Ansible基础一Playbook(二)
摘自:http://www.ansible.com.cn/docs/playbooks_intro.html
Handlers: 在发生改变时执行的操作
(当发生改动时)’notify’ actions 会在 playbook 的每一个 task 结束时被触发,而且即使有多个不同的 task 通知改动的发生, ‘notify’ actions 只会被触发一次.
举例来说,比如多个 resources 指出因为一个配置文件被改动,所以 apache 需要重新启动,但是重新启动的操作只会被执行一次.
- name: template configuration file
template: src=template.j2 dest=/etc/foo.conf
notify:
- restart memcached
- restart apache
‘notify’ 下列出的即是 handlers.
Handlers 是由通知者进行 notify, 如果没有被 notify,handlers 不会执行.不管有多少个通知者进行了 notify,等到 play 中的所有 task 执行完成之后,handlers 也只会被执行一次.
handlers:
- name: restart memcached
service: name=memcached state=restarted
- name: restart apache
service: name=apache state=restarted
Handlers 最佳的应用场景是用来重启服务,或者触发系统重启操作.
如果你想立即执行所有的 handler 命令,在1.2及以后的版本,你可以这样做:
tasks:
- shell: some tasks go here
- meta: flush_handlers
- shell: some other tasks
在以上的例子中,任何在排队等候的 handlers 会在执行到 ‘meta’ 部分时,优先执行.这个技巧在有些时候也能派上用场.
执行一个playbook
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-playbook -h
Usage: ansible-playbook playbook.yml
Options:
--ask-vault-pass ask for vault password
-C, --check don't make any changes; instead, try to predict some
of the changes that may occur
-D, --diff when changing (small) files and templates, show the
differences in those files; works great with --check
-e EXTRA_VARS, --extra-vars=EXTRA_VARS
set additional variables as key=value or YAML/JSON
--flush-cache clear the fact cache
--force-handlers run handlers even if a task fails
-f FORKS, --forks=FORKS
specify number of parallel processes to use
(default=5)
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INVENTORY, --inventory-file=INVENTORY
specify inventory host path
(default=/etc/ansible/hosts) or comma separated host
list.
-l SUBSET, --limit=SUBSET
further limit selected hosts to an additional pattern
--list-hosts outputs a list of matching hosts; does not execute
anything else
--list-tags list all available tags
--list-tasks list all tasks that would be executed
-M MODULE_PATH, --module-path=MODULE_PATH
specify path(s) to module library (default=None)
--new-vault-password-file=NEW_VAULT_PASSWORD_FILE
new vault password file for rekey
--output=OUTPUT_FILE output file name for encrypt or decrypt; use - for
stdout
--skip-tags=SKIP_TAGS
only run plays and tasks whose tags do not match these
values
--start-at-task=START_AT_TASK
start the playbook at the task matching this name
--step one-step-at-a-time: confirm each task before running
--syntax-check perform a syntax check on the playbook, but do not
execute it
-t TAGS, --tags=TAGS only run plays and tasks tagged with these values
--vault-password-file=VAULT_PASSWORD_FILE
vault password file
-v, --verbose verbose mode (-vvv for more, -vvvv to enable
connection debugging)
--version show program's version number and exit
Connection Options:
control as whom and how to connect to hosts
-k, --ask-pass ask for connection password
--private-key=PRIVATE_KEY_FILE, --key-file=PRIVATE_KEY_FILE
use this file to authenticate the connection
-u REMOTE_USER, --user=REMOTE_USER
connect as this user (default=None)
-c CONNECTION, --connection=CONNECTION
connection type to use (default=smart)
-T TIMEOUT, --timeout=TIMEOUT
override the connection timeout in seconds
(default=30)
--ssh-common-args=SSH_COMMON_ARGS
specify common arguments to pass to sftp/scp/ssh (e.g.
ProxyCommand)
--sftp-extra-args=SFTP_EXTRA_ARGS
specify extra arguments to pass to sftp only (e.g. -f,
-l)
--scp-extra-args=SCP_EXTRA_ARGS
specify extra arguments to pass to scp only (e.g. -l)
--ssh-extra-args=SSH_EXTRA_ARGS
specify extra arguments to pass to ssh only (e.g. -R)
Privilege Escalation Options:
control how and which user you become as on target hosts
-s, --sudo run operations with sudo (nopasswd) (deprecated, use
become)
-U SUDO_USER, --sudo-user=SUDO_USER
desired sudo user (default=root) (deprecated, use
become)
-S, --su run operations with su (deprecated, use become)
-R SU_USER, --su-user=SU_USER
run operations with su as this user (default=root)
(deprecated, use become)
-b, --become run operations with become (does not imply password
prompting)
--become-method=BECOME_METHOD
privilege escalation method to use (default=sudo),
valid choices: [ sudo | su | pbrun | pfexec | doas |
dzdo | ksu ]
--become-user=BECOME_USER
run operations as this user (default=root)
--ask-sudo-pass ask for sudo password (deprecated, use become)
--ask-su-pass ask for su password (deprecated, use become)
-K, --ask-become-pass
ask for privilege escalation password
示例:
ansible-playbook playbook.yml -f 10
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/hdlptz/1899806
相关文章:

