总结
CCL: Cross-modal Correlation Learning with Multi-grained Fusion by Hierarchical Network
Yuxin Peng, Jinwei Qi, Xin Huang and Yuxin Yuan
常见方法
使用深度神经网络(DNN)的跨模态检索大体分为两个步骤:
1 The first learning stage is to generate separate representation for each modality.
2 The second learning stage is to get the cross-modal common representation.
前人缺点
1 第一步中未考虑模型间的联系
2 第二步loss过于简单,也没有考虑模型间的联系
3 未考虑细粒度的影响
In the first learning stage, they only model intra-modality correlation, but ignore inter-modality one which can provide rich complementary context for learning better separate representation;
in the second learning stage, they only adopt shallow network structures with single-loss regularization, which ignores the intrinsic relevance of intra-modality and inter-modality correlation, so cannot effectively exploit and balance them to improve generalization performance;
only original instances are considered while the complementary fine-grained clues provided by their patches are ignored.
本文贡献点
针对前人缺点,作者提出了相对应的方法加以优化(显然前人缺点就是本文优点)。
(1) Cross-modal correlation exploiting. In the first learning stage, CCL exploits multi-level association with joint optimization to preserve the complementary context from intra-modality and inter-modality correlation simultaneously.
(2) Multi-task learning. In the second learning stage, a multi-task learning strategy is designed to adaptively balance the intra-modality semantic category constraints and inter-modality pairwise similarity constraints.
(3) Multi-grained fusion. CCL adopts multi-grained modeling, which fuses the coarse-grained instances and fine-grained patches to make cross-modal correlation more precise.
本文在三个数据集上与九种方法进行了比较证明所提方法的优越性。
本文方法
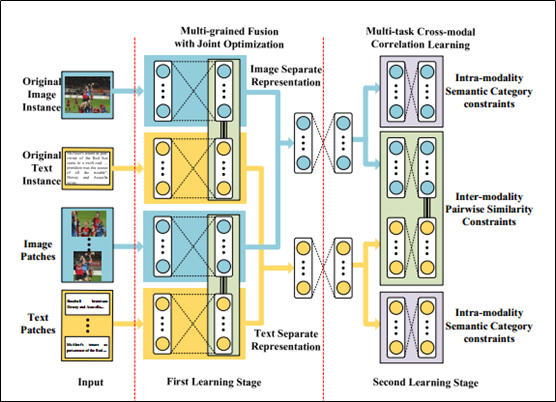
网络结构如上图所示。
A. The First Learning Stage: Multi-grained Fusion with Joint Optimization
1) Coarse-grained learning with original instances
两层DBN。First, two types of Deep Belief Network (DBN) [35] are used to model the distribution over the features of each modality, where Gaussian Restricted Boltzmann Machine (RBM) is adopted to model the image instances and Replicated Softmax model [29] is for text instances. We define the probability functions of each DBN as follows:
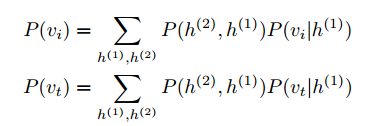
Then we simultaneously model intra-modality and inter-modality correlation by joint optimization for Q(i) of image instance and Q(t) of text instance. We minimize the following loss function to jointly optimize the reconstruction learning error and correlation learning error:

2) Fine-grained learning with patches
We first divide each original image and text instance into several patches.
细粒度的具体分割方法:
图像分割:Specifically, we adopt selective search [36] to extract several region proposals, which can find the visual objects in the image instance containing rich fine-grained information. For the image, all 3 datasets share the same segmentation method. Selective search [36] is adopted to divide the image into several region proposals and then up to largest 10 patches.
