2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 
mvc:annotation-driven会将每一个Controllor内的被@RequestMapping注解标注的方法解析为HandlerMethod对象,并存储在RequestMappingHandlerMapping的MappingRegistry属性中,寻址就是根据request请求信息,找到正确的HandlerMethod对象的过程。
HandlerMethod和RequestMappingInfo的关系
HandlerMethod意为方法相关的信息封装,RequestMappingInfo则是方法所要求的条件信息,HandlerMethod和RequestMappingInfo的映射关系,通过MappingRegistry的Map<T, HandlerMethod>已经做好了映射,T即为RequestMappingInfo。
HandlerMethod
public class HandlerMethod {// method所在的Controllor实例private final Object bean;private final BeanFactory beanFactory;// Controllor的class类型private final Class<?> beanType;// method本身private final Method method;private final Method bridgedMethod;// method的参数信息private final MethodParameter[] parameters;private HttpStatus responseStatus;private String responseStatusReason;private HandlerMethod resolvedFromHandlerMethod;
//...
}RequestCondition
public interface RequestCondition<T> {// 类上的条件和方法上的条件进行合并(并集)T combine(T other);// 返回该请求所匹配的条件T getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request);// 如果条件要求是一个人,但来了一个胖子和瘦子,该方法决定选胖子,还是瘦子int compareTo(T other, HttpServletRequest request);}combine()举例:Class条件是GET,Method条件是POST,combine()的结果是GET或者POST。
getMatchingCondition()举例:条件是GET或者POST,当前request是GET请求,则返回GET条件。
compareTo()举例:条件有/emp*和/emp?,现在的request请求是/emp1,/emp1同时符合/emp*和/emp?,选谁呢?最终选择/emp?,因为/emp?粒度更小,范围更小,compareTo()具有决定权。
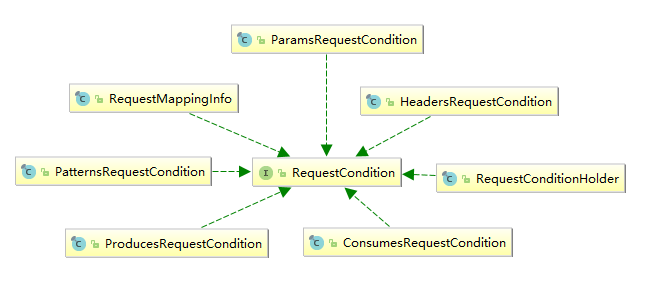
RequestCondition的各种实现类类图:
(Made In IntelliJ IDEA)
(Made In Edraw Max)
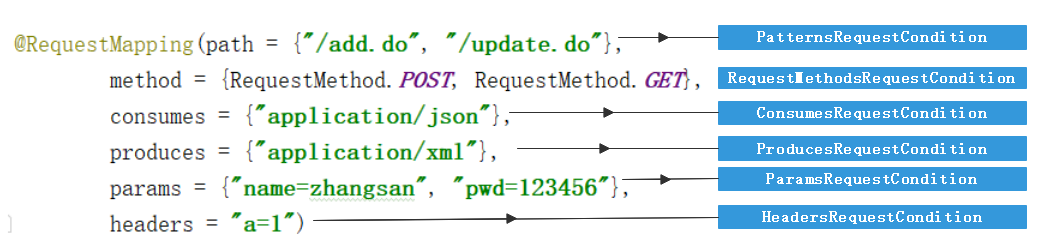
再对照这幅图,读者大概就知道每个条件对应哪一个配置了。
RequestMappingInfo
RequestMappingInfo较为特殊,它是一个典型的装饰器设计模式(Decorator),它装饰了具体的条件。
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> {private final PatternsRequestCondition patternsCondition;private final RequestMethodsRequestCondition methodsCondition;private final ParamsRequestCondition paramsCondition;private final HeadersRequestCondition headersCondition;private final ConsumesRequestCondition consumesCondition;private final ProducesRequestCondition producesCondition;private final RequestConditionHolder customConditionHolder;
//...
