python字典{:4}_Python字典101:详细的视觉介绍
python字典{:>4}
欢迎 (Welcome)
In this article, you will learn how to work with Python dictionaries, an incredibly helpful built-in data type that you will definitely use in your projects.
在本文中,您将学习如何使用Python字典,Python字典是一种非常有用的内置数据类型,您肯定会在项目中使用。
In particular, you will learn:
特别是,您将学到:
- What dictionaries are used for and their main characteristics.词典的用途及其主要特征。
- Why they are important for your programming projects.为什么它们对您的编程项目很重要。
- The "anatomy" of a dictionary: keys, values, and key-value pairs.字典的“解剖结构”:键,值和键值对。
- The specific rules that determine if a value can be a key.确定值是否可以为键的特定规则。
- How to access, add, modify, and delete key-value pairs.如何访问,添加,修改和删除键值对。
- How to check if a key is in a dictionary.如何检查键是否在字典中。
- What the length of a dictionary represents.字典的长度代表什么。
- How to iterate over dictionaries using for loops.如何使用for循环遍历字典。
- What built-in dictionary methods you can use to leverage the power of this data type.您可以使用哪些内置词典方法来利用此数据类型的功能。
At the end of this article, we will dive into a simple project to apply your knowledge: we will write a function that creates and returns a dictionary with a particular purpose.
在本文的结尾,我们将深入一个简单的项目来应用您的知识:我们将编写一个函数,该函数创建并返回具有特定用途的字典。
Let's begin! 🔅
让我们开始! 🔅
🔸上下文词典 (🔸 Dictionaries in Context)
Let's start by discussing the importance of dictionaries. To illustrate this, let me do a quick comparison with another data type that you are probably familiar with: lists.
让我们从讨论字典的重要性开始。 为了说明这一点,让我与您可能熟悉的另一种数据类型进行快速比较:列表。
When you work with lists in Python, you can access an element using a index, an integer that describes the position of the element in the list. Indices start from zero for the first element and increase by one for every subsequent element in the list. You can see an example right here:
在Python中使用列表时,可以使用索引访问元素,该索引是描述元素在列表中位置的整数 。 对于第一个元素,索引从零开始,对于列表中的每个后续元素,索引从一开始增加。 您可以在这里看到一个示例:
But what if we need to store two related values and keep this "connection" in our code? Right now, we only have single, independent values stored in a list.
但是,如果我们需要存储两个相关值并将此“连接”保留在代码中怎么办? 现在,我们只有一个独立的值存储在列表中。
Let's say that we want to store names of students and "connect" each name with the grades of each particular student. We want to keep the "connection" between them. How would you do that in Python?
假设我们要存储学生的姓名,并将每个姓名与每个特定学生的成绩“连接”起来。 我们要保持它们之间的“联系”。 您将如何在Python中做到这一点?
If you use nested lists, things would get very complex and inefficient after adding only a few items because you would need to use two or more indices to access each value, depending on the final list. This is where Python dictionaries come to the rescue.
如果使用嵌套列表,则仅添加少量项目后,事情就会变得非常复杂且效率低下,因为您需要使用两个或多个索引来访问每个值,具体取决于最终列表。 这就是Python字典的得力助手。
认识字典 (Meet Dictionaries)
A Python dictionary looks like this (see below). With a dictionary, you can "connect" a value to another value to represent the relationship between them in your code. In this example,"Gino" is "connected" to the integer 15 and the string "Nora" is "connected" to the integer 30.
Python字典看起来像这样(见下文)。 使用字典,您可以将一个值“连接”到另一个值,以表示代码中它们之间的关系。 在此示例中,“ Gino”被“连接”到整数15,而字符串“ Nora”被“连接”到整数30。
Let's see the different elements that make a dictionary.
让我们看看构成字典的不同元素。
Dictionary Python词典的“解剖” (🔹 The "Anatomy" of a Python Dictionary)
Since a dictionary "connects" two values, it has two types of elements:
由于字典“连接”两个值,因此它具有两种类型的元素:
Keys: a key is a value used to access another value. Keys are the equivalent of "indices" in strings, lists, and tuples. In dictionaries, to access a value, you use the key, which is a value itself.
密钥:密钥是用于访问另一个值的值。 键等效于字符串,列表和元组中的“索引”。 在字典中,要访问值,请使用键,键本身就是值。
Values: these are the values that you can access with their corresponding key.
值:这些是您可以使用其相应的键访问的值。
These two elements form what is called a key-value pair (a key with its corresponding value).
这两个元素形成所谓的键值对 (具有对应值的键)。
句法 (Syntax)
This is an example of a Python Dictionary mapping the string "Gino" to the number 15 and the string "Nora" to the number 30:
这是Python字典将字符串“ Gino”映射为数字15并将字符串“ Nora”映射为数字30的示例:
>>> {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30}To create a dictionary, we use curly brackets
{ }.要创建字典,请使用大括号
{ }。- Between these curly brackets, we write key-value pairs separated by a comma.在这些大括号之间,我们编写了以逗号分隔的键/值对。
- For the key-value pairs, we write the key followed by a colon, a space, and the value that corresponds to the key.对于键值对,我们编写键,后跟冒号,空格以及与键对应的值。
💡 Tips:
💡 提示:
- For readability and style purposes, it is recommended to add a space after each comma to separate the key-value pairs.出于可读性和样式目的,建议在每个逗号后添加一个空格以分隔键值对。
You can create an empty dictionary with an empty pair of curly brackets
{}.您可以创建一个空的带有一对大括号
{}字典。
按键重要规则 (Important Rules for Keys)
Not every value can be a key in a Python dictionary. Keys have to follow a set of rules:
