版权声明:本文出自汪磊的博客,转载请务必注明出处。
对于稍有自定义View经验的安卓开发者来说,onMeasure,onLayout,onDraw这三个方法都不会陌生,起码多少都有所接触吧。
在安卓中,一个View显示到屏幕上基本上都是经过测量,摆放,绘制这三个过程才显示出来,那么这三个过程到底是怎么执行的呢?本文与大家一起探讨一下安卓中View的绘制流程。
一,View树绘制流程开始的地方(API23)
对一个布局进项测量,摆放,绘制肯定要有开始的地方吧,这里就直接跟大家说了,View绘制流程开始的地方是ViewRootImpl类的performTraversals()方法(至于为什么是这里不是本篇重点,后续有时间写一篇针对这里的文章说明一下),接下来我们看下performTraversals()方法(此方法过长,只列出重要逻辑代码)
1 private void performTraversals() {2 ......3 int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);4 int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);5 ......6 // Ask host how big it wants to be7 performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);8 ......9 performLayout(lp, desiredWindowWidth, desiredWindowHeight);
10 ......
11 performDraw();
12 ......
13 }第3,4行代码调用getRootMeasureSpec方法生成对应宽高,我们先看下getRootMeasureSpec都做了什么,源码如下:
1 /**2 * Figures out the measure spec for the root view in a window based on it's3 * layout params.4 *5 * @param windowSize6 * The available width or height of the window7 *8 * @param rootDimension9 * The layout params for one dimension (width or height) of the
10 * window.
11 *
12 * @return The measure spec to use to measure the root view.
13 */
14 private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
15 int measureSpec;
16 switch (rootDimension) {
17
18 case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
19 // Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
20 measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
21 break;
22 case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
23 // Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
24 measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
25 break;
26 default:
27 // Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
28 measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
29 break;
30 }
31 return measureSpec;
32 }先说一下MeasureSpec这个概念:也叫测量规格,MeasureSpec是一个32位整数,由SpecMode和SpecSize两部分组成,其中,高2位为SpecMode,低30位为SpecSize。SpecMode为测量模式,SpecSize为相应测量模式下的测量尺寸。
View(包括普通View和ViewGroup)的SpecMode由本View的LayoutParams结合父View的MeasureSpec生成(普通View的MeasureSpec是由其父类ViewGroup生成的,后面会详细讲到)。
SpecMode的取值可为以下三种:
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY //确定模式,父View希望子View的大小是确定的,由specSize决定;
MeasureSpec.AT_MOST //最多模式,父View希望子View的大小最多是specSize指定的值;
MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED //未指定模式,父View对子View的大小不做限制,完全由子View自己决定;
getRootMeasureSpec方法就是生成根视图的MeasureSpec,还记得我们上一篇《Android之View绘制流程开胃菜---setContentView(...)详细分析》中分析的吗,平时我们自己写的布局都是被添加到DecorView中id为content的布局中的,这里传入进来的windowSize参数是window的可用宽高信息,rootDimension宽高参数均为MATCH_PARENT。
我们上面说普通View的MeasureSpec是由其父类ViewGroup生成的,但是根视图DecorView是没有父类的,所以getRootMeasureSpec就是给根视图生成测量规格的,生成的MeasureSpec中SpecMode为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,SpecSize则为窗口的可用尺寸。
回到performTraversals()方法中:
3,4行代码分别生成宽高的测量规格
7,9,11行代码分别执行performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec), performLayout(lp, desiredWindowWidth, desiredWindowHeight),performDraw();
方法,我们看下这三个方法源码:都经过简化处理
1 private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
2 Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
3 try {
4 mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
5 } finally {
6 Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
7 }
8 }1 private void performLayout(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, int desiredWindowWidth,
2 int desiredWindowHeight) {
3
4 ...
5 final View host = mView;
6
7 host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight());
8 ...
9 } 1 private void performDraw() {
2 ...
3 draw(fullRedrawNeeded);
4 ...
5 }1 private void draw(boolean fullRedrawNeeded) {
2
3 ...
4 if (!drawSoftware(surface, mAttachInfo, xOffset, yOffset, scalingRequired, dirty)) {
5 return;
6 }
7 ...
8 }1 private boolean drawSoftware(Surface surface, AttachInfo attachInfo, int xoff, int yoff,
2 boolean scalingRequired, Rect dirty) {
3 ...