文本分割(根据数据集不同而不同):For text, the segmentation is performed according to the form of text, where the text is divided into paragraphs, sentences or words. are automatically selected. Besides, the texts vary among different datasets, so different segmentation methods are adopted. The texts of Wikipedia dataset are in the form of articles with several paragraphs, thus we divide them by paragraph. The texts in Pascal Sentence are made up by several sentences, so it is divided by each sentence. Since the text instances in NUSWIDE-10k dataset are made up of several tags which has no context relationship, we divide them by word if the number of words is less than 4, otherwise divide them into 4 patches for uniformity where each patch has the same number of words. It is noted that for each dataset, the feature extraction on the patches is same as that on the original instances.
同粗粒度一样,细粒度也采用两层DBN。Similar with the original instances, a two-pathway network structure is constructed with two types of DBN adopted over the features extracted from the patches of image and text. For the patches within one original instance, average fusion is adopted to combine their representations obtained from DBN, and the results are denoted as U (i) and U (t). Then we link the two pathway network at the code layer, and minimize the following loss function to model intra-modality and inter-modality correlation with joint optimization:
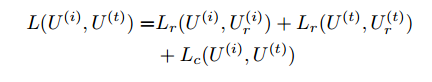
3) Multi-grained Fusion
On the top of joint RBM, a three-layer feed-forward network is used for further optimization with softmax loss.
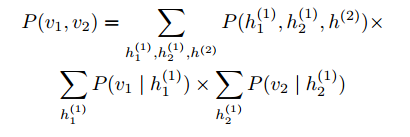
B. The Second Learning Stage: Multi-task Cross-modal Correlation Learning
Specifically, a neighborhood graph G = (V; E) is constructed in a mini-batch of data for one iteration, where the vertices V represent the image and text instances, and E is the similarity matrix between data of two modalities according to their labels, which is defined as follows:

Thus, the contrastive loss between the image and text pairs is defined to model the pairwise similar and dissimilar constraints as follows:

Then, for intra-modality semantic category constraints, a classification process is employed to exploit the intrinsic semantic information within each modality, which can classify data of each modality into one of n categories. Thus, we present intra-modality semantic category constraints as an n-way softmax layer, where n is number of categories. Cross entropy loss is minimized as follows:
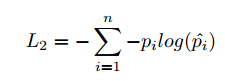
严重怀疑文章中这个式子多写了一个负号。
where the predicted probability distribution is denoted as p^ i, and pi is the target probability distribution. By minimizing the above loss function, the semantically discrimination ability of common representation can be greatly enhanced.
具体的参数设置(神经元数目设定等依据数据集而改变,文章在实验部分以Wikipedia为例提到过)。
DBN、RBM、feed-back等实现作者均使用了deepnet:
https://github.com/nitishsrivastava/deepnet
第二部分的三层全连接层使用caffe[41]实现。
实验
文章中的实验可分为四个方面:
1 文章中实验将手动提取特征和CNN提取特征进行了比较。
2 文章中使用自己的CCL与九种其他方法就两方面进行了比较:一方面是跨模态检索,即文搜图或图搜文;另一方面是单一模态搜索全部模态。
3 文章就粗粒度、细粒度进行了单独实验作为对比。
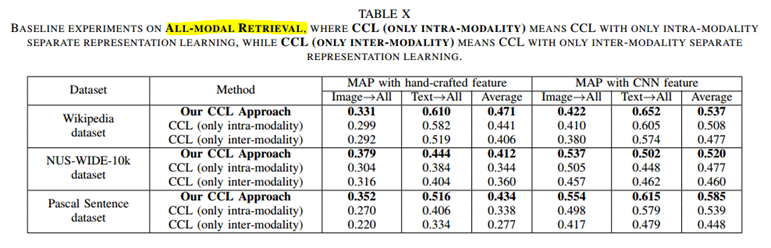
4 文章中就第一部分是否使用联合损失约束进行了实验比对。
数据集
Wikipedia dataset [7] is the most widely-used dataset for cross-modal retrieval task. This dataset consists of 2,866 image/text pairs of 10 categories, and is randomly divided as follows: 2,173 pairs for training, 231 pairs for validation and 462 pairs for testing.