}我们看看它的combine()方法,都是调用了具体的条件的combine()方法,将结果返回。
public RequestMappingInfo combine(RequestMappingInfo other) {String name = combineNames(other);PatternsRequestCondition patterns = this.patternsCondition.combine(other.patternsCondition);RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.combine(other.methodsCondition);ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.combine(other.paramsCondition);HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.combine(other.headersCondition);ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.combine(other.consumesCondition);ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.combine(other.producesCondition);RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.combine(other.customConditionHolder);return new RequestMappingInfo(name, patterns,methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom.getCondition());
}PatternsRequestCondition.combine()
我们以PatternsRequestCondition.combine()为例,它调用了AntPathMatcher.combine()方法:
public String combine(String pattern1, String pattern2) {if (!StringUtils.hasText(pattern1) && !StringUtils.hasText(pattern2)) {return "";}if (!StringUtils.hasText(pattern1)) {return pattern2;}if (!StringUtils.hasText(pattern2)) {return pattern1;}boolean pattern1ContainsUriVar = (pattern1.indexOf('{') != -1);if (!pattern1.equals(pattern2) && !pattern1ContainsUriVar && match(pattern1, pattern2)) {// /* + /hotel -> /hotel ; "/*.*" + "/*.html" -> /*.html// However /user + /user -> /usr/user ; /{foo} + /bar -> /{foo}/barreturn pattern2;}// /hotels/* + /booking -> /hotels/booking// /hotels/* + booking -> /hotels/bookingif (pattern1.endsWith(this.pathSeparatorPatternCache.getEndsOnWildCard())) {return concat(pattern1.substring(0, pattern1.length() - 2), pattern2);}// /hotels/** + /booking -> /hotels/**/booking// /hotels/** + booking -> /hotels/**/bookingif (pattern1.endsWith(this.pathSeparatorPatternCache.getEndsOnDoubleWildCard())) {return concat(pattern1, pattern2);}int starDotPos1 = pattern1.indexOf("*.");if (pattern1ContainsUriVar || starDotPos1 == -1 || this.pathSeparator.equals(".")) {// simply concatenate the two patternsreturn concat(pattern1, pattern2);}String ext1 = pattern1.substring(starDotPos1 + 1);int dotPos2 = pattern2.indexOf('.');String file2 = (dotPos2 == -1 ? pattern2 : pattern2.substring(0, dotPos2));String ext2 = (dotPos2 == -1 ? "" : pattern2.substring(dotPos2));boolean ext1All = (ext1.equals(".*") || ext1.equals(""));boolean ext2All = (ext2.equals(".*") || ext2.equals(""));if (!ext1All && !ext2All) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot combine patterns: " + pattern1 + " vs " + pattern2);}String ext = (ext1All ? ext2 : ext1);return file2 + ext;
}作者的注释,已经明确了路径映射合并的规则。
不过,在路径合并之前,它做了一项操作,将不以/开头的路径,加上/,譬如“index”,会被处理为"/index"。
PatternsRequestCondition.prependLeadingSlash():
private static Set<String> prependLeadingSlash(Collection<String> patterns) {if (patterns == null) {return Collections.emptySet();}Set<String> result = new LinkedHashSet<String>(patterns.size());for (String pattern : patterns) {if (StringUtils.hasLength(pattern) && !pattern.startsWith("/")) {pattern = "/" + pattern;}result.add(pattern);}return result;
}RequestMethodsRequestCondition.combine()
RequestMethodsRequestCondition.combine()直接采用了取并集的操作,这也是类条件为GET,method条件为POST,最终是GET或者POST关系的原因。
public RequestMethodsRequestCondition combine(RequestMethodsRequestCondition other) {Set<RequestMethod> set = new LinkedHashSet<RequestMethod>(this.methods);set.addAll(other.methods);return new RequestMethodsRequestCondition(set);
}其余的条件合并,大都于此类似,读者自行查看。
RequestCondition条件选择优先级
我们还是得从装饰器角色RequestMappingInfo入手,其条件优先级基本是:pattern > param > header > consume > produce > method > custom。
public int compareTo(RequestMappingInfo other, HttpServletRequest request) {int result;// HEAD请求时,method条件优先if (HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(request.getMethod())) {result = this.methodsCondition.compareTo(other.getMethodsCondition(), request);if (result != 0) {return result;}}result = this.patternsCondition.compareTo(other.getPatternsCondition(), request);if (result != 0) {return result;}result = this.paramsCondition.compareTo(other.getParamsCondition(), request);if (result != 0) {return result;}result = this.headersCondition.compareTo(other.getHeadersCondition(), request);if (result != 0) {return result;}result = this.consumesCondition.compareTo(other.getConsumesCondition(), request);if (result != 0) {return result;}result = this.producesCondition.compareTo(other.getProducesCondition(), request);if (result != 0) {return result;}result = this.methodsCondition.compareTo(other.getMethodsCondition(), request);if (result != 0) {return result;}result = this.customConditionHolder.compareTo(other.customConditionHolder, request);if (result != 0) {return result;}return 0;
}如何理解pattern > param > header > consume > produce > method > custom的优先级顺序呢?