4 mView.draw(canvas);
5 ...
6 return true;
7 }performMeasure方法最核心的是第4行调用mView的measure方法。
performLayout方法通过5,7行代码发现其实也是调用的mView的layout方法。
performDraw最终调用的也是调用的mView的draw方法。
上面的mView就是DecorView,我们知道DecorView是FrameLayout,FrameLayout继承自ViewGroup,ViewGroup继承自View,所以最终都会调用View类中measure,
layout,draw方法。实际上View的绘制流程可以分为三个阶段:
- measure: 判断是否需要重新计算View的大小,需要的话则计算;
- layout: 判断是否需要重新计算View的位置,需要的话则计算;
- draw: 判断是否需要重新绘制View,需要的话则重绘制。
大体流程如图:
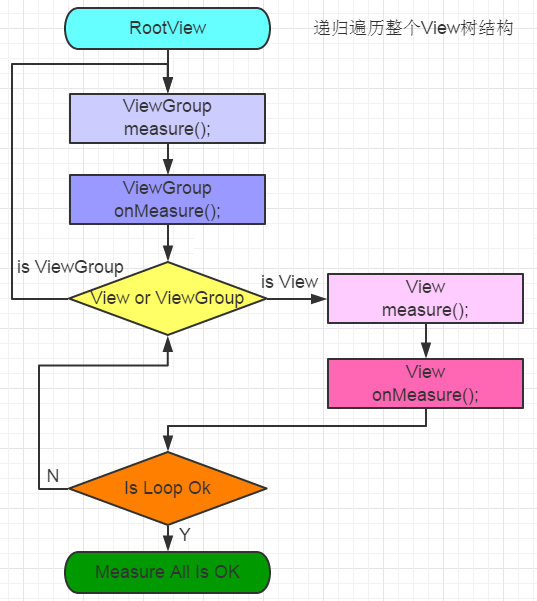
二,View绘制流程第一步measure过程分析(API23)
接下来我们看下View中的measure源码:简化处理
1 /**2 * <p>3 * This is called to find out how big a view should be. The parent4 * supplies constraint information in the width and height parameters.5 * </p>6 *7 * <p>8 * The actual measurement work of a view is performed in9 * {@link #onMeasure(int, int)}, called by this method. Therefore, only
10 * {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} can and must be overridden by subclasses.
11 * </p>
12 *
13 *
14 * @param widthMeasureSpec Horizontal space requirements as imposed by the
15 * parent
16 * @param heightMeasureSpec Vertical space requirements as imposed by the
17 * parent
18 *
19 * @see #onMeasure(int, int)
20 */
21 public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
22 ...
23 // measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
24 onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
25 ...
26 }注释已经给出大体描述:这个被调用用来测算出view大小,并且其父类提供了约束信息widthMeasureSpec与heightMeasureSpec。
我们发现measure方法被final修饰,所以这个方法不能被子类重写。
实际的测量是在onMeasure方法进行,所以在View的普通子类中需要重写onMeasure方法来实现自己的测量逻辑。
对于普通View,调用View类的onMeasure()方法来进行实际的测量工作即可,当然我们也可以重载onMeasure并调用setMeasuredDimension来设置任意大小的布局。
接下来我们看下默认情况下View类中onMeasure方法都做了什么,源码如下;
1 /**2 * <p>3 * Measure the view and its content to determine the measured width and the4 * measured height. This method is invoked by {@link #measure(int, int)} and5 * should be overridden by subclasses to provide accurate and efficient6 * measurement of their contents.7 * </p>8 *9 * <p>
10 * <strong>CONTRACT:</strong> When overriding this method, you
11 * <em>must</em> call {@link #setMeasuredDimension(int, int)} to store the
12 * measured width and height of this view. Failure to do so will trigger an
13 * <code>IllegalStateException</code>, thrown by
14 * {@link #measure(int, int)}. Calling the superclass'
15 * {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} is a valid use.
16 * </p>
17 *
18 * <p>
19 * The base class implementation of measure defaults to the background size,
20 * unless a larger size is allowed by the MeasureSpec. Subclasses should
21 * override {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} to provide better measurements of
22 * their content.
23 * </p>
24 *
25 * <p>
26 * If this method is overridden, it is the subclass's responsibility to make
27 * sure the measured height and width are at least the view's minimum height
28 * and width ({@link #getSuggestedMinimumHeight()} and
29 * {@link #getSuggestedMinimumWidth()}).