并非每个值都可以是Python字典中的键。 密钥必须遵循一组规则:
According to the Python Documentation:
根据Python文档 :
- Keys have to be unique within one dictionary.键在一个字典中必须唯一。
It is best to think of a dictionary as a set of key: value pairs, with the requirement that the keys are unique (within one dictionary).
最好将字典视为一组键:值对,并要求键是唯一的 (在一个字典中)。
- Keys have to be immutable.键必须是不可变的。
Unlike sequences, which are indexed by a range of numbers, dictionaries are indexed by keys, which can be any immutable type; strings and numbers can always be keys.
与通过数字范围索引的序列不同,字典通过key索引, key可以是任何不可变的类型。 字符串和数字始终可以是键。
- If the key is a tuple, it can only contain strings, numbers or tuples.如果键是元组,则只能包含字符串,数字或元组。
Tuples can be used as keys if they contain only strings, numbers, or tuples; if a tuple contains any mutable object either directly or indirectly, it cannot be used as a key.
如果元组仅包含字符串,数字或元组,则它们可用作键。 如果元组直接或间接包含任何可变对象,则不能将其用作键。
- Lists cannot be keys because they are mutable. This is a consequence of the previous rule.列表不能是键,因为它们是可变的。 这是先前规则的结果。
You can’t use lists as keys, since lists can be modified in place using index assignments, slice assignments, or methods like
append()andextend().您不能将列表用作键,因为可以使用索引分配,切片分配或诸如
append()和extend()类的方法在适当位置修改列表。
💡 Note: Values have no specific rules, they can be either mutable or immutable values.
💡 注意:值没有特定的规则,它们可以是可变值或不可变值。
🔸行动字典 (🔸 Dictionaries in Action)
Now let's see how we can work with dictionaries in Python. We are going to access, add, modify, and delete key-value pairs.
现在让我们看看如何在Python中使用字典。 我们将访问,添加,修改和删除键值对。
We will start working with this dictionary, assigned to the ages variable:
我们将开始使用分配给ages变量的该词典:
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30}使用键访问值 (Access Values using Keys)
If we need to access the value associated with a specific key, we write the name of the variable that references the dictionary followed by square brackets [] and, within the square brackets, the key that corresponds to the value:
如果需要访问与特定键相关联的值,请编写引用字典的变量的名称,后跟方括号[]并在方括号内编写与该值对应的键:
<variable>[<key>]This is an example of how we can access the value that corresponds to the string "Gino":
这是如何访问与字符串"Gino"相对应的值的示例:
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30}
>>> ages["Gino"]
15Notice that the syntax is very similar to indexing a string, tuple, or list, but now we are using the key as the index instead of an integer.
注意,语法与索引字符串,元组或列表非常相似,但是现在我们使用键作为索引而不是整数。
If we want to access the value that corresponds to "Nora", we would do this:
如果要访问与“ Nora”相对应的值,则可以这样做:
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30}
>>> ages["Nora"]
30💡 Tip: If you try to access a key that does not exist in the dictionary, you will get a KeyError:
提示:如果您尝试访问字典中不存在的键,则会收到KeyError :
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30}
>>> ages["Talina"]
Traceback (most recent call last):File "<pyshell#10>", line 1, in <module>ages["Talina"]
KeyError: 'Talina'添加键值对 (Add Key-Value Pairs)
If a key-value pair doesn't exist in the dictionary, we can add it. To do this, we write the variable that references the dictionary followed by the key within square brackets, an equal sign, and the new value:
如果字典中不存在键/值对,则可以添加它。 为此,我们编写引用字典的变量,其后跟随方括号,等号和新值的键:
This is an example in IDLE:
这是IDLE中的一个示例:
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30}# Add the key-value pair "Talina": 24
>>> ages["Talina"] = 24# The dictionary now has this key-value pair
>>> ages
{'Gino': 15, 'Nora': 30, 'Talina': 24}修改键值对 (Modify a Key-Value Pair)
To modify the value associated to a specific key, we use the same syntax that we use to add a new key-value pair, but now we will be assigning the new value to an existing key:
要修改与特定键相关联的值,我们使用与添加新键值对相同的语法,但是现在我们将为现有键分配新值:
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30}# The key "Gino" already exists in the dictionary, so its associated value
# will be updated to 45.
>>> ages["Gino"] = 45# The value was updated to 45.
>>> ages
{'Gino': 45, 'Nora': 30}删除键值对 (Deleting a Key-Value Pair)
To delete a key-value pair, you would use the del keyword followed by the name of the variable that references the dictionary and, within square brackets [], the key of the key-value pair:
要删除键值对,可以使用del关键字,后跟引用字典的变量的名称,并在方括号[] ,键值对的键:
This is an example in IDLE:
这是IDLE中的一个示例:
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30, "Talina": 45}# Delete the key-value pair "Gino": 15.
>>> del ages["Gino"]# The key-value pair was deleted.
>>> ages
{'Nora': 30, 'Talina': 45}🔹检查钥匙是否在字典中 (🔹 Check if a Key is in a Dictionary)
Sometimes, it can be very helpful to check if a key already exists in a dictionary (remember that keys have to be unique).
有时,检查字典中是否已存在键可能非常有帮助(请记住,键必须是唯一的)。
According to the Python Documentation:
根据Python文档 :
