深度学习中的优化算法之MBGD
之前在https://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/75351323 介绍过梯度下降,常见的梯度下降有三种形式:BGD、SGD、MBGD,它们的不同之处在于我们使用多少数据来计算目标函数的梯度。
大多数深度学习算法都涉及某种形式的优化。优化指的是改变x以最小化或最大化某个函数f(x)的任务。我们通常以最小化f(x)指代大多数最优化问题。我们把要最小化或最大化的函数称为目标函数(objective function)或准则(criterion)。当我们对其进行最小化时,我们也把它称为成本函数(cost function)、损失函数(loss function)或误差函数(error function)。
梯度下降是深度学习中一种常用的优化技术。梯度是函数的斜率。它衡量一个变量响应另一个变量的变化而变化的程度。在数学上,梯度下降是一个凸函数,其输出是输入的一组参数的偏导数。梯度越大,坡度越陡(the greater the gradient, the steeper the slope)。从初始值开始,迭代运行梯度下降以找到参数的最佳值,以找到给定成本函数的最小可能值。
梯度下降是一种优化算法,通常用于寻找深度学习算法中的权值及系数(weights or coefficients),如逻辑回归。它的工作原理是让模型对训练数据进行预测,并使用预测中的error来更新模型从而减少error(It works by having the model make predictions on training data and using the error on the predictions to update the model in such a way as to reduce the error)。
该算法的目标是找到使模型在训练数据集上的误差最小化的模型参数(e.g. coefficients or weights)。它通过对模型进行更改,使其沿着误差的梯度或斜率向下移动到最小误差值来实现这一点。这使该算法获得了"梯度下降"的名称。
梯度下降是深度学习中非常流行的优化算法。它的目标是搜索目标函数或成本函数(objective function or cost function)的全局最小值。这只有在目标函数是凸函数时才有可能,这间接意味着该函数将是碗形的。在非凸函数的情况下,梯度下降会找到最近的最小值,这个函数的最小值称为局部最小值。
梯度下降是一种一阶优化算法。这意味着在更新参数时它只考虑函数的一阶导数。我们的主要目标是在每次迭代中使梯度沿最陡斜率的方向行进,我们在与目标函数的梯度相反的方向上更新参数。
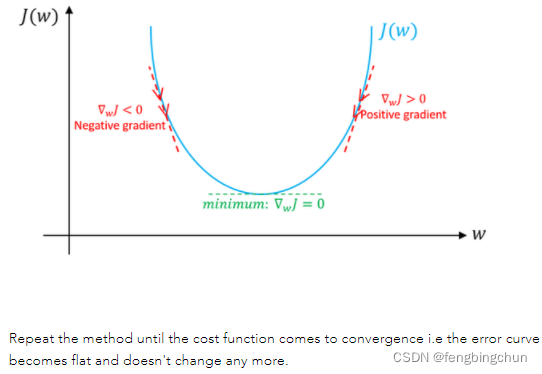
图解说明:假设只有weight没有bias。如果weight(w)的特定值的斜率>0,则表示我们在最优w*的右侧,在这种情况下,更新将是负数,并且w将开始接近最优w*。但是,如果weight(w)的特定值的斜率<0,则更新将为正值,并将当前值增加到w以收敛到w*的最佳值。以下截图来自于https://www.machinelearningman.com:重复该方法,直到成本函数收敛。
在https://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/79370310中有梯度下降应用于二分类的公式推导。
MBGD(Mini-Batch Gradient Descent, MBGD):小批量梯度下降,它将训练数据集分成小批量用于计算模型误差和更新模型参数。小批量梯度下降寻求在随机梯度下降的鲁棒性和批量梯度下降的效率之间找到平衡。它是深度学习领域中最常见的梯度下降实现。
梯度下降是一种最小化目标函数的方法:θ为模型的参数,J(θ)为目标函数,以下截图来自:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1609.04747.pdf

有时提到SGD的时候,其实指的是MBGD。
小批量的大小通常由以下几个因素决定:
(1).更大的批量会计算更精确的梯度估计,但是回报却是小于线性的。
(2).极小批量通常难以充分利用多核架构。这促使我们使用一些绝对最小批量,低于这个值的小批量处理不会减少计算时间。
(3).如果批量处理中的所有样本可以并行地处理(通常确是如此),那么内存消耗和批量大小会正比。对于很多硬件设施,这是批量大小的限制因素。
(4).在某些硬件上使用特定大小的数组时,运行时间会更少。尤其是在使用GPU时,通常使用2的幂数作为批量大小可以获得更少的运行时间。一般,2的幂数的取值范围是32到256,16有时>在尝试大模型时使用。
(5).可能是由于小批量在学习过程中加入了噪声,它们会有一些正则化效果。泛化误差通常在批量大小为1时最好。因为梯度估计的高方差,小批量训练需要较小的学习率以保持稳定性。因
为降低的学习率和消耗更多步骤来遍历整个训练集都会产生更多的步骤,所以会导致总的运行时间非常大。
小批量是随机抽取的这点也很重要。从一组样本中计算出梯度期望的无偏估计要求这些样本是独立的。我们也希望两个连续的梯度估计是互相独立的,因此两个连续的小批量样本也应该是>彼此独立的。很多现实的数据集自然排列,从而使得连续的样本之间具有高度相关性。实践中通常将样本顺序打乱一次,然后按照这个顺序存储起来就足够了。之后训练模型时会用到的一>组组小批量连续样本是固定的,每个独立的模型每次遍历训练数据时都会重复使用这个顺序。
优点:
(1).模型更新频率高于批量梯度下降,这允许更稳健的收敛,避免局部极小值。
(2).批量更新提供了比随机梯度下降计算上更有效的过程。
(3).批量处理既可以提高内存中没有所有训练数据的效率,也可以实现算法。
缺点:
(1).小批量需要为学习算法配置一个额外的"mini-batch size"超参数。
(2).错误信息(error information)必须在像批量梯度下降这样的小批量训练样本中累积。
一般"batch size"为32、64、128、256等的2的幂。"batch size"是学习过程中的一个滑块(slider)。较小的值会提供一个快速收敛的学习过程,但会以训练过程中的噪声为代价。较大的值会给出一个缓慢收敛的学习过程并准确估计误差梯度。
以上内容主要参考:
1. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1609.04747.pdf
2. https://machinelearningmastery.com/
3. https://www.machinelearningman.com
以下的测试代码以https://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/79346691中逻辑回归实现的基础上进行调整:
logistic_regression2.hpp:
#ifndef FBC_SRC_NN_LOGISTIC_REGRESSION2_HPP_
#define FBC_SRC_NN_LOGISTIC_REGRESSION2_HPP_#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <memory>namespace ANN {enum class ActivationFunction {Sigmoid // logistic sigmoid function
};enum class LossFunction {MSE // Mean Square Error
};enum class Optimization {BGD, // Batch Gradient DescentSGD, // Stochastic Gradient DescentMBGD // Mini-batch Gradient Descent
};struct Database {Database() = default;std::vector<std::vector<float>> samples; // training setstd::vector<int> labels; // ground truth labels
};class LogisticRegression2 { // two categories
public:LogisticRegression2(Optimization optim = Optimization::BGD, int batch_size = 1) : optim_(optim), batch_size_(batch_size) {}int init(std::unique_ptr<Database> data, int feature_length, float learning_rate = 0.00001, int epochs = 1000);int train(const std::string& model);int load_model(const std::string& model);float predict(const float* data, int feature_length) const; // y = 1/(1+exp(-(wx+b)))void set_error(float error) { error_ = error; }private:int store_model(const std::string& model) const;float calculate_z(const std::vector<float>& feature) const; // z(i)=w^T*x(i)+bfloat calculate_cost_function() const;static int generate_random(int i) { return std::rand()%i; }float calculate_activation_function(float value) const;float calculate_loss_function() const;float calculate_loss_function_derivative() const;float calculate_loss_function_derivative(float predictive_value, float true_value) const;void calculate_gradient_descent(int start = 0, int end = 0);std::unique_ptr<Database> data_; // train data(images, labels)std::vector<int> random_shuffle_; // shuffle the training data at every epochstd::vector<float> o_; // predict valueint epochs_ = 100; // epochsint m_ = 0; // train samples numint feature_length_ = 0; // weights lengthfloat alpha_ = 0.00001; // learning ratestd::vector<float> w_; // weightsfloat b_ = 0.; // thresholdfloat error_ = 0.00001;int batch_size_ = 1;ActivationFunction activation_func_ = ActivationFunction::Sigmoid;LossFunction loss_func_ = LossFunction::MSE;Optimization optim_ = Optimization::BGD;
}; // class LogisticRegression2} // namespace ANN#endif // FBC_SRC_NN_LOGISTIC_REGRESSION2_HPP_logistic_regression2.cpp:
#include "logistic_regression2.hpp"
#include <fstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <random>
#include <cmath>
#include "common.hpp"namespace ANN {int LogisticRegression2::init(std::unique_ptr<Database> data, int feature_length, float learning_rate, int epochs)
