider().setCredentials(
- new AuthScope("localhost", 443),
- new UsernamePasswordCredentials("username", "password"));
- HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet("https://localhost/protected");
- System.out.println("executing request" + httpget.getRequestLine());
- HttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(httpget);
- HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
- System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
- System.out.println(response.getStatusLine());
- if (entity != null) {
- System.out.println("Response content length: " + entity.getContentLength());
- }
- EntityUtils.consume(entity);
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/longlongchang/1170999
相关文章:
赠书 | 新手指南——如何通过HuggingFace Transformer整合表格数据
作者 | Ken Gu翻译| 火火酱~,责编 | 晋兆雨出品 | AI科技大本营头图 | 付费下载于视觉中国*文末有赠书福利不可否认,Transformer-based模型彻底改变了处理非结构化文本数据的游戏规则。截至2020年9月,在通用语言理解评估(General …

在HTML网页中巧用URL
http://www.cnbruce.com/blog/showlog.asp?cat_id5&log_id657 首先,先放出一个地址给大家测试http://cnbruce.com/test/htmlpro/?namecnbruce&emailcnbruce126.com 1,时下流行的(可能是吧,因为最近问的人比较多…

《iOS 8应用开发入门经典(第6版)》——第1章,第1.6节小结
本节书摘来自异步社区《iOS 8应用开发入门经典(第6版)》一书中的第1章,第1.6节小结,作者 【美】John Ray(约翰 雷),更多章节内容可以访问云栖社区“异步社区”公众号查看 1.6 小结iOS 8应用开发…

用Visual C#创建Windows服务程序
一.Windows服务介绍: Windows服务以前被称作NT服务,是一些运行在Windows NT、Windows 2000和Windows XP等操作系统下用户环境以外的程序。在以前,编写Windows 服务程序需要程序员很强的C或C功底。然而现在在Visual Studio.Net下&a…

poj 3321 Apple Tree
树状数组 题意:一个树,以树枝连接两个点的形式给出,固定以1为整棵树的根。苹果长在树的节点上,节点上只可能0或1个苹果,一开始每个节点都有1个苹果 有两种操作,C表示更改某个节点的苹果数,0变1,…
人工智能在网络贷款中鲜为人知的事
作者 | Laksh Mohan翻译| 火火酱~,责编 | 晋兆雨出品 | AI科技大本营头图 | 付费下载于视觉中国现在,科技已经成为推动企业发展壮大的基本要素之一。人工智能(AI)就是一个证明此类技术在商业领域走红的好例子,比如网络…

《HTML5与CSS3实战指南》——2.5 构建The HTML5 Herald
本节书摘来自异步社区《HTML5与CSS3实战指南》一书中的第2章,第2.5节,作者: 【美】Estelle Weyl , Louis Lazaris , Alexis Goldstein 更多章节内容可以访问云栖社区“异步社区”公众号查看。 2.5 构建The HTML5 Herald 我们已经介绍了页面结构的基础以及…

用.NET创建Windows服务
用.NET创建Windows服务 译者说明:我是通过翻译来学习C#的,文中涉及到的有Visual Studio.NET有关操作,我都根据中文版的VS.NET显示信息来处理的,可以让大家不致有误解。作者:Mark Strawmyer 我们将研究如何…

BGP local-preference MED属性实验
实验拓扑 实验配置 建立两个AS 65001、65000 AS65000内跑OSPF,并在R1上发布三个网段100.1.1.1 100.1.2.1 100.1.3.1 在R3 R5上聚合后发布给R4。 每台路由器都有一个对应的loopback地址。 实验过程 <R1>dis bgp ro Total Number of Routes: 10 BGP Local route…
加速产业生态算力升级,华为鲲鹏展翅福州
11月20日,为了让更多开发者了解鲲鹏计算生态体系,并且助力行业人才培养,由福建鲲鹏生态创新中心、福州市大数据基地开发有限责任公司联合举办的鲲鹏开发者训练营圆满完成。此次活动现场吸引到了大量的开发者参与,产、学、研各界人…
《CCNP TSHOOT 300-135认证考试指南》——2.2节故障检测与排除及网络维护工具箱
本节书摘来自异步社区《CCNP TSHOOT 300-135认证考试指南》一书中的第2章,第2.2节故障检测与排除及网络维护工具箱,作者 【加】Raymond Lacoste , 【美】Kevin Wallace,更多章节内容可以访问云栖社区“异步社区”公众号查看 2.2 故障检测与排…

在linux系统下实现音视频即时通讯的部分代码
由于使用习惯,Linux在中国受欢迎程度远不如windows,相应的软件也比较少,尤其是音视频类的软件,但是,这并不代表就完全没有。下面介绍一款强大的音视频即时通讯平台给大家,它就是——Anychat for Linux SDK。AnyChat是一…
文本分类六十年
作者 | Lucy出品 | AI科技大本营文本分类是自然语言处理中最基本而且非常有必要的任务,大部分自然语言处理任务都可以看作是个分类任务。近年来,深度学习所取得的前所未有的成功,使得该领域的研究在过去十年中保持激增。这些文献中已经提出了…