NUS-WIDE-10K dataset [38] is generated from NUSWIDE dataset. NUS-WIDE dataset consists of about 270,000 images with their tags categorized into 81 categories. While NUS-WIDE-10k dataset has totally 10,000 image/text pairs
selected evenly from the 10 largest categories of NUS-WIDE dataset, which are animal, cloud, flower, food, grass, person, sky, toy, water and window. The dataset are split into three subsets: Training set with 8,000 pairs, testing set with 1,000 pairs and validation set with 1,000 pairs.
Pascal Sentence dataset [39] is generated from 2008 PASCAL development kit. This dataset contains 1,000 images which are evenly categorized into 20 categories, and each image has 5 corresponding sentences which makes up one document. For each category, 40 documents are selected for training, 5 documents for testing and 5 documents for validation.
特征提取
图片手动特征提取根据数据集而变化,均是由三种不同的特征串联而成。文本特征均使用BOW。
CNN特征使用VGGNet[40]的fc7层的4096维特征。
对比方法
• CCA [18] learns project matrices to maximize the correlation between the projected features of different modalities in a common space.
• CFA [22] minimizes the Frobenius norm between the data of different modalities after projecting them into one common space.
• KCCA [19] uses kernel function to project the features into a higher-dimensional space, and then learns a common space by CCA. In the experiments, we use not only Gaussian kernel (Gaussian) as [19], but also an additional polynomial kernel (Poly).
• JRL [10] learns a common space by using semantic information, with semi-supervised regularization and sparse regularization.
• LGCFL [37] jointly learns basis matrices of different modalities, by using a local group based priori in the formulation to fully take advantage of popular block based features.
• Bimodal AE [17] is based on a deep autoencoder network. Multiple instances are input into the network to learn common representation at the joint layer, which also has the ability to reconstruct both modalities.