{CHECK(data->samples.size() == data->labels.size());m_ = data->samples.size();if (m_ < 2) {fprintf(stderr, "logistic regression train samples num is too little: %d\n", m_);return -1;}if (learning_rate <= 0) {fprintf(stderr, "learning rate must be greater 0: %f\n", learning_rate);return -1;}if (epochs < 1) {fprintf(stderr, "number of epochs cannot be zero or a negative number: %d\n", epochs);return -1;}alpha_ = learning_rate;epochs_ = epochs;feature_length_ = feature_length;data_ = std::move(data);o_.resize(m_);return 0;
}int LogisticRegression2::train(const std::string& model)
{w_.resize(feature_length_, 0.);generator_real_random_number(w_.data(), feature_length_, -0.01f, 0.01f, true);generator_real_random_number(&b_, 1, -0.01f, 0.01f);if (optim_ == Optimization::BGD) {for (int iter = 0; iter < epochs_; ++iter) {calculate_gradient_descent();auto cost_value = calculate_cost_function();fprintf(stdout, "epochs: %d, cost function: %f\n", iter, cost_value);if (cost_value < error_) break;}} else {random_shuffle_.resize(data_->samples.size(), 0);for (int i = 0; i < data_->samples.size(); ++i)random_shuffle_[i] = i;float cost_value = 0.;for (int iter = 0; iter < epochs_; ++iter) {std::srand(unsigned(std::time(0)));std::random_shuffle(random_shuffle_.begin(), random_shuffle_.end(), generate_random);int loop = (m_ + batch_size_ - 1) / batch_size_;for (int i = 0; i < loop; ++i) {int start = i * batch_size_;int end = start + batch_size_ > m_ ? m_ : start + batch_size_;calculate_gradient_descent(start, end);for (int i = 0; i < m_; ++i)o_[i] = calculate_activation_function(calculate_z(data_->samples[i]));cost_value = calculate_cost_function();fprintf(stdout, "epochs: %d, loop: %d, cost function: %f\n", iter, i, cost_value);if (cost_value < error_) break;}if (cost_value < error_) break;}}CHECK(store_model(model) == 0);return 0;
}int LogisticRegression2::load_model(const std::string& model)
{std::ifstream file;file.open(model.c_str(), std::ios::binary);if (!file.is_open()) {fprintf(stderr, "open file fail: %s\n", model.c_str());return -1;}int length{ 0 };file.read((char*)&length, sizeof(length));w_.resize(length);feature_length_ = length;file.read((char*)w_.data(), sizeof(float)*w_.size());file.read((char*)&b_, sizeof(float));file.close();return 0;
}float LogisticRegression2::predict(const float* data, int feature_length) const
{CHECK(feature_length == feature_length_);float value{0.};for (int t = 0; t < feature_length_; ++t) {value += data[t] * w_[t];}value += b_;return (calculate_activation_function(value));
}int LogisticRegression2::store_model(const std::string& model) const