web service 和 remoting 有什么区别
其实现的原理并没有本质的区别,在应用开发层面上有以下区别:1、Remoting可以灵活的定义其所基于的协议,如果定义为HTTP,则与Web Service就没有什么区别了,一般都喜欢定义为TCP,这样比Web Service稍为高效一…
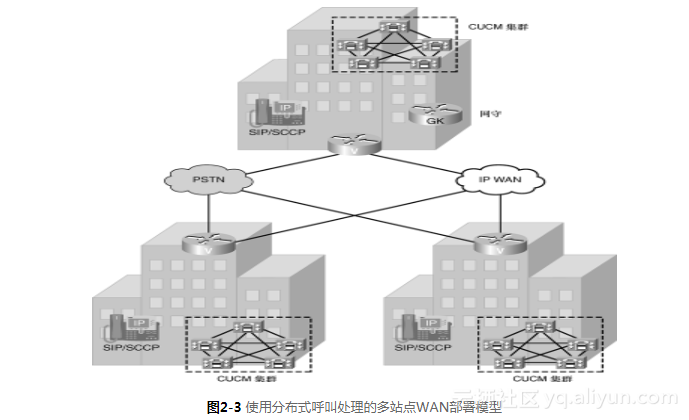
《实施Cisco统一通信管理器(CIPT1)》一2.4 使用分布式呼叫处理的多站点WAN部署模型...
本节书摘来异步社区《实施Cisco统一通信管理器(CIPT1)》一书中的第2章,第2.4节,作者: 【美】Dennis Hartmann译者: 刘丹宁 , 陈国辉 , 卢铭 责编: 傅道坤, 更多章节内容可以访问云栖社区“异步社…

【转】 LDA必读的资料
时间总是不够用,这里就不自己写了,摘自一篇转发的博客,感觉挺有用! 一个大牛写的介绍,貌似需FQ http://tedunderwood.wordpress.com/2012/04/07/topic-modeling-made-just-simple-enough/David M.Blei主页:…

sizeof 操作符详解
1. 定义: sizeof是何方神圣? sizeof 乃 C/C 中的一个操作符(operator)是也。简单说其作用就是返回一个对象或者类型所占的内存字节数。 MSDN上的解释为: The sizeof keyword gives the amount of storage, in bytes, a…
石锤!谷歌排名第一的编程语言,死磕这点,程序员都收益
日本最大的证券公司之一野村证券首席数字官马修汉普森,在Quant Conference上发表讲话:“用Excel的人越来越少,大家都在码Python代码。”甚至直接说:“Python已经取代了Excel。”事实上,为了追求更高的效率和质量&#…

《关系营销2.0——社交网络时代的营销之道》一T表示Technology(技术)
本节书摘来异步社区《关系营销2.0——社交网络时代的营销之道》一书中的第1章,作者: 【美】Mari Smith 译者: 张猛 , 于宏 , 赵俐 责编: 陈冀康, 更多章节内容可以访问云栖社区“异步社区”公众号查看。 T表示Technologyÿ…

jquery拖拽实现UI设计组件
想做一个UI设计的组件,左侧是控件列表,右边是编辑区域,左侧的控件可以重复拖拽到右侧然后进行编辑。 效果草图: 部分js代码: function domop(){//set drag and drop $( "#compls .component" ).each(functi…
六年磨一剑,全时发布音视频会议平台TANG,多款新品亮相
作者 | 高卫华出品 | AI科技大本营时隔六年,全时于11月26日在北京举办了“时间的力量2020新产品发布会“。发布会现场,全时创始人&CEO陈学军回顾了全时近年来的发展历程,并正式推出了全时云会议2020版,全时小智和全时云直播三…

考察新人的两道c语言题目
1> 如何判断一个板子的cpu 是big-endian 还是 Little-endian的?用c实现非常简单,10行左右,就可以判断了, 关键考察新人是否了解了什么是endian ,big-endian与little-endian的区别在哪里, 如果…

《Adobe After Effects CC经典教程》——导读
前 言 After Effects CC提供了一套完整的2D和3D工具,动态影像专业人员、视频特效艺术家、网页设计人员以及电影和视频专业人员都可以用这些工具创建合成图像、动画和特效。After Effects被广泛应用于电影、视频、DVD以及Web的后期数字制作之中。After Effects可以以…

scanf()函数的用法和实践
scanf()函数的用法和实践摘要: 本文阐述了基于ANSI,Win 95,Win NT上的 C/C语言中scanf()函数的用法,以及在实际使用中常见错误及对策。 关键词: scanf()一、 序言 在CSDN论坛的C/C版块,我时常见…
邢波出任全球第一所AI大学校长,履历横跨三门学科
整理 | 高卫华出品 | AI科技大本营近日,世界上第一家研究型人工智能大学——Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence,简称MBZUAI大学(MBZUAI),任命著名华人AI学术教授邢波为校长。据悉,首…

Ubuntu 10.10 安装 libx11-dev
今天(2013-04-11)尝试安装 ImageMagick,结果发现 config.log 文件中包含了如下错误信息: fatal error: X11/Xlib.h: No such file or directory 也就是说缺少了 libx11-dev 包,心想这有什么难的,直接通过 a…
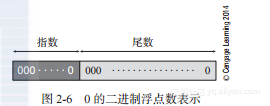
《计算机组成原理》----2.6 浮点数
本节书摘来自华章出版社《计算机组成原理》一书中的第2章,第2.6节, 作 者 Computer Organization and Architecture: Themes and Variations[英]艾伦克莱门茨(Alan Clements) 著,沈 立 王苏峰…

javascript/dom:原生的JS写选项卡方法
来源:http://www.jb51.net/article/30108.htm <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html xmlns"http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"><head><meta http-…
CSDN 星城大巡礼,长沙“科技之星”年度企业评选正式开启
2020年,长沙市委主要领导发出“软件产业再出发”的号召,颁布了软件三年行动计划。今年5月,CSDN 作为专业的 IT 社区,与长沙高新区签约,将全国总部落户长沙,这一战略决策,让CSDN与长沙的联结进一…

Linux下用C获取当前系统时间
#include <time.h> time_t time(time_t calptr); 返回的是日历时间,即国际标准时间公元1970年1月1日00 : 00 : 00以来经过的秒数。然后再调用 char *ctime(const time_t calptr) ; 转化为字符串表示 #include <stdio.h> #inc…