• Multimodal DBN [16] first adopts two separate DBN to model each modality separately, and then learns the joint representation by using a joint RBM on the top of two DBN.
• Corr-AE [12] consists of two autoencoder networks coupled at the code layer to simultaneously model the reconstruction error and correlation loss. It should be noted that Corr-AE has two extensions as discussed in Section II, and in the experiments we compare with the best results of the three models.
• CMDN (our previous conference paper [13]) adopts multiple deep networks to generate separate representation and learns common representation with a stacked network.
评判标准
mean average precision (MAP)
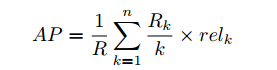
n:查询结果总数
R:相关总数
R_k:前k个中的相关数
rel_k:第k个相关则为1,反之为0
实验结果
(1)
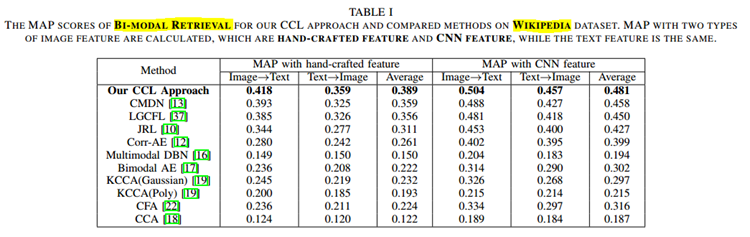
CCL:以图搜文 以文搜图 即BI-MODEL


(2)
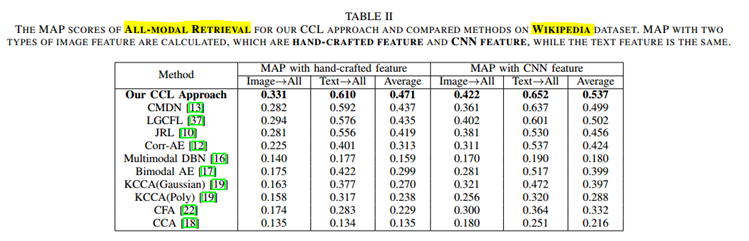
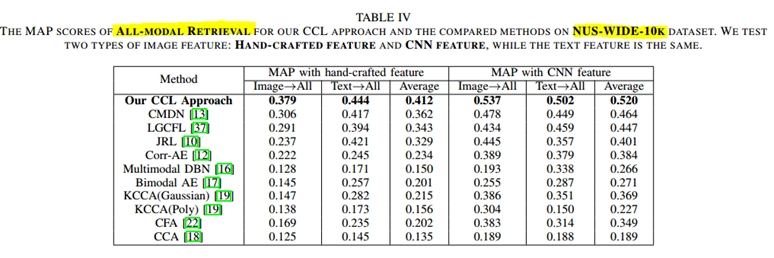
CCL:以文(或图)搜索全部结果 即 ALL-MODEL
KCCA(Poly)说明CNN特征不一定绝对会取得更好的效果。
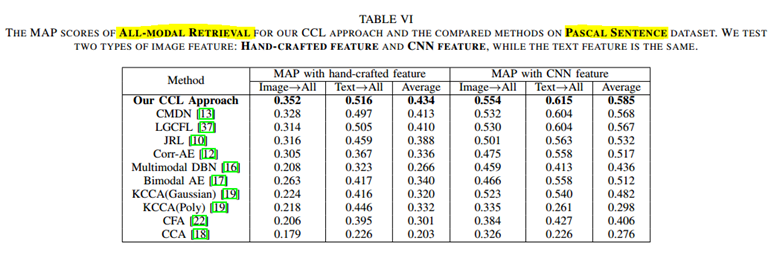
(3)
不同数据集下粒度的影响
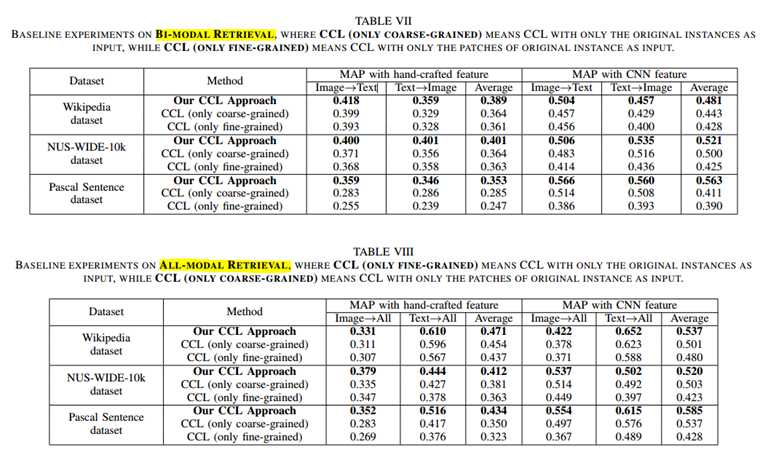
(4)
不同数据集下是否加入联合约束的影响

参考文献
[1] Y. Hu, X. Cheng, L.-T. Chia, X. Xie, D. Rajan, and A.-H. Tan,
“Coherent phrase model for efficient image near-duplicate retrieval,”
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (TMM), vol. 11, no. 8, pp. 1434–
1445, 2009.
[2] Y. Peng and C.-W. Ngo, “Clip-based similarity measure for querydependent clip retrieval and video summarization,” IEEE Transactions
on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT), vol. 16, no. 5,
pp. 612–627, 2006.
[3] A. Znaidia, A. Shabou, H. Le Borgne, C. Hudelot, and N. Paragios,
“Bag-of-multimedia-words for image classification,” in International
Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2012, pp. 1509–1512.
[4] Y. Liu, W.-L. Zhao, C.-W. Ngo, C.-S. Xu, and H.-Q. Lu, “Coherent bagof audio words model for efficient large-scale video copy detection,” in
ACM International Conference on Image and Video Retrieval (CIVR),
2010, pp. 89–96.