30 * </p>
31 *
32 * @param widthMeasureSpec horizontal space requirements as imposed by the parent.
33 * The requirements are encoded with
34 * {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec}.
35 * @param heightMeasureSpec vertical space requirements as imposed by the parent.
36 * The requirements are encoded with
37 * {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec}.
38 *
39 * @see #getMeasuredWidth()
40 * @see #getMeasuredHeight()
41 * @see #setMeasuredDimension(int, int)
42 * @see #getSuggestedMinimumHeight()
43 * @see #getSuggestedMinimumWidth()
44 * @see android.view.View.MeasureSpec#getMode(int)
45 * @see android.view.View.MeasureSpec#getSize(int)
46 */
47 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
48 setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
49 getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
50 }这个方法看注释就已经大体明白了,简单翻译一下吧:这个方法用来测量view以及自身内容来决定宽高,子类应该重写这个方法提供更精确更高效的测量的内容。当重写这个方法的时候子类必须调用setMeasuredDimension(int, int)来存储已经测量出来的宽高。我们看到系统默认的onMeasure方法只是直接调用了setMeasuredDimension,setMeasuredDimension函数是一个很关键的函数,它对View的成员变量mMeasuredWidth和mMeasuredHeight变量赋值,measure的主要目的就是对View树中的每个View的mMeasuredWidth和mMeasuredHeight进行赋值,所以一旦这两个变量被赋值意味着该View的测量工作结束。
接下来我们看看设置的默认View宽高,默认宽高都是通过getDefaultSize方法来获取的,而getDefaultSize又调用了getSuggestedMinimumXXX方法,我们先看下getSuggestedMinimumXXX方法:
1 protected int getSuggestedMinimumHeight() {
2 return (mBackground == null) ? mMinHeight : max(mMinHeight, mBackground.getMinimumHeight());
3 }1 protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
2 return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
3 }mMinHeight或mMinWidth就是我们设置的android:minHeight或android:minWidth参数。
如果我们没有设置背景则直接返回mMinHeight或mMinWidth,如果设置了背景,则返回miniXXX属性与mBackground二者中较大者。如背景以及miniXXX属性都没设置呢?那就返回0了。
接下来再看getDefaultSize方法源码:
1 public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {2 int result = size;3 int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);4 int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);5 6 switch (specMode) {7 case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:8 result = size;9 break;
10 case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
11 case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
12 result = specSize;
13 break;
14 }
15 return result;
16 }
getDefaultSize返回值由上面讲到的getSuggestedMinimumXXX方法获取的Size以及父类传递过来的measureSpec共同决定。
可以看到如果specMode等于AT_MOST或EXACTLY就返回specSize,这也是系统默认的规格。
到此为止,普通View(非ViewGroup)的测量就基本讲完了。但是ViewGroup这种容器类布局是怎么测量其内每个子View的呢?
ViewGroup容器类布局大部分情况下是用来嵌套具体子View的,所以需要负责其子View的测量,在ViewGroup中定义了
measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,int parentHeightMeasureSpec)
以及measureChildWithMargins(View child,int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed)
三个方法来供其子类调用对具体子View进行测量。
measureChildren,measureChild源码如下:
1 protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {2 final int size = mChildrenCount;3 final View[] children = mChildren;4 for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {5 final View child = children[i];6 if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {7 measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);8 }9 }
10} 1 protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,2 int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {3 final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();4 5 final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,6 mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);7 final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,8 mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);9
10 child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
11}看到了吧,measureChildren只是循环调用measureChild方法,而measureChild方法中会根据父类提供的测量规格parentXXXMeasureSpec一级子类自己LayoutParams调用getChildMeasureSpec方法生成子类自己具体的测量规格。(getChildMeasureSpec稍后会具体分析)
接下来我们看下measureChildWithMargins方法源码:
1 protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,2 int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,3 int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {4 final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();5 6 final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,7 mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin8 + widthUsed, lp.width);9 final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
10 mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
11 + heightUsed, lp.height);
12
13 child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
14 }与measureChild相比最主要的区别就是measureChildWithMargins额外将具体子View LayoutParams参数的margin也当作参数来生成测量规格。
measureChild与measureChildWithMargins均调用了getChildMeasureSpec方法来生成具体测量规格,接下来我们重点看下这个方法:
1 public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {2 int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);//获取父View的mode 3 int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);//获取父View的size4 //父View的size减去padding与0比较取其大,specSize - padding得到的值是父View可以用来盛放子View的空间大小5 int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);6 7 int resultSize = 0;8 int resultMode = 0;9
10 switch (specMode) {
11 // Parent has imposed an exact size on us
12 case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY://父View希望子View是明确大小
13 if (childDimension >= 0) {//子View设置了明确的大小:如 10dp,20dp
14 resultSize = childDimension;//设置子View测量规格大小为其本身设置的大小
15 resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;//mode设置为EXACTLY
16 } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {//子VIEW的宽或者高设置为MATCH_PARENT,表明子View想和父View一样大小
17 // Child wants to be our size. So be it.