To check whether a single key is in the dictionary, use the
inkeyword.要检查字典中是否有单个键 ,请使用
in关键字。
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30, "Talina": 45}
>>> "Talina" in ages
True
>>> "Gino" in ages
True
>>> "Lulu" in ages
FalseThe in operator checks the keys, not the values. If we write this:
in运算符将检查键,而不是值。 如果我们这样写:
>>> 15 in ages
FalseWe are checking if the key 15 is in the dictionary, not the value. This is why the expression evaluates to False.
我们正在检查键 15是否在字典中,而不是值中。 这就是为什么表达式求值为False 。
💡 Tip: You can use the in operator to check if a value is in a dictionary with <dict>.values().
提示:您可以使用in运算符通过<dict> .values()检查值是否在字典中。
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30, "Talina": 45}
>>> 30 in ages.values()
True
>>> 10 in ages.values()
FalseDictionary Python字典的长度 (🔸 Length of a Python Dictionary)
The length of a dictionary is the number of key-value pairs it contains. You can check the length of a dictionary with the len() function that we commonly use, just like we check the length of lists, tuples, and strings:
字典的长度是它包含的键值对的数量。 您可以使用我们常用的len()函数检查字典的长度,就像我们检查列表,元组和字符串的长度一样:
# Two key-value pairs. Length 2.
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30}
>>> len(ages)
2# Three key-value pairs. Length 3.
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30, "Talina": 45}
>>> len(ages)
3Python在Python中遍历字典 (🔹 Iterating over Dictionaries in Python)
You can iterate over dictionaries using a for loop. There are various approaches to do this and they are all equally relevant. You should choose the approach that works best for you, depending on what you are trying to accomplish.
您可以使用for循环遍历字典。 有多种方法可以做到这一点,并且它们都是同等重要的。 您应该根据自己要实现的目标选择最适合自己的方法。
第一种选择-遍历键 (First Option - Iterate over the Keys)
We can iterate over the keys of a dictionary like this:
我们可以像这样遍历字典的键:
for <key> in <dictionary>:# Do thisFor example:
例如:
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30, "Talina": 45}
>>> for student in ages:print(student)Gino
Nora
Talina第二种选择-遍历键值对 (Second Option - Iterate over the Key-Value Pairs)
To do this, we need to use the built-in method .items(), which allows us to iterate over the key-value pairs as tuples of this format (key, value).
为此,我们需要使用内置方法.items() ,该方法允许我们将键值对作为此格式的元组(key, value)进行迭代。
for <key-value-pair-as-tuple> in <dictionary>.items():# Do thisFor example:
例如:
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30, "Talina": 45}>>> for pair in ages.items():print(pair)('Gino', 15)
('Nora', 30)
('Talina', 45)第三种选择-将键和值分配给各个变量 (Third Option - Assign Keys and Values to Individual Variables)
With .items() and for loops, you can use the power of a tuple assignment to directly assign the keys and values to individual variables that you can use within the loop:
通过.items()和for循环,您可以使用元组分配的功能将键和值直接分配给可以在循环中使用的各个变量:
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30, "Talina": 45}# Tuple assignment to assign the key to the variable key
# and the value to the variable value.
>>> for key, value in ages.items():print("Key:", key, "; Value:", value)Key: Gino ; Value: 15
Key: Nora ; Value: 30
Key: Talina ; Value: 45第四种选择-遍历值 (Fourth Option - Iterate over the Values)
You can iterate over the values of a dictionary using the .values() method.
您可以使用.values()方法遍历字典的值。
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30, "Talina": 45}
>>> for age in ages.values():print(age)15
30
45🔸字典方法 (🔸 Dictionary Methods)
Dictionaries include very helpful built-in methods that can save you time and work to perform common functionality:
词典包含非常有用的内置方法,可以节省您的时间和精力来执行常见功能:
。明确() (.clear())
This method removes all the key-value pairs from the dictionary.
此方法从字典中删除所有键-值对。
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30, "Talina": 45}
>>> ages.clear()
>>> ages
{}.get(<键>,<默认>) (.get(<key>, <default>))
This method returns the value associated with the key. Otherwise, it returns the default value that was provided as the second argument (this second argument is optional).
此方法返回与键关联的值。 否则,它将返回作为第二个参数提供的默认值(此第二个参数是可选的)。
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30, "Talina": 45}
>>> ages.get("Nora")
30
>>> ages.get("Nor", "Not Found")
'Not Found'If you don't add a second argument, this is equivalent to the previous syntax with square brackets []that you learned:
如果您不添加第二个参数,则这与您之前所学的带方括号[]语法等效:
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30, "Talina": 45}
>>> ages["Nora"]
30
>>> ages.get("Nora")
30.pop(<键>,<默认>) (.pop(<key>, <default>))
This method removes the key-value pair from the dictionary and returns the value.
此方法从字典中删除键值对并返回值。
>>> ages = {"Gino": 15, "Nora": 30, "Talina": 45}
>>> ages.pop("Talina")
45
>>> ages
{'Gino': 15, 'Nora': 30}.update(<其他>) (.update(<other>))
This method replaces the values of a dictionary with the values of another dictionary only for those keys that exist in both dictionaries.