{std::ofstream file;file.open(model.c_str(), std::ios::binary);if (!file.is_open()) {fprintf(stderr, "open file fail: %s\n", model.c_str());return -1;}int length = w_.size();file.write((char*)&length, sizeof(length));file.write((char*)w_.data(), sizeof(float) * w_.size());file.write((char*)&b_, sizeof(float));file.close();return 0;
}float LogisticRegression2::calculate_z(const std::vector<float>& feature) const
{float z{0.};for (int i = 0; i < feature_length_; ++i) {z += w_[i] * feature[i];}z += b_;return z;
}float LogisticRegression2::calculate_cost_function() const
{/*// J+=-1/m([y(i)*loga(i)+(1-y(i))*log(1-a(i))])// Note: log0 is not definedfloat J{0.};for (int i = 0; i < m_; ++i)J += -(data_->labels[i] * std::log(o_[i]) + (1 - labels[i]) * std::log(1 - o_[i]) );return J/m_;*/float J{0.};for (int i = 0; i < m_; ++i)J += 1./2*std::pow(data_->labels[i] - o_[i], 2);return J/m_;
}float LogisticRegression2::calculate_activation_function(float value) const
{switch (activation_func_) {case ActivationFunction::Sigmoid:default: // Sigmoidreturn (1. / (1. + std::exp(-value))); // y = 1/(1+exp(-value))}
}float LogisticRegression2::calculate_loss_function() const
{switch (loss_func_) {case LossFunction::MSE:default: // MSEfloat value = 0.;for (int i = 0; i < m_; ++i) {value += 1/2.*std::pow(data_->labels[i] - o_[i], 2);}return value/m_;}
}float LogisticRegression2::calculate_loss_function_derivative() const
{switch (loss_func_) {case LossFunction::MSE:default: // MSEfloat value = 0.;for (int i = 0; i < m_; ++i) {value += o_[i] - data_->labels[i];}return value/m_;}
}float LogisticRegression2::calculate_loss_function_derivative(float predictive_value, float true_value) const
{switch (loss_func_) {case LossFunction::MSE:default: // MSEreturn (predictive_value - true_value);}
}void LogisticRegression2::calculate_gradient_descent(int start, int end)
{float db = 0.;std::vector<float> dw(feature_length_, 0.);switch (optim_) {case Optimization::SGD:case Optimization::MBGD: {int len = end - start;std::vector<float> z(len, 0), dz(len, 0);for (int i = start, x = 0; i < end; ++i, ++x) {z[x] = calculate_z(data_->samples[random_shuffle_[i]]);dz[x] = calculate_loss_function_derivative(calculate_activation_function(z[x]), data_->labels[random_shuffle_[i]]);for (int j = 0; j < feature_length_; ++j) {dw[j] += data_->samples[random_shuffle_[i]][j] * dz[x]; // dw(i)+=x(i)(j)*dz(i)}db += dz[x]; // db+=dz(i)}for (int j = 0; j < feature_length_; ++j) {dw[j] /= len;w_[j] -= alpha_ * dw[j];}b_ -= alpha_*(db/len);}break;case Optimization::BGD:default: // BGDstd::vector<float> z(m_, 0), dz(m_, 0);for (int i = 0; i < m_; ++i) {z[i] = calculate_z(data_->samples[i]);o_[i] = calculate_activation_function(z[i]);dz[i] = calculate_loss_function_derivative(o_[i], data_->labels[i]);for (int j = 0; j < feature_length_; ++j) {dw[j] += data_->samples[i][j] * dz[i]; // dw(i)+=x(i)(j)*dz(i)}db += dz[i]; // db+=dz(i)}for (int j = 0; j < feature_length_; ++j) {dw[j] /= m_;w_[j] -= alpha_ * dw[j];}b_ -= alpha_*(db/m_);}