原理是:
1、当多个HandlerMethod均满足条件,此时使用pattern排序规则,取排序后的第一个HandlerMethod。如果pattern排序规则返回0(未获得实质排序),则再选择param排序规则,以此类推。最后,选择第一个HandlerMethod作为目标方法。
举例:请求URL为/emp1,发现HandlerMethod(/emp*)和HandlerMethod(/emp?)均满足要求,此时使用pattern条件的排序规则,排序后变成[/emp?, /emp*],然后取第一个HandlerMethod,那么HandlerMethod(/emp?)就被选中了。
再举例:当URL相同时,URL参数?name=张三&pwd=123,此时HandlerMethod({name=张三})和HandlerMethod({name=张三, pwd=123})均满足条件,根据param排序规则,参数多的优先级高,于是HandlerMethod({name=张三, pwd=123})会被最终选中。
@RequestMapping(path = {"/index"}, params = {"pwd=123"})
public String index(Model model, HttpServletRequest request) {
model.addAttribute("msg", "Hello controllor.");
return "hello";
}@RequestMapping(path = {"/index"}, params = {"name=张三", "pwd=123"})
public String index2(Model model, HttpServletRequest request) {
model.addAttribute("msg", "Hello controllor.");
return "hello";
}AntPatternComparator.compare()
PatternsRequestCondition通过AntPatternComparator.compare()方法,来指定排序规则:
public int compare(String pattern1, String pattern2) {PatternInfo info1 = new PatternInfo(pattern1);PatternInfo info2 = new PatternInfo(pattern2);// path为空和path=/**等价if (info1.isLeastSpecific() && info2.isLeastSpecific()) {return 0;}else if (info1.isLeastSpecific()) {return 1;}else if (info2.isLeastSpecific()) {return -1;}// path直接匹配pattern,譬如path=/emp/emp*, pattern=/emp/emp*boolean pattern1EqualsPath = pattern1.equals(path);boolean pattern2EqualsPath = pattern2.equals(path);if (pattern1EqualsPath && pattern2EqualsPath) {return 0;}else if (pattern1EqualsPath) {return -1;}else if (pattern2EqualsPath) {return 1;}// path=/emp/emp/**和path=/emp/emp/abcif (info1.isPrefixPattern() && info2.getDoubleWildcards() == 0) {return 1;}else if (info2.isPrefixPattern() && info1.getDoubleWildcards() == 0) {return -1;}// 比较Uri变量数量+*数量+**的数量if (info1.getTotalCount() != info2.getTotalCount()) {return info1.getTotalCount() - info2.getTotalCount();}if (info1.getLength() != info2.getLength()) {return info2.getLength() - info1.getLength();}// 比较*的数量if (info1.getSingleWildcards() < info2.getSingleWildcards()) {return -1;}else if (info2.getSingleWildcards() < info1.getSingleWildcards()) {return 1;}if (info1.getUriVars() < info2.getUriVars()) {return -1;}else if (info2.getUriVars() < info1.getUriVars()) {return 1;}return 0;
}查找HandlerMethod
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#lookupHandlerMethod()
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>();// 解析时不带通配符(*|?)条件直接放入urlLookup中// 此处直接使用urlLookup查找List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);if (directPathMatches != null) {addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);}if (matches.isEmpty()) {// 遍历系统中所有的RequestMappingInfo,找到满足条件的HandlerMethod集合addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);}if (!matches.isEmpty()) {Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));// 使用RequestMappingInfo的compareTo方法进行排序Collections.sort(matches, comparator);//...// 取第一个HandlerMethodMatch bestMatch = matches.get(0);//...// 返回HandlerMethodreturn bestMatch.handlerMethod;}else {return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);}