此方法仅针对两个词典中都存在的键将词典的值替换为另一个词典的值。
An example of this would be a dictionary with the original grades of three students (see code below). We only want to replace the grades of the students who took the make-up exam (in this case, only one student took the make-up exam, so the other grades should remain unchanged).
这样的一个例子是原始成绩为三个学生的字典(请参见下面的代码)。 我们只想替换参加补考的学生的成绩(在这种情况下,只有一个学生补考了,所以其他成绩应该保持不变)。
>>> grades = {"Gino": 0, "Nora": 98, "Talina": 99}
>>> new_grades = {"Gino": 67}
>>> grades.update(new_grades)
>>> grades
{'Gino': 67, 'Nora': 98, 'Talina': 99}By using the .update() method, we could update the value associated with the string "Gino" in the original dictionary since this is the only common key in both dictionaries.
通过使用.update()方法,我们可以更新与原始字典中的字符串“ Gino”相关联的值,因为这是两个字典中唯一的公用键。
The original value would be replaced by the value associated with this key in the dictionary that was passed as argument to .update().
原始值将替换为字典中与此键关联的值,该键作为参数传递给.update()。
💡 Tips: To learn more about dictionary methods, I recommend reading this article in the Python Documentation.
💡 提示:要了解有关字典方法的更多信息,建议阅读Python文档中的本文 。
🔹迷你项目-频率字典 (🔹 Mini Project - A Frequencies Dictionary)
Now you will apply your knowledge by writing a function freq_dict that creates and returns a dictionary with the frequency of each element of a list, string, or tuple (the number of times the element appears). The elements will be the keys and the frequencies will be the values.
现在,您将通过编写函数freq_dict来运用您的知识,该函数创建并返回一个字典,该字典具有列表,字符串或元组中每个元素的出现频率(该元素出现的次数)。 元素将是键,而频率将是值。
码 (Code)
We will be writing the function step-by-step to see the logic behind each line of code.
我们将逐步编写函数,以查看每一行代码背后的逻辑。
Step 1: The first thing that we need to do is to write the function header. Notice that this function only takes one argument, the list, string or tuple, which we call
data.步骤1:我们要做的第一件事是编写函数标头。 注意,此函数仅采用一个参数,即列表,字符串或元组,我们将其称为
data。
def freq_dict(data):Step 2: Then, we need to create an empty dictionary that will map each element of the list, string, or tuple to its corresponding frequency.
步骤2:然后,我们需要创建一个空字典,该字典将列表,字符串或元组的每个元素映射到其对应的频率。
def freq_dict(data):freq = {}Step 3: Then, we need to iterate over the list, string, or tuple to determine what to do with each element.
步骤3:然后,我们需要遍历列表,字符串或元组,以确定如何处理每个元素。
def freq_dict(data):freq = {}for elem in data:Step 4: If the element has already been included in the dictionary, then the element appears more than once and we need to add 1 to its current frequency. Else, if the element is not in the dictionary already, it's the first time it appears and its initial value should be 1.
步骤4:如果该元素已经包含在字典中,则该元素会出现多次,我们需要在其当前频率上加1。 否则,如果该元素尚未在字典中,则这是它第一次出现,其初始值应为1。
def freq_dict(data):freq = {}for elem in data:if elem in freq:freq[elem] += 1else:freq[elem] = 1Step 5: Finally, we need to return the dictionary.
步骤5:最后,我们需要返回字典。
def freq_dict(data):freq = {}for elem in data:if elem in freq:freq[elem] += 1else:freq[elem] = 1return freq🔔 Important: Since we are assigning the elements as the keys of the dictionary, they have to be of an immutable data type.
🔔 重要:由于我们将元素分配为字典的键,因此它们必须是不可变的数据类型。
例子 (Examples)
Here we have an example of the use of this function. Notice how the dictionary maps each character of the string to how many times it occurs.
在这里,我们有一个使用此功能的示例。 注意字典如何将字符串的每个字符映射到它出现的次数。
>>> def freq_dict(data):freq = {}for elem in data:if elem in freq:freq[elem] += 1else:freq[elem] = 1return freq>>> freq_dict("Hello, how are you?")
{'H': 1, 'e': 2, 'l': 2, 'o': 3, ',': 1, ' ': 3, 'h': 1, 'w': 1, 'a': 1, 'r': 1, 'y': 1, 'u': 1, '?': 1}This is another example applied to a list of integers:
这是应用于整数列表的另一个示例:
>>> def freq_dict(data):freq = {}for elem in data:if elem in freq:freq[elem] += 1else:freq[elem] = 1return freq>>> freq_dict([5, 2, 6, 2, 6, 5, 2, 2, 2])
{5: 2, 2: 5, 6: 2}Great Work! Now we have the final function.
做得好! 现在我们有了最终功能。
Summary总结 (🎓 In Summary )
- Dictionaries are built-in data types in Python that associate (map) keys to values, forming key-value pairs.字典是Python中的内置数据类型,可将键关联(映射)到值,形成键值对。
- You can access a value with its corresponding key.您可以使用相应的键访问值。
- Keys have to be of an immutable data type.键必须是不可变的数据类型。
- You can access, add, modify, and delete key-value pairs.您可以访问,添加,修改和删除键值对。
- Dictionaries offer a wide variety of methods that can help you perform common functionality.词典提供了多种方法,可以帮助您执行常见功能。
I really hope you liked my article and found it helpful. Now you can work with dictionaries in your Python projects. Check out my online courses. Follow me on Twitter. 👍
我真的希望您喜欢我的文章并发现它对您有所帮助。 现在,您可以在Python项目中使用字典。 查看我的在线课程 。 在Twitter上关注我。 👍
翻译自: https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-dictionaries-detailed-visual-introduction/
python字典{:>4}
相关文章:

asp.net提交危险字符处理方法之一
在form表单提交前,可以在web页面,submit按钮的click事件中,使用js函数对,可能有危险字符的内容进行编码。 有3个函数可用: encodeURI() 函数可把字符串作为 URI 进行编码。 escape() 函数可对字符串进行编码࿰…

mysql帐号,权限管理
-> use mysql; //选择数据库 -> select host,user,password from user; //查询已有用户 -> insert into user (host,user,password) values(localhost,kiscms,password(kiscms)); //插入一个用户 -> select host,user,password from user; //再次查询用户 -> fl…
样式集(10) - 滑动删除功能实现,VUE完整源码附效果图
先看效果图 实现方式: 使用 scroll-view 标签,进行横向滑动,达到左滑出现删除按钮, 注:如果不是使用uni-app或者小程序框架,没有 scroll-view 组件的话可以通过CSS实现哦 下面看uni-app的实现代码&#…

机器学习关键的几门课程_互联网上每门机器学习课程,均按您的评论排名
机器学习关键的几门课程by David Venturi大卫文图里(David Venturi) 互联网上每门机器学习课程,均按您的评论排名 (Every single Machine Learning course on the internet, ranked by your reviews) A year and a half ago, I dropped out of one of the best com…

[POJ2104]K-th Number(区间第k值 记录初始状态)
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id2104 给n个数和m个查询,查询[i, j]内第k小的数是多少。(主席树、划分树那种高大上的姿势叒不会啊QAQ 可以在维护这n个数的同时维护刚刚输入的时候他们的下标,之后预处理排序一次,查…

Geant4采用make和cmake编译运行geant4自带例子的方法
该教程介绍如何将geant4中自带的例子通过camke编译成可执行文件,并运行程序。 1 在linux主目录下创建一个geant4_workdir目录,并将geant4自带的例子B1复制到该目录下,如图1所示,geant4自带的B1源文件所在目录为geant4安装目录&…
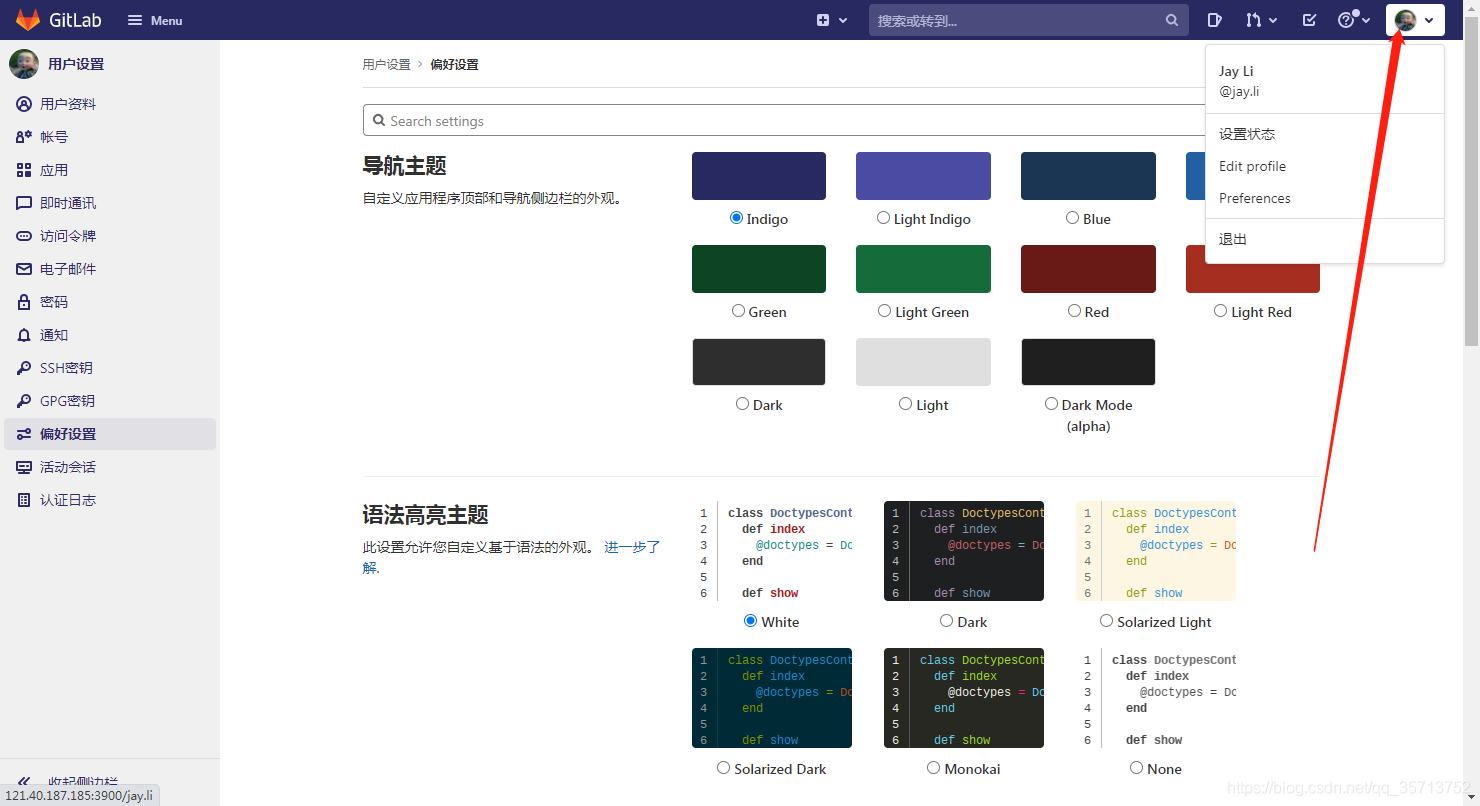
GitLab设置中文
第一步,点击右上角的头像 点击Preferences,选择语言 选择简体中文然后保存

java python算法_用Python,Java和C ++示例解释的排序算法
java python算法什么是排序算法? (What is a Sorting Algorithm?) Sorting algorithms are a set of instructions that take an array or list as an input and arrange the items into a particular order.排序算法是一组指令,这些指令采用数组或列表…

c++运算符重载总结
c的一大特性就是重载(overload),通过重载可以把功能相似的几个函数合为一个,使得程序更加简洁、高效。在c中不止函数可以重载,运算符也可以重载。由于一般数据类型间的运算符没有重载的必要,所以运算符重载主要是面向对象之间的。…

