第十周课下作业(补做课堂测试)
一、知识点总结
1、单链表
- 创建单链表
- 链表中数据的插入
list.add("**"); - 链表中数据的排序
Collections.sort(); - 链表中数据的删除
lsit.remove("");
2、排序
- 树集概念
- 树映射
TreeMap<K,V>**适合用于数据的排序** - 通过关键字进行排序
TreeMap<StudentKey,Student> treemap= new TreeMap<StudentKey,Student>(); - 对数据进行排序(比较comparable和comparator)
在List或数组中的对象如果没有实现Comparable接口时,那么就需要调用者为需要排序的数组或List设置一个Compartor,Compartor的compare方法用来告诉代码应该怎么去比较两个实例,然后根据比较结果进行排序 - comparatorpackage java.util;
public interface Comparator<T> {int compare(T o1, T o2);boolean equals(Object obj);
}- comparablepackage java.lang;
import java.util.*;
public interface Comparable<T> {public int compareTo(T o);
}- 总结Comparable 是排序接口;若一个类实现了 Comparable 接口,就意味着 “该类支持排序”。而 Comparator 是比较器;我们若需要控制某个类的次序,可以建立一个 “该类的比较器” 来进行排序。
前者应该比较固定,和一个具体类相绑定,而后者比较灵活,它可以被用于各个需要比较功能的类使用。可以说前者属于 “静态绑定”,而后者可以 “动态绑定”。
Comparable 相当于 “内部比较器”,而 Comparator 相当于 “外部比较器”。二、补做内容与截图
1、单链表
创建链表
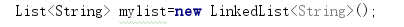
创建结点

插入自己的学号并排序

删除自己的学号并打印

- 整体代码
import java.util.*;
public class MyList {public static void main(String [] args) {List<String> mylist=new LinkedList<String>();
//选用合适的构造方法,用你学号前后各两名同学的学号创建四个结点mylist.add("20165224");mylist.add("20165225");mylist.add("20165227");mylist.add("20165228");
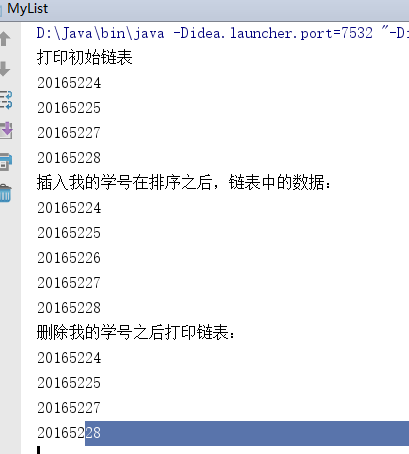
//把上面四个节点连成一个没有头结点的单链表System.out.println("打印初始链表");
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的Iterator<String> iter=mylist.iterator();while (iter.hasNext()){String num=iter.next();System.out.println(num);}
//把你自己插入到合适的位置(学号升序)mylist.add("20165226");Collections.sort(mylist);
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的System.out.println("插入我的学号在排序之后,链表中的数据:");iter =mylist.iterator();while(iter.hasNext()){String num=iter.next();System.out.println(num);}
//从链表中删除自己mylist.remove("20165226");System.out.println("删除我的学号之后打印链表:");
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的iter=mylist.iterator();while(iter.hasNext()){String num=iter.next();System.out.println(num);}}
}- 运行结果
2、排序
创建
Student类的对象
调用comparator方法