sendmail服务器案例配置
Linux/UNIX下的老牌邮件服务器。Sendmail作为一种免费的邮件服务器软件,已被广泛的应用于各种服务器中,它在稳定性、可移植性、及确保没有bug等方面具有一定的特色,且可以在网络中搜索到大量的使用资料。 实验拓扑图: 注ÿ…

网页制作的中的一些工具代码
1. οncοntextmenu"window.event.returnvaluefalse" 将彻底屏蔽鼠标右键 <table border οncοntextmenureturn(false)><td>no</table> 可用于Table2. <body onselectstart"return false"> 取消选取、防止复制3. οnpaste"r…
神经网络其实和人一样懒惰,喜欢走捷径......
作者 | Jrn-Henrik Jacobsen, Robert Geirhos, Claudio Michaelis,深度学习研究专家译者 | Arvin,责编 | 夕颜出品 | CSDN(ID:CSDNnews)以下为译文:人工智能会很快取代放射科医生吗?最近,研究人…

nodejs获取ASP.Net WebAPI(IIS Windows验证)
处理了很多天,终于使用Nodejs可以发出请求至WebAPI,能够正常处理数据了 首先加入npm包 npm install httpntlm 在app.js中加入代码 var httpntlm require(httpntlm); var fs require(fs);var options {url: http://get001.mygroup.com/InstantNoodle_S…

ubb代码转化html代码
ubb代码转化html代码 public static string UbbDecode(string str){str HtmlEncode(str);str Regex.Replace(str, "/[url](?<url>.?)/[/url]", "<a href${url} target_blank>${url}</a>", RegexOptions.Compiled | RegexOptions.Ig…

如何定位EXC_BAD_ACCESS错误 (info malloc-history)
在 iphone 开发中使用内存时,我们经常会遇到 EXC_BAD_ACCESS 的错误。 出现这个错误的原因是我们访问了一个已经被释放掉的对象,如: implementation FeedbackViewController - (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];_scrollView [[UIScro…
一周内咸鱼疯转2.4W次,最终被所有大厂封杀!
(含答案)所有面试资料及技术好文精选文档都整理到网盘了。Java面试官手册需要加微信免费领取Java面试官手册需要加微信免费领取长按扫码或搜索微信号:gh16670101550,免费领取

java 基础知识三 java变量
1、作用域 {} 包围起来的代码称之为代码块,在块中声明的变量只能在块中使用 2、常量 就是固定不变的量,一旦被定义,它的值就不能再被改变。 3、变量 变量必须在程序中被定义(或声明)后才能使用,而且为每个变…
打通语言理论和统计NLP,Transformers/GNNs架构能做到吗?
作者 | Chaitanya K. Joshi译者 | 苏本如,责编 | 夕颜来源 | CSDN(ID:CSDNnews)我的工程师朋友经常问我:图深度学习听起来很棒,但是有没有实际应用呢?虽然图神经网络被用于Pinterest、阿里巴巴和推特的推荐…