[5] Y. Zhuang, Y. Yang, and F. Wu, “Mining semantic correlation of heterogeneous multimedia data for cross-media retrieval,” IEEE Transactions
on Multimedia (TMM), vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 221–229, 2008.
[6] Y. Yang, Y. Zhuang, F. Wu, and Y. Pan, “Harmonizing hierarchical
manifolds for multimedia document semantics understanding and crossmedia retrieval,” IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (TMM), vol. 10,
no. 3, pp. 437–446, 2008.
[7] N. Rasiwasia, J. Costa Pereira, E. Coviello, G. Doyle, G. R. Lanckriet, R. Levy, and N. Vasconcelos, “A new approach to cross-modal
multimedia retrieval,” in ACM International Conference on Multimedia
(ACM-MM), 2010, pp. 251–260.
[8] P. Daras, S. Manolopoulou, and A. Axenopoulos, “Search and retrieval
of rich media objects supporting multiple multimodal queries,” IEEE
Transactions on Multimedia (TMM), vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 734–746, 2012.
[9] L. Zhang, B. Ma, G. Li, Q. Huang, and Q. Tian, “Cross-modal retrieval
using multi-ordered discriminative structured subspace learning,” IEEE
Transactions on Multimedia (TMM), vol. PP, no. 99, pp. 1–1, 2016.
[10] X. Zhai, Y. Peng, and J. Xiao, “Learning cross-media joint representation
with sparse and semi-supervised regularization,” IEEE Transactions on
Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT), vol. 24, pp. 965–
978, 2014.
[11] Y. Gong, Q. Ke, M. Isard, and S. Lazebnik, “A multi-view embedding
space for modeling internet images, tags, and their semantics,” International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV), vol. 106, no. 2, pp. 210–233,
2014.
[12] F. Feng, X. Wang, and R. Li, “Cross-modal retrieval with correspondence
autoencoder,” in ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACMMM), 2014, pp. 7–16.
[13] Y. Peng, X. Huang, and J. Qi, “Cross-media shared representation by
hierarchical learning with multiple deep networks,” in International Joint
Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), 2016, pp. 3846–3853.
[14] G. Andrew, R. Arora, J. A. Bilmes, and K. Livescu, “Deep canonical
correlation analysis,” in International Conference on Machine Learning
(ICML), 2013, pp. 1247–1255.
[15] F. Yan and K. Mikolajczyk, “Deep correlation for matching images
and text,” in Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
(CVPR), 2015, pp. 3441–3450.
[16] N. Srivastava and R. Salakhutdinov, “Learning representations for multimodal data with deep belief nets,” in International Conference on
Machine Learning (ICML) Workshop, 2012.
[17] J. Ngiam, A. Khosla, M. Kim, J. Nam, H. Lee, and A. Y. Ng,
“Multimodal deep learning,” in International Conference on Machine
Learning (ICML), 2011, pp. 689–696.
[18] H. Hotelling, “Relations between two sets of variates,” Biometrika, pp.
321–377, 1936.
[19] D. R. Hardoon, S. Szedmak, and J. Shawe-Taylor, “Canonical correlation ´
analysis: An overview with application to learning methods,” Neural
Computation, vol. 16, no. 12, pp. 2639–2664, 2004.
[20] H. Bredin and G. Chollet, “Audio-visual speech synchrony measure
for talking-face identity verification,” in International Conference on
Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), vol. 2, 2007, p.
233.
[21] B. Klein, G. Lev, G. Sadeh, and L. Wolf, “Associating neural word
embeddings with deep image representations using fisher vectors,” in
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2015,
pp. 4437–4446.
[22] D. Li, N. Dimitrova, M. Li, and I. K. Sethi, “Multimedia content
processing through cross-modal association,” in ACM International
Conference on Multimedia (ACM-MM), 2003, pp. 604–611.
[23] Y. Hua, S. Wang, S. Liu, A. Cai, and Q. Huang, “Cross-modal correlation
learning by adaptive hierarchical semantic aggregation,” IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (TMM), vol. 18, no. 6, pp. 1201–1216, 2016.