18 resultSize = size;//设置子View测量规格大小为父View可用空间的大小
19 resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;//mode设置为EXACTLY
20 } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {//子VIEW的宽或者高设置为WRAP_CONTENT,表明子View大小是动态的
21 // Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
22 // bigger than us.
23 resultSize = size;//设置子View测量规格大小为父View可用空间的大小
24 resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;//mode设置为AT_MOST,表明子View宽高最大值不能超过resultSize
25 }
26 break;27 //其余情况请自行分析
28 ......
29 return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
30 }想说的注释已经给出。
上面的方法展现了根据父View的MeasureSpec和子View的LayoutParams生成子View的MeasureSpec的过程, 子View的LayoutParams表示了子View的期待大小。这个产生的MeasureSpec用于指导子View自身的测量。
在我们自定义View的时候一般会重写onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)方法其中的widthMeasureSpec与heightMeasureSpec参数就是父类通过getChildMeasureSpec方法生成的。一个好的自定义View会根据父类传递过来的测量规格动态设置大小,而不是直接写死其大小。
好了,到此为止View的测量过程想说的就差不多都说完了,我们稍微总结一下关键的部分;
View的measure方法是final的,不允许重载,View子类只能重载onMeasure来完成自己的测量逻辑。
最顶层DecorView测量时的MeasureSpec是由ViewRootImpl中getRootMeasureSpec方法确定的。
ViewGroup类提供了measureChild,measureChild和measureChildWithMargins方法,以供容器类布局测量自身子View使用
使用View的getMeasuredWidth()和getMeasuredHeight()方法来获取View测量的宽高,必须保证这两个方法在onMeasure流程之后被调用才能返回有效值,只有onMeasure流程完后mMeasuredWidth与mMeasuredHeight才会被赋值
- View的布局大小是由父View和子View共同决定的。我们平时设置的宽高可以理解为希望的大小,具体大小还要结合父类大小来确定。
最后附上View绘制流程图:相信你会理解的更加深刻:
三,View绘制流程第二步layout过程分析(API23)performMeasure执行完,接着就会执行performLayout:
1 private void performLayout(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, int desiredWindowWidth,
2 int desiredWindowHeight) {
3
4 ...
5 final View host = mView;
6
7 host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight());
8 ...
9 }
mView为根View,即DecorView,DecorView是FrameLayout的子类,最终会调用ViewGroup中layout方法。
所以接下来我们看下ViewGroup中layout方法源码:
1 @Override2 public final void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {3 if (!mSuppressLayout && (mTransition == null || !mTransition.isChangingLayout())) {4 if (mTransition != null) {5 mTransition.layoutChange(this);6 }7 super.layout(l, t, r, b);8 } else {9 // record the fact that we noop'd it; request layout when transition finishes
10 mLayoutCalledWhileSuppressed = true;
11 }
12 }第7行代码表明又调用父类View的layout方法。所以我们看下View的layout源码,如下:
1 public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
2 // l为本View左边缘与父View左边缘的距离
// t为本View上边缘与父View上边缘的距离 // r为本View右边缘与父View左边缘的距离 // b为本View下边缘与父View上边缘的距离
3 ...
4 boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
5 setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
6
7 if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
8 onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
9 ...
10 }4,5行代码主要判断View的位置是否发生变化,发生变化则changed 会为true,并且setOpticalFrame也是调用的setFrame方法
我们看下setFrame方法源码:
1 protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {2 boolean changed = false;3 4 5 ...6 if (mLeft != left || mRight != right || mTop != top || mBottom != bottom) {7 changed = true;8 9 ...