艰辛的面向对象
为什么80%的码农都做不了架构师?>>> 所有的操作系统都不是面向对象的。 所有的操作系统都是基于函数的。ANDROID框架里面的好多类也是基于函数的。很多都是静态的方法。这个框架包括两个部分:一是JAVA部分,一是本地类。本地类不…

计算机网络第一课
1.IPv4与IPv6的区别是什么?在windows 7以上系统中,在设置本地IP地址的时候经常会看到同事含有IPV4协议项与IPV6协议项,并不同于以往windows xp系统中仅有TCP/IP协议项,不少朋友都觉得比较奇怪,询问编辑IPv4与IPv6的区别…

常用函数集农历函数
常用函数集农历函数原来是vb代码,重新整理为VB.NET版的,并在VS2003中编译通过Imports System.MathPublic Class UCnCalendarPrivate Structure SolarHolidayStructDim Month As IntegerDim Day As IntegerDim Recess As IntegerDim HolidayName As Strin…
微软发布代码智能新基准数据集CodeXGLUE,多角度衡量模型优劣
来源 | 微软研究院AI头条编者按:代码智能(code intelligence)目的是让计算机具备理解和生成代码的能力,并利用编程语言知识和上下文进行推理,支持代码检索、补全、翻译、纠错、问答等场景。以深度学习为代表的人工智能…

Spring从菜鸟到高手(四)(上)使用JdbcTemplate类实现用户登陆验证、批量更新
标签:Spring java JdbcTemplate Spring从菜鸟到高手 绝缘材料原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 、作者信息和本声明。否则将追究法律责任。http://tonyaction.blog.51cto.com/227462/42042看了我前面几篇文章的朋…
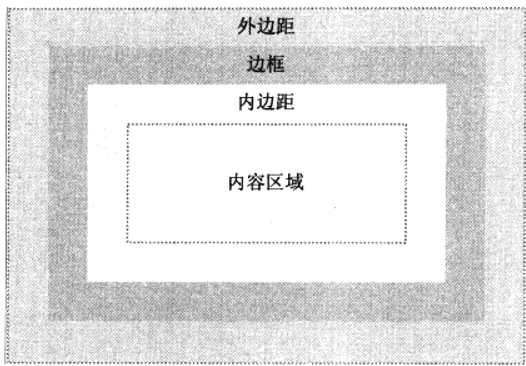
CSS盒模型及边距问题
盒模型是CSS的基石之一,页面的每一个元素都被看作一个矩形框,分别由外边距,边框,内边距,内容组成, 在CSS中,width和height的值指的是内容的宽高,增加外边距,边框…

区分C语言中getch、getche、fgetc、getc、getchar、fgets、gets
首先,这两个函数不是C标准库中的函数, int getch(void) //从标准输入读入一个字符,当你用键盘输入的时候,屏幕不显示你所输入的字符。也就是,不带回显。 int getche(void) //从标准输入读入一个字符&…
无限想象空间,用Python玩转3D人体姿态估计
前言姿态估计,一直是近几年的研究热点。它就是根据画面,捕捉人体的运动姿态,比如 2D 姿态估计:再比如 3D 姿态估计:看着好玩,那这玩应有啥用呢?自动驾驶,大家应该都不陌生࿰…

Mac中将delete键定义为删除键
在Mac中,delete键实际是退格键(Backspace),fndelete才是删除键。这也是从Windows转到Mac时不习惯的地方之一。 通过安装DoubleCommand软件可以解决这个问题。安装后,在System Preferences中找到DoubleCommand找打开在E…