}request请求寻址HandlerMethod实战
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/emp")
public class EmpControllor {@RequestMapping(value = "/emp1")public ModelAndView index1(ModelAndView mav) {mav.setViewName("employee");mav.addObject("path", "/emp/emp1");return mav;}@RequestMapping(value = "/emp?")public ModelAndView index2(ModelAndView mav) {mav.setViewName("employee");mav.addObject("path", "/emp/emp?");return mav;}@RequestMapping("/emp*")public ModelAndView list(ModelAndView mav) {mav.setViewName("employee");mav.addObject("path", "/emp/emp*");return mav;}@RequestMapping("/emp/*")public ModelAndView add(ModelAndView mav) {mav.setViewName("employee");mav.addObject("path", "/emp/emp/*");return mav;}@RequestMapping("/emp/**")public ModelAndView update(ModelAndView mav) {mav.setViewName("employee");mav.addObject("path", "/emp/emp/**");return mav;}}创建一个WEB-INF/jsp/employee.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page isELIgnored="false"%>
<html>
<head><title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
path = <b>${path}</b>
</body>
</html>
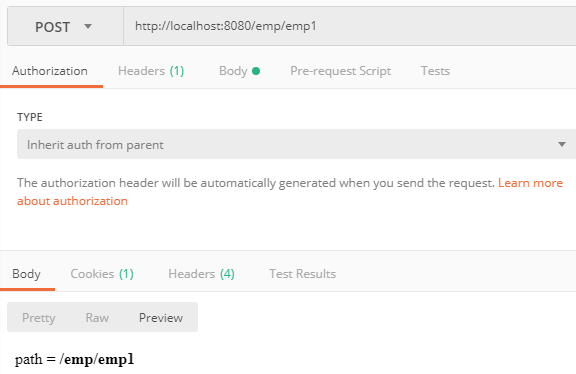
1、http://localhost:8080/emp/emp1
输出:path = /emp/emp1
原理:由于不带*|?通配符,urlLookup直接寻址/emp1
(Made In Postman)
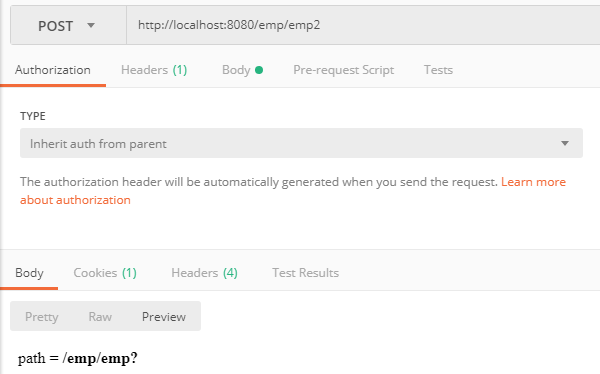
2、http://localhost:8080/emp/emp2
输出:path = /emp/emp?
原理:/emp2同时匹配/emp*和/emp?,但是/emp*的*号数量大于/emp?,最终选择了/emp?
(Made In Postman)
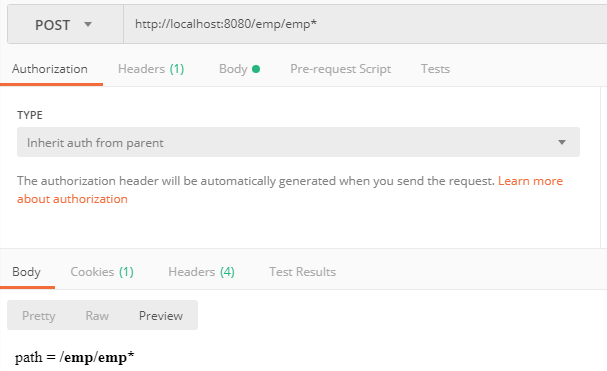
3、http://localhost:8080/emp/emp*
输出:path = /emp/emp*
原理:pattern1.equals(path)直接比较匹配的结果
(Made In Postman)
4、http://localhost:8080/emp/emp/abc
输出:path = /emp/emp/*
原理:/emp/**的通配符多于/emp*,最终选择了/emp/*

(Made In Postman)
5、方法多的会优先么?
@RequestMapping(value = "/emp/**", method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public ModelAndView update1(ModelAndView mav) {
mav.setViewName("employee");
mav.addObject("path", "/emp/emp/**[GET]");
return mav;
}@RequestMapping(value = "/emp/**", method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST})
public ModelAndView update2(ModelAndView mav) {
mav.setViewName("employee");
mav.addObject("path", "/emp/emp/**[GET, POST]");
return mav;
}http://localhost:8080/emp/emp/abc/123
请求:GET
输出:java.lang.IllegalStateException: Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path 'xxx'
原理:当条件是GET或者POST,当前request是GET请求,getMatchingCondition()方法将返回GET条件,即当前reqeust请求的GET条件,于是系统中找到了2个完全一样的GET方法,报错退出。
我们将GET修改为POST请求后,输出:path = /emp/emp/**[GET, POST]
原理:条件是GET或者POST,当前request是POST请求,getMatchingCondition()方法将返回POST条件,唯一找到上面的update2()方法,执行成功。

(Made In Postman)
所以,一定要注意,匹配时使用getMatchingCondition(request)返回的当前reqeust的条件进行匹配,而不是我们配置的所有条件。
原文出处:http://my.oschina.net/zudajun