10 mLeft = left;
11 mTop = top;
12 mRight = right;
13 mBottom = bottom;
14 ...
15 }
16 return changed;
17 } 第6行代码分别比较之前的记录的mLeft,mRight,mTop,mBottom 与新传入的参数如果有一个不同则进入判断,将changed变量置为true,并且将新传入的参数分别重新赋值给mLeft,mRight,mTop,mBottom,最后返回changed。
这里还有一点要说,getWidth()、getHeight()和getMeasuredWidth()、getMeasuredHeight()这两对方法之间的区别,先看一下源码;
1 public final int getMeasuredWidth() {2 return mMeasuredWidth & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;3 }4 5 public final int getMeasuredHeight() {6 return mMeasuredHeight & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;7 }8 9 public final int getWidth() {
10 return mRight - mLeft;
11 }
12
13 public final int getHeight() {
14 return mBottom - mTop;
15 }在讨论View的measure过程时提到过mMeasuredWidth与mMeasuredHeight只有测量过程完成才会被赋值,所以只有测量过程完成调用getMeasuredWidth()、getMeasuredHeight()才会获取正确的值。
同样getWidth()、getHeight()只有在layout过程完成时mLeft,mRight,mTop,mBottom才会被赋值,调用才会获取正确返回值,所以二者调用时机是不同的。
继续看View中layout源码第7行,如果changed为true,也就是说View的位置发生了变化,或者标记为PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED则进入判断执行onLayout方法。
我们继续看View中onLayout方法源码:
1 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
2 }看到了吧,竟然是个空方法。
对比View的layout和ViewGroup的layout方法发现,View的layout方法是可以在子类重写的,而ViewGroup的layout是不能在子类重写的,那么容器类View是怎么对其子View进行摆放的呢?别急,在ViewGroup中同样也有onLayout方法,源码如下;
1 /**
2 * {@inheritDoc}
3 */
4 @Override
5 protected abstract void onLayout(boolean changed,
6 int l, int t, int r, int b);看到了吧,还是个抽象方法,因为具体ViewGroup摆放规则不同,所以其具体子类需要重写这个方法来实现对其子View的摆放逻辑。
既然这样我们就只能分析一个继承自ViewGroup的具体子类了,我们选取FrameLayout,其onLayout源码如下:
1 @Override2 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {3 layoutChildren(left, top, right, bottom, false /* no force left gravity */);4 }5 6 void layoutChildren(int left, int top, int right, int bottom,7 boolean forceLeftGravity) {8 final int count = getChildCount();9
10 ......
11
12 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
13 final View child = getChildAt(i);
14 if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
15 .....
16
17 child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childLeft + width, childTop + height);
18 }
19 }
20 }看到了吧,onLayout方法调用layoutChildren方法,在layoutChildren方法中遍历每个子View调用其layout方法。
好了,到此Layout过程就讨论的差不多了,相比measure过程还是简单不少的,其也是递归调用逻辑。如图:
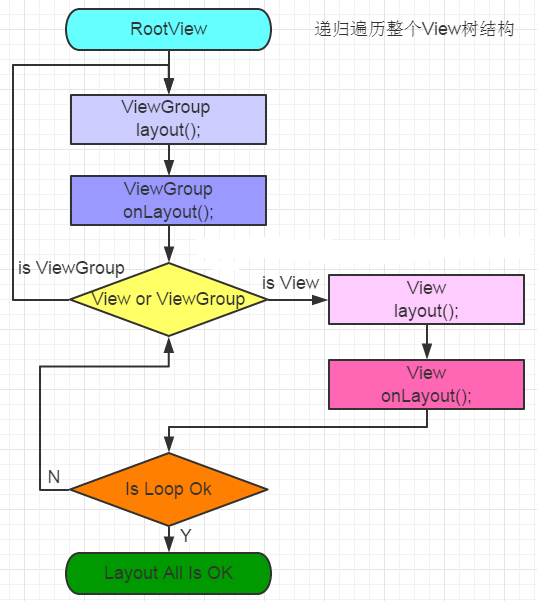
我们总结一下主要部分:
View.layout方法可被重写,ViewGroup.layout为final的不可重写,ViewGroup.onLayout为abstract的,具体ViewGroup子类必须重载来按照自己规则对子View进行摆放。
measure操作完成后得到的是对每个View经测量过的measuredWidth和measuredHeight,layout操作完成之后得到的是对每个View进行位置分配后的mLeft、mTop、mRight、mBottom,这些值都是相对于父View来说的。
使用View的getWidth()和getHeight()方法来获取View测量的宽高,必须保证这两个方法在onLayout流程之后被调用才能返回有效值。
测量,摆放过程都分析完了,接下来我们分析View的draw过程。
四,View绘制流程第三步draw过程分析(API23)
performMeasure, performLayout过程执行完,接下来就执行performDraw()逻辑了,ViewGroup没有重写View的draw方法,最终调用的是View中的draw方法,源码如下:
1 public void draw(Canvas canvas) {final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags;
2 final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) == PFLAG_DIRTY_OPAQUE &&
(mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState);3 4 /*5 * Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed6 * in the appropriate order:7 *8 * 1. Draw the background9 * 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
10 * 3. Draw view's content
11 * 4. Draw children
12 * 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