CHIL-SQL-MIN() 函数
MIN() 函数 MIN 函数返回一列中的最小值。NULL 值不包括在计算中。 SQL MIN() 语法 SELECT MIN(column_name) FROM table_name 注释:MIN 和 MAX 也可用于文本列,以获得按字母顺序排列的最高或最低值。 SQL MIN() 实例 我们拥有下面这个 "Orders&quo…
Google排名第一的语言,引数十万人关注:搞定它,技术大牛都甘拜下风
毋庸置疑,Python越来越被认可为程序员新时代的风口语言。无论是刚入门的程序员,还是年薪百万的 BATJ 的大牛都无可否认:Python的应用能力是成为一名码农大神的必要项。 所以,很多程序员把Python当做第一语言来学习。 但对于Python…

CSS滤镜详解
CSS滤镜详解 简介〓 设置文字透明层次,模糊效果,给文字加光晕等这些本来要靠图片才能处理的效果,现在CSS可以既简单又快速的把它实现了……接着往下看就知道了。 〓正文〓 语法:STYLE"filter:filtername(fparameter1, fpa…

php实现单链表
<?php //单链表的存储结构 class Node{ public $data;//数据域 public $next;//指针域 指向下一个结点 function __construct(){ $this->data null; $this->next null; } } //单链表数据类型 class LinkList{ public $data; public $next; function _…

2017-2-23 C#基础 中间变量
用中间变量做这个题 1、“请输入年份:”(1-9999) “请输入月份:”(1-12) “请输入日期:”(要判断大小月,判断闰年) 判断输入的时间日期是否正确 2、计算输入的…

HTA的简单应用
HTA简介:HTA是HTML Application的缩写(HTML应用程序),是软件开发的新概念,直接将HTML保存成HTA的格式,就是一个独立的应用软件,与VB、C等程序语言所设计的软件没什么差别。下面是一个HTA的例子&…
300亿美元,AMD为什么要买Xilinx?
作者 | Just来源 | CSDN(ID:CSDNnews)自2015年5月,Intel(英特尔)以167亿美元收购FPGA生产商Altera后,半导体行业接连传出大整合。上个月,NVIDIA(英伟达)宣布以400亿美元收购芯片设计公司Arm&…

PIM-SSM简介
源特定组播(SSM:Source Specific Multicast)是一种区别于传统组播的新的业务模型,它使用组播组地址和组播源地址同时来标识一个组播会话,而不是向传统的组播服务那样只使用组播组地址来标识一个组播会话。SSM保留了传统PIM-SM模式中的主机显示…

MyBatis开发入门二:一对多连表查询
1. 步骤: (1). 加包(2). 编写db.properties;编写conf.xml,将db.properties加入到conf.xml;引入别名(3). 建立实体类(4). 编写sql操作对应的***Mapper.xml文件(5). 将sql操作对应的***Mapper.xml文件注册到conf.xml文件中(6). 编写…

ASP.NET里的事务处理
出自: http://blog.csdn.net/ycl111/ 事务是一组组合成逻辑工作单元的数据库操作,虽然系统中可能会出错,但事务将控制和维护每个数据库的一致性和完整性。如果在事务过程中没有遇到错误,事务中的所有修改都将永久成为数据库的一部…

JAVA的正则表达式语法
Java 正则表达式表达式意义:1.字符x 字符 x。例如a表示字符a\\ 反斜线字符。在书写时要写为\\\\。(注意:因为java在第一次解析时,把\\\\解析成正则表达式\\,在第二次解析时再解析为\,所以凡是不是1.1列举到的转义…
应届生失业率或继续上升?别怕,这份秋招指南请收好!
受疫情影响,今年的就业形势基本上没跑了:“各行各业,大小企业,全面缩招!”据国家统计局7月份的最新数据显示:20-24岁大专及以上人员(主要为新毕业大学生)失业率比去年同期高 3.3 个百…