一道面试题:js返回函数, 函数名后带多个括号的用法及join()的注意事项
博客搬迁,给你带来的不便,敬请谅解! http://www.suanliutudousi.com/2017/11/13/js%E8%BF%94%E5%9B%9E%E5%87%BD%E6%95%B0%E4%B8%AD%EF%BC%8C%E5%87%BD%E6%95%B0%E5%90%8D%E5%90%8E%E5%B8%A6%E5%A4%9A%E4%B8%AA%E6%8B%AC%E5%8F%B7%E7%9A%84%E…
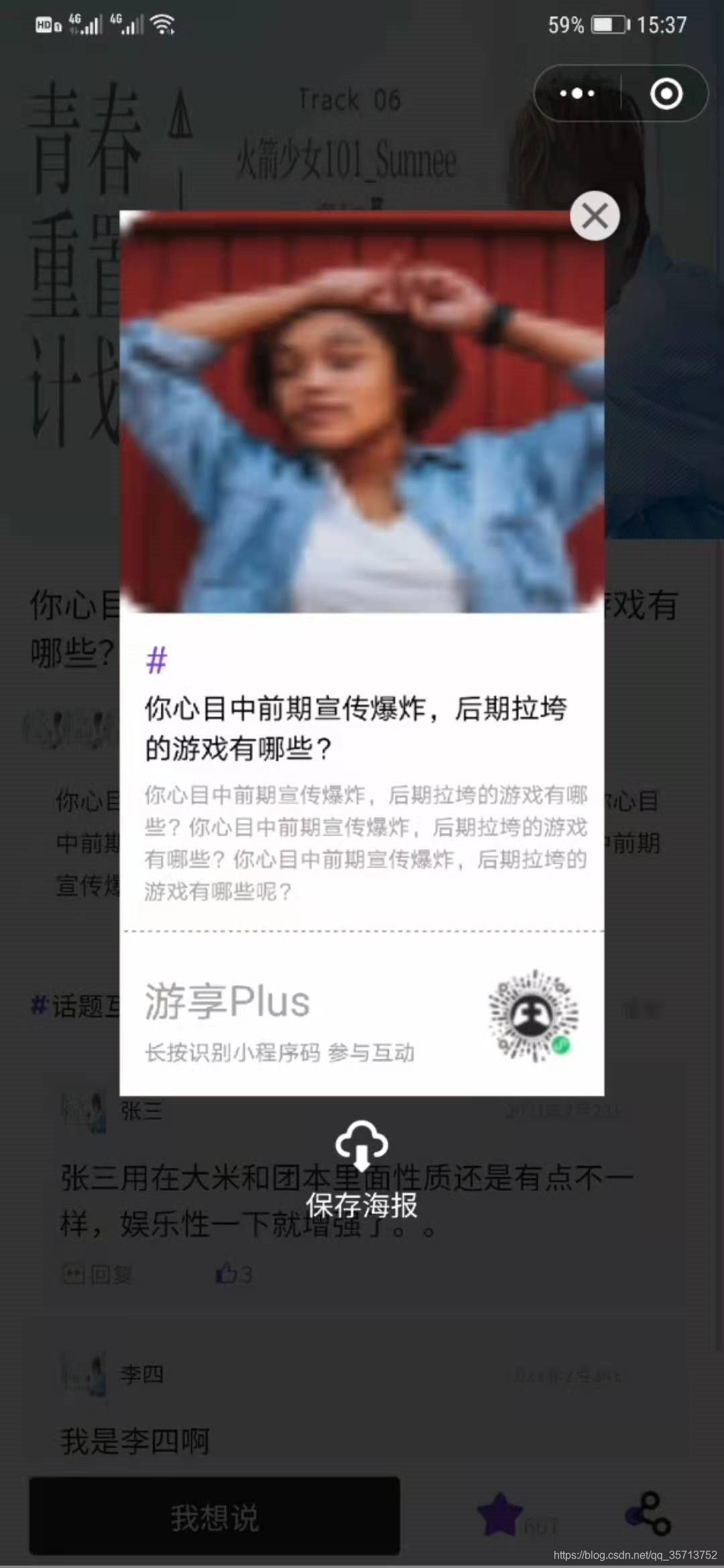
小程序画布画海报保存成图片可以保存实现完整代码
老规矩先来个效果图: 因为是截图所以会有些模糊,在真机上会比较清晰 下面针对效果图来看看里面都画了什么元素,代码在文章的最后,大家想直接拷代码可以略过这,这里是方便大家理解代码。 首先,咱们的海报有…

fcm和firebase_我如何最终使Netlify Functions,Firebase和GraphQL一起工作
fcm和firebaseIn a previous post I confessed defeat in attempting to get an AWS Lambda GraphQL server to connect to a Firebase server. I didn’t give up right away, though, and a short time later found a different Node package to achieve what I couldn’t be…