13 * 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
14 */
15
16 // Step 1, draw the background, if needed
17 int saveCount;
18
19 if (!dirtyOpaque) {
20 drawBackground(canvas);
21 }
22
23 // skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case)
24 final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
25 boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0;
26 boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0;
27 if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) {
28 // Step 3, draw the content
29 if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
30
31 // Step 4, draw the children
32 dispatchDraw(canvas);
33
34 // Overlay is part of the content and draws beneath Foreground
35 if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
36 mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
37 }
38
39 // Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars)
40 onDrawForeground(canvas);
41
42 // we're done...
43 return;
44 }
45 ...
46 // Step 2, save the canvas' layers
47 ....
48 // Step 3, draw the content
49 if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
50
51 // Step 4, draw the children
52 dispatchDraw(canvas);
53
54 // Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers
55 ....
56 // Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars)
57 onDrawForeground(canvas);
58 }5到14行注释可以看到draw过程分为6步,再看23行提示大部分情况下跳过第2,5步。所以我们着重分析其余4步。
19-21行执行第一步,绘制背景源码如下:
1 private void drawBackground(Canvas canvas) {2 final Drawable background = mBackground;3 if (background == null) {4 return;5 }6 ....7 setBackgroundBounds();8 ....9 background.draw(canvas);
10
11 }
12
13
14 void setBackgroundBounds() {
15 if (mBackgroundSizeChanged && mBackground != null) {
16 mBackground.setBounds(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop);
17 mBackgroundSizeChanged = false;
18 rebuildOutline();
19 }
20 }只要逻辑就是获取我们在xml文件或者代码中设置的背景,然后根据layout过程摆放的位置绘制出来。
第29行执行绘制内容逻辑,源码如下:
1 /**
2 * Implement this to do your drawing.
3 *
4 * @param canvas the canvas on which the background will be drawn
5 */
6 protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
7 }看到了吧,是一个空方法,需要具体子类自己去实现,因为每个具体View要绘制的内容是不同的,所以子类需要实现这个方法来绘制自身的内容。
第32行执行绘制子View逻辑,源码如下:
1 /**
2 * Called by draw to draw the child views. This may be overridden
3 * by derived classes to gain control just before its children are drawn
4 * (but after its own view has been drawn).
5 * @param canvas the canvas on which to draw the view
6 */
7 protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
8
9 }看到了吧,也是空方法,这个方法被用来绘制子View的,如果有子View则需要调用这个方法去绘制,我们知道一般只有容器类View才可以盛放子View,所以我们看下ViewGroup中有没有相关逻辑,在ViewGroup中果然实现了这个方法,源码如下:
1 @Override2 protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {3 boolean usingRenderNodeProperties = canvas.isRecordingFor(mRenderNode);4 final int childrenCount = mChildrenCount;5 final View[] children = mChildren;6 .......7 for (int i = 0; i < childrenCount; i++) {8 while (transientIndex >= 0 && mTransientIndices.get(transientIndex) == i) {9 final View transientChild = mTransientViews.get(transientIndex);
10 if ((transientChild.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE ||
11 transientChild.getAnimation() != null) {
12 more |= drawChild(canvas, transientChild, drawingTime);
13 }
14 .......
15 }
16 ......
17 }
18 ......