[24] X. Zhai, Y. Peng, and J. Xiao, “Heterogeneous metric learning with joint
graph regularization for cross-media retrieval,” in AAAI Conference on
Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2013.
[25] K. Wang, R. He, L. Wang, W. Wang, and T. Tan, “Joint feature selection
and subspace learning for cross-modal retrieval,” IEEE Transactions on
Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), vol. 38, no. 10, pp.
2010–2023, 2016.
[26] D. Wang, P. Cui, M. Ou, and W. Zhu, “Learning compact hash codes
for multimodal representations using orthogonal deep structure,” IEEE
Transactions on Multimedia (TMM), vol. 17, no. 9, pp. 1404–1416,
2015.
[27] L. Pang, S. Zhu, and C. Ngo, “Deep multimodal learning for affective analysis and retrieval,” IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (TMM),
vol. 17, no. 11, pp. 2008–2020, 2015.
[28] D. Wang, P. Cui, M. Ou, and W. Zhu, “Deep multimodal hashing
with orthogonal regularization,” in International Joint Conference on
Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), 2015, pp. 2291–2297.
[29] R. Salakhutdinov and G. E. Hinton, “Replicated softmax: an undirected
topic model,” in Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems
(NIPS), 2009, pp. 1607–1614.
[30] P. Vincent, H. Larochelle, Y. Bengio, and P. Manzagol, “Extracting and
composing robust features with denoising autoencoders,” in International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2008, pp. 1096–1103.
[31] Y. Sun, X. Wang, and X. Tang, “Deep learning face representation by
joint identification-verification,” vol. 27, 2014, pp. 1988–1996.
[32] S. Ren, K. He, R. B. Girshick, and J. Sun, “Faster R-CNN: towards realtime object detection with region proposal networks,” in Conference on
Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), 2015, pp. 91–99.
[33] A. H. Abdulnabi, G. Wang, J. Lu, and K. Jia, “Multi-task CNN model for
attribute prediction,” IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (TMM), vol. 17,
no. 11, pp. 1949–1959, 2015.
[34] Y. Peng, X. Zhai, Y. Zhao, and X. Huang, “Semi-supervised crossmedia feature learning with unified patch graph regularization,” IEEE
Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT),
vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 583–596, 2016.
[35] G. E. Hinton, S. Osindero, and Y. W. Teh, “A fast learning algorithm for
deep belief nets,” Neural Computation, vol. 18, no. 7, pp. 1527–1554,
2006.
[36] J. R. R. Uijlings, K. E. A. van de Sande, T. Gevers, and A. W. M. Smeulders, “Selective search for object recognition,” International Journal of
Computer Vision (IJCV), vol. 104, no. 2, pp. 154–171, 2013.
[37] C. Kang, S. Xiang, S. Liao, C. Xu, and C. Pan, “Learning consistent feature representation for cross-modal multimedia retrieval,” IEEE
Transactions on Multimedia (TMM), vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 370–381, 2015.
[38] T. Chua, J. Tang, R. Hong, H. Li, Z. Luo, and Y. Zheng, “Nus-wide: a
real-world web image database from national university of singapore,”
in ACM International Conference on Image and Video Retrieval (CIVR),
2009, pp. 1–9.
[39] A. Farhadi, S. M. M. Hejrati, M. A. Sadeghi, P. Young, C. Rashtchian,
J. Hockenmaier, and D. A. Forsyth, “Every picture tells a story: Generating sentences from images,” in European Conference on Computer
Vision (ECCV), 2010, pp. 15–29.
[40] M. Simon, E. Rodner, and J. Denzler, “Imagenet pre-trained models with
batch normalization,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1612.01452, 2016.
[41] Y. Jia, E. Shelhamer, J. Donahue, S. Karayev, J. Long, R. Girshick,
S. Guadarrama, and T. Darrell, “Caffe: Convolutional architecture for
fast feature embedding,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1408.5093, 2014.