深入了解Mvc路由系统
请求一个MVC页面的处理过程 1.浏览器发送一个Home/Index 的链接请求到iis。iis发现时一个asp.net处理程序。则调用asp.net_isapi 扩展程序发送asp.net框架 2.在asp.net的第七个管道事件中会遍历UrlRoutingModule中RouteCollection的RoteBase集合 通过调用其GetRouteData方法进行…
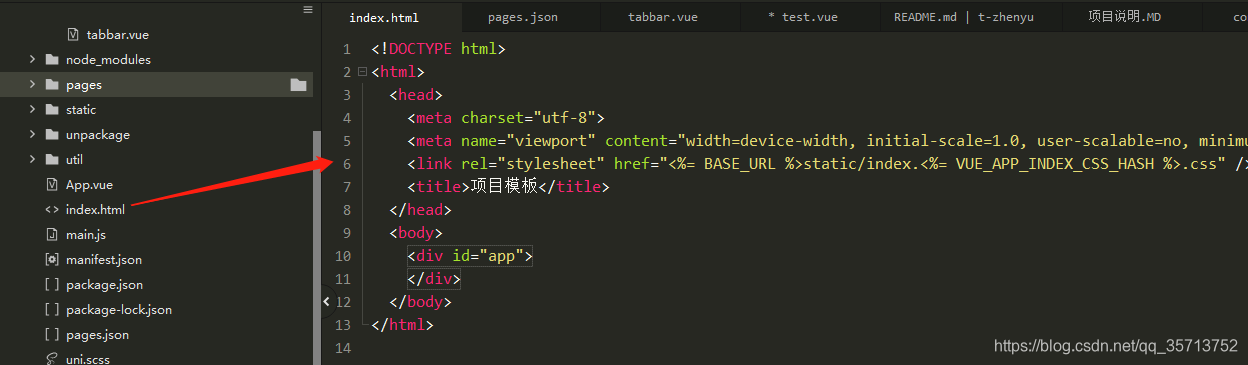
uni-app h5页面左上角出现“取消“字眼解决办法
在项目根目录的index.html中加上一行代码 <link rel"stylesheet" href"<% BASE_URL %>static/index.<% VUE_APP_INDEX_CSS_HASH %>.css" /> 如图:

unity编辑器扩展_01(在工具栏中创建一个按钮)
代码: [MenuItem("Tools/Test",false,1)] static void Test() { Debug.Log("test"); } 注意:MenuItem中第一个参数:需要创建选项在工具栏中的路径,此路径的父目录可以是Unity中已存在的,也…

postgres语法_SQL Create Table解释了MySQL和Postgres的语法示例
postgres语法A table is a group of data stored in a database.表是存储在数据库中的一组数据。 To create a table in a database you use the CREATE TABLE statement. You give a name to the table and a list of columns with its datatypes.要在数据库中创建表&#…

jquery-ajax请求:超时设置,增加 loading 提升体验
前端发送Ajax请求到服务器,服务器返回数据这一过程,因原因不同耗时长短也有差别,且这段时间内页面显示空白。如何优化这段时间内的交互体验,以及长时间内服务器仍未返回数据这一问题,是我们开发中不容忽视的重点。 常见…

第三章.SQL编程
2016年3月2日13:55:17(记忆笔记) 变量是存储数据的容器。 如何在SQL中定义自己的变量! First:第一套变量定义 整型 Declare num int Set num10 Print num 第二套变量定义 字符串类型(char varchar nvarchar) Declare name nvarchar(32) Set name’小帅’ Pri…

移动端自动播放音视频实现代码
视频组件 <video :custom-cache"false" :src"item.voideoUrl" :id"audio index" :vslide-gesture-in-fullscreen"false" :direction0 :enable-progress-gesture"false" :show-fullscreen-btn"false" loop obj…

grafana美人鱼_编码美人鱼–我如何从海洋生物学家转到前端开发人员
grafana美人鱼I have wanted to share my story for a while, but I didn’t know exactly how to start, or even what name to give it. 我想分享我的故事一段时间,但我不知道确切的开头,甚至不知道用什么名字。 But recently I was talking with som…

网络安全基础扫盲
1. 名词解释 APT 高级持续性威胁。利用先进的攻击手段对特定目标进行长期持续性网络攻击的攻击形式。其高级性主要体现在APT在发动攻击之前需要对攻击对象的业务流程和目标系统进行精确的收集。 VPN 虚拟专用网络(Virtual private network) VPN是Virtual…

Install Package and Software
svn http://tortoisesvn.sourceforge.net/ git https://download.tortoisegit.org/ http://git-for-windows.github.io/转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/exmyth/p/5246529.html

小程序保存网络图片
小程序保存网络实现流程: 1.把图片下载到本地 2.检查用户的授权状态(三种状态:未授权,已授权,未同意授权),判断是否授权保存图片的能力,如果是用户点击了不同意授权给小程序保存图…

aws 认证_引入#AWSCertified挑战:您的第一个AWS认证之路
aws 认证You may already know that Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the largest, oldest, and most popular cloud service provider. But did you know they offer professional certifications, too?您可能已经知道Amazon Web Services(AWS)是最大,最古老和最受欢…
node!!!
node.js Node是搞后端的,不应该被被归为前端,更不应该用前端的观点去理解,去面试node开发人员。所以这份面试题大全,更侧重后端应用与对Node核心的理解。 github地址: https://github.com/jimuyouyou/node-interview-questions 注…