19 }在dispatchDraw方法中遍历每个子View并且调用drawChild方法,接下来我们看下drawChild源码:
1 protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) {
2 return child.draw(canvas, this, drawingTime);
3 }看到了吧,最终调用每个子View的draw方法来完成自身的绘制。
接下来40行执行onDrawForeground逻辑,这一部分只要绘制一些装饰物,比如ScrollBar。这部分就不分析了,也不是重点。
到这里,View的主要绘制流程我们也分析完了,也不复杂。
但是,但是!!!!!!细心的你有没有发现在执行第一步,第三步的时候都有个if判断(if (!dirtyOpaque)),也就是说只有判断成立才会执行绘制背景和自身内容,难道还有View不绘制自身内容吗? 这里就直接说了,ViewGroup子类默认情况下就是不执行onDraw方法的,在ViewGroup源码中的initViewGroup()方法中设置了一个标记,源码如下:
1 private void initViewGroup() {
2 // ViewGroup doesn't draw by default
3 if (!debugDraw()) {
4 setFlags(WILL_NOT_DRAW, DRAW_MASK);
5 }
6 ......
7 } 看第二行注释也知道,ViewGroup默认情况下是不会draw的。
第四行调用setFlags方法设置标记WILL_NOT_DRAW,
我们在回到View中draw方法看第2行代码:
1 final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags;
2 final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) == PFLAG_DIRTY_OPAQUE &&
3 (mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState);setFlags方法就是对View中mPrivateFlags值进行相应改变,我们设置标记WILL_NOT_DRAW那么dirtyOpaque得到的值就为true,从而if (!dirtyOpaque)不成立,也就不会执行onDraw方法。
估计这点很多同学有疑问ViewGroup默认情况下onDraw方法是不执行的???别急,动手写个小demo验证一下就是了。
布局如下:极其简单
1 <com.wanglei.clearheart.MyView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"2 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"3 android:layout_width="match_parent"4 android:layout_height="match_parent"5 android:gravity="center"6 android:orientation="vertical"7 tools:context=".MainActivity" >8 9
10 </com.wanglei.clearheart.MyView >MyView源码如下:同样极其简单
1 public class MyView extends ViewGroup {2 3 private Paint mPaint;4 public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {5 super(context, attrs);6 mPaint = new Paint();7 mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);8 mPaint.setStyle(Style.STROKE);9 mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10);
10
11 }
12
13 @Override
14 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
15
16 super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
17 }
18
19 @Override
20 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
21 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
22
23 }
24
25 @Override
26 protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
27 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
28 canvas.drawCircle(getMeasuredWidth()/2, getMeasuredHeight()/2, 360, mPaint);
29 }
30 }运行程序会看到就是一个大白板,没有绘制出任何图形,那我们怎么让ViewGroup调用onDraw方法呢?
很简单View类中给我们提供了一个方法供外部调用:
1 public void setWillNotDraw(boolean willNotDraw) {
2 setFlags(willNotDraw ? WILL_NOT_DRAW : 0, DRAW_MASK);
3 }看到了吧,本质也是调用的setFlags方法。如果我们传入true则绘制的时候不会调用onDraw方法,传入false则使其调用onDraw方法。
我们修改MyView代码:构造方法中调用setWillNotDraw(false);
1 public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
2 super(context, attrs);
3 mPaint = new Paint();
4 mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
5 mPaint.setStyle(Style.STROKE);
6 mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10);
7 setWillNotDraw(false);
8
9 }运行程序,会看到手机屏幕中间画出一个红色的圆。还有一种方法我们在布局中给MyView添加背景同样会达到调用onDraw方法的目的。
容器类布局(ViewGroup子类)为什么默认情况下不绘制背景和自身内容呢?答案是为了性能啊,大家想想容器类布局如果没有背景,只是用来盛放子类有必要调用onDraw方法吗?
有什么可绘制的吗?子类会自己实现onDraw方法绘制自己内容的。
接下来我们总结一下draw流程的重点:
容器类布局需要递归绘制其所包含的所有子View。
View中onDraw默认是空方法,需要子类自己实现来完成自身容内的绘制。
- 容器类布局默认情况下不会调用onDraw方法,我们可以为其设置背景或者调用setWillNotDraw(false)方法来使其主动调用onDraw方法
最后附上draw流程图:

好了,到此本篇就该结束了,用了很长的篇幅来探讨View的绘制流程,希望对大家有用,废话就不多说了,咱们下篇见。