按关键字
总成绩进行排序
按关键字
学号进行排序
- 整体代码
import java.lang.String;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
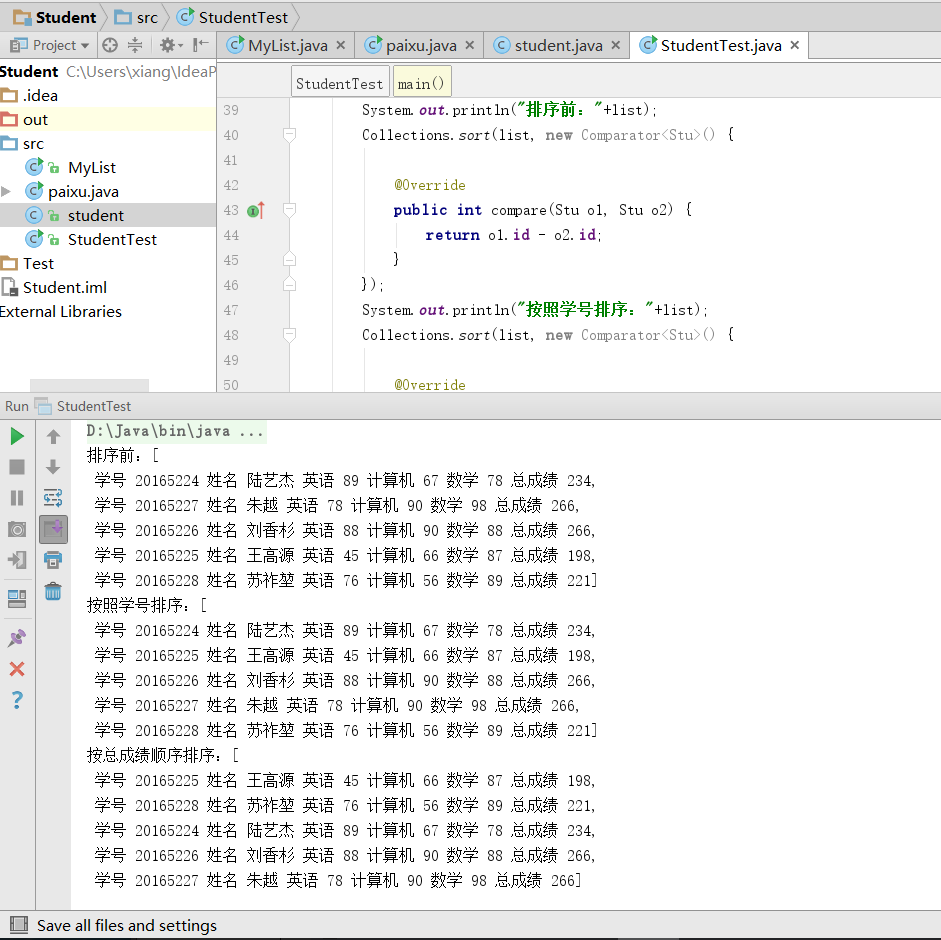
public class StudentTest {class Stu{public int age;public String name;public int id;public int english_score;public int computer_score;public int maths_score;public int total_score;public Stu(int id, String name,int english_score,int computer_score,int maths_score,int total_score) {super();this.id = id;this.name = name;this.english_score = english_score;this.computer_score = computer_score;this.maths_score = maths_score;this.total_score = total_score;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return ( "\n"+" 学号 " + id + " 姓名 " + name +" 英语 "+english_score+" 计算机 "+computer_score+" 数学 "+maths_score+" 总成绩 "+total_score+"\n");}}public static void main(String[] args) {List<Stu> list= new ArrayList<>();list.add(new StudentTest().new Stu(20165224, "陆艺杰",89,67,78,234));list.add(new StudentTest().new Stu(20165227, "朱越",78,90,98,266));list.add(new StudentTest().new Stu(20165225, "王高源",45,66,87,198));list.add(new StudentTest().new Stu(20165226, "刘香杉",88,90,88,266));list.add(new StudentTest().new Stu(20165228, "苏祚堃",76,56,89,221));Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Stu>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Stu o1, Stu o2) {return o1.id - o2.id;}});System.out.println("按照学号排序:"+list);Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Stu>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Stu o1, Stu o2) {return o1.total_score - o2.total_score;}});System.out.println("按总成绩顺序排序:"+list);}
}- 运行结果
三、补做教材第十五章编程题目
1、使用堆栈结构输出an的若干项,其中an=2an-1 +2an-2 ,a1=3,a2=8
import java.util.*;
public class E {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<Integer();stack.push(new Integer(3));stack.push(new Integer(8));int k=1;while(k<=10) {for(int i=1;i<=2;i++) {Integer F1=stack.pop();int f1=F1.intValue();Integer F2=stack.pop();int f2=F2.intValue(); Integer temp=new Integer(2*f1+2*f2);System.out.println(""+temp.toString());stack.push(temp);stack.push(F2);k++;}}}}2、编写一个程序,将链表中的学生英语成绩单存放到一个树集中,使得按成绩自动排序,并输出排序结果
import java.util.*;
class Student implements Comparable {int english=0;
String name; Student(int english,String name) {this.name=name;this.english=english;} public int compareTo(Object b) {Student st=(Student)b;return (this.english-st.english);}}
public class E { public static void main(String args[]) { List<Student> list=new LinkedList<Student>();int score []={65,76,45,99,77,88,100,79}; String name[]={"张三","李四","旺季","加戈","为哈","周和","赵李","将集"};for(int i=0;i<score.length;i++){ list.add(new Student(score[i],name[i]));} Iterator<Student> iter=list.iterator(); TreeSet<Student> mytree=new TreeSet<Student>();while(iter.hasNext()){Student stu=iter.next();mytree.add(stu);} Iterator<Student> te=mytree.iterator();while(te.hasNext()) {Student stu=te.next(); System.out.println(""+stu.name+" "+stu.english);}}}3、有10个U盘,有两个重要的属性:价格和容量。编写一个应用程序,使用TreeMap<K,V>类,分别按照价格和容量排序来输出10个U盘的详细信息
import java.util.*;
class UDiscKey implements Comparable {double key=0;UDiscKey(double d) {key=d;} public int compareTo(Object b) {UDiscKey disc=(UDiscKey)b; if((this.key-disc.key)==0)return -1;else return (int)((this.key-disc.key)*1000);}}
class UDisc{int amount;double price; UDisc(int m,double e) {amount=m;price=e;}}
public class E { public static void main(String args[ ]) { TreeMap<UDiscKey,UDisc> treemap= new TreeMap<UDiscKey,UDisc>();int amount[]={1,2,4,8,16};double price[]={867,266,390,556};UDisc UDisc[]=new UDisc[4];for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) { UDisc[k]=new UDisc(amount[k],price[k]);} UDiscKey key[]=new UDiscKey[4];for(int k=0;k<key.length;k++) { key[k]=new UDiscKey(UDisc[k].amount); } for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) { treemap.put(key[k],UDisc[k]); } int number=treemap.size(); Collection<UDisc> collection=treemap.values();Iterator<UDisc> iter=collection.iterator();while(iter.hasNext()) {UDisc disc=iter.next(); System.out.println(""+disc.amount+"G "+disc.price+"元"); } treemap.clear(); for(int k=0;k<key.length;k++) { key[k]=new UDiscKey(UDisc[k].price); } for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {treemap.put(key[k],UDisc[k]); } number=treemap.size();collection=treemap.values();iter=collection.iterator();while(iter.hasNext()) {UDisc disc=iter.next(); System.out.println(""+disc.amount+"G "+disc.price+"元");}}}