POJ 1556 The Doors(计算几何+最短路)
这题就是,处理出没两个点。假设能够到达,就连一条边,推断可不能够到达,利用线段相交去推断就可以。最后求个最短路就可以 代码: #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #inclu…

* core-js/modules/es6.array.fill in ./node_modules/_cache-loader@2.0.1@cache-loader/dist/cjs.js??ref
运行Vue项目报错,报错截图如下: 导致该错误的原因是core-js版本不对: 解决方法:安装淘宝镜像 $ cnpm install core-js2 安装完成重新运行就可以了 外: 清除npm缓存命令 : npm cache clean -f

github创建静态页面_如何在10分钟内使用GitHub Pages创建免费的静态站点
github创建静态页面Static sites have become all the rage, and with good reason – they are blazingly fast and, with an ever growing number of supported hosting services, pretty easy to set up. 静态站点已成为流行,并且有充分的理由-它们非常快速&…
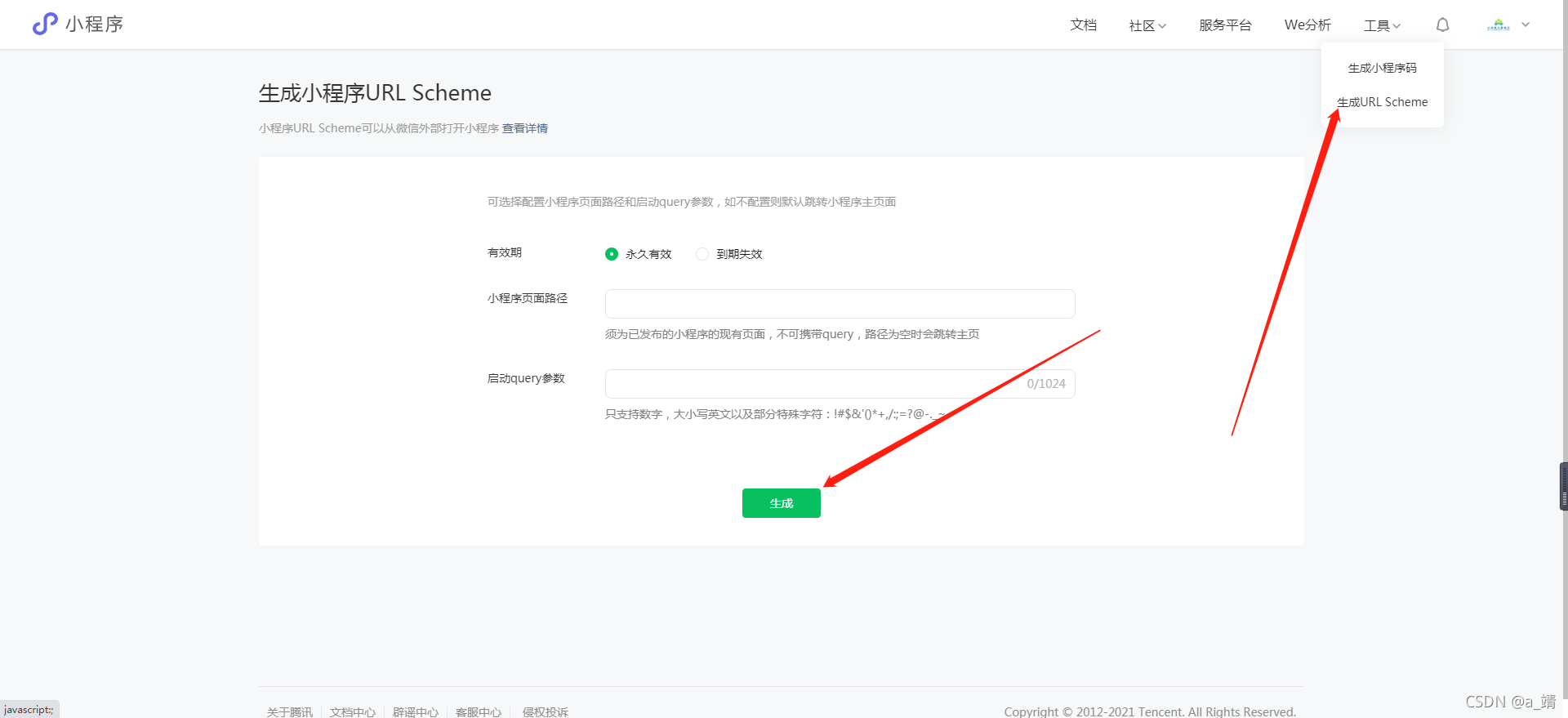
小程序生成网址链接,网址链接跳转小程序
登录小程序后台,点击右上角的工具,生成小程序URL Scheme , 可以得出一个 weixin://dl/business/?tbAXXXXX 这样的链接,点击就可以调整到小程序拉,但是这种只能在微信打开哦。
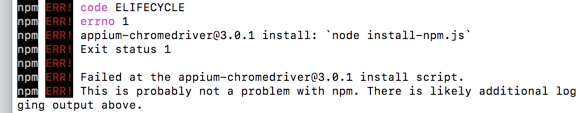
appium-chromedriver@3.0.1 npm ERR! code ELIFECYCLE npm ERR! errno 1
解决方法: npm install appium-chromedriver3.0.1 --ignore-scripts 或者(安装方法): npm install appium-chromedriver --chromedriver_cdnurlhttp://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/chromedriver 官网地址:https://www.npmj…