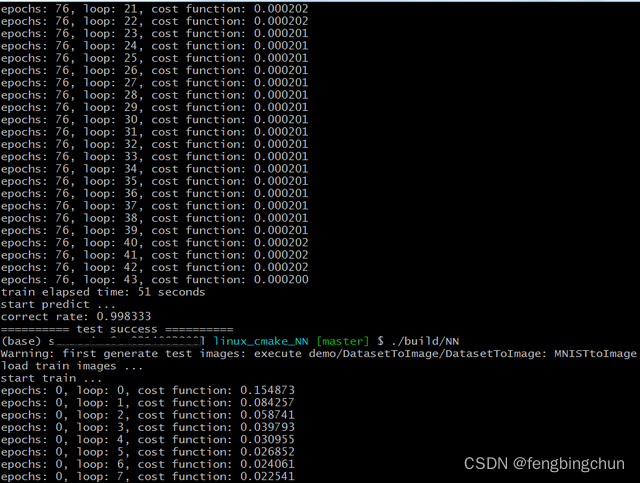
}} // namespace ANNtest_logistic_regression2_gradient_descent:以MNIST为数据集,取0和1,在训练时取训练集各5000张,预测时取测试集各900张
int test_logistic_regression2_gradient_descent()
{fprintf(stdout,"Warning: first generate test images: execute demo/DatasetToImage/DatasetToImage: MNISTtoImage\n");fprintf(stdout, "load train images ...\n");
#ifdef _MSC_VERconst std::vector<std::string> image_path{ "E:/GitCode/NN_Test/data/tmp/MNIST/train_images/", "E:/GitCode/NN_Test/data/tmp/MNIST/test_images/"};const std::string model{ "E:/GitCode/NN_Test/data/logistic_regression2.model" };
#elseconst std::vector<std::string> image_path{ "data/tmp/MNIST/train_images/", "data/tmp/MNIST/test_images/"};const std::string model{ "data/logistic_regression2.model" };
#endifconst int image_size = 28*28;const int samples_single_class_num = 5000;auto data1 = std::make_unique<ANN::Database>();data1->samples.resize(samples_single_class_num*2);data1->labels.resize(samples_single_class_num*2);if (read_images(image_path[0], samples_single_class_num, image_size, data1) == -1) return -1;fprintf(stdout, "start train ...\n");auto start = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();//ANN::LogisticRegression2 lr(ANN::Optimization::BGD, samples_single_class_num * 2); // Batch Gradient Descent, epochs = 10000, correct rete: 0.997778//ANN::LogisticRegression2 lr(ANN::Optimization::SGD, 1); // Stochastic Gradient Descent, epochs = 5, correct rete: 0.998889ANN::LogisticRegression2 lr(ANN::Optimization::MBGD, 128); // Mini-batch Gradient Descent, epochs = 100, correct rete: 0.997778lr.set_error(0.0002);int ret = lr.init(std::move(data1), image_size, 0.00001, 5);if (ret != 0) {fprintf(stderr, "logistic regression init fail: %d\n", ret);return -1;}ret = lr.train(model);if (ret != 0) {fprintf(stderr, "logistic regression train fail: %d\n", ret);return -1;}auto end = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();fprintf(stdout, "train elapsed time: %d seconds\n", std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(end - start).count());fprintf(stdout, "start predict ...\n");const int test_single_class_num = 900;const std::vector<std::string> prefix_name {"0_", "1_"};ANN::LogisticRegression2 lr2;lr2.load_model(model);int count = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= test_single_class_num; ++i) {for (const auto& prefix : prefix_name) {std::string name = std::to_string(i);if (i < 10) {name = "0000" + name;} else if (i < 100) {name = "000" + name;} else if (i < 1000) {name = "00" + name;}name = image_path[1] + prefix + name + ".jpg";cv::Mat mat = cv::imread(name, 0);if (mat.empty()) {fprintf(stderr, "read image fail: %s\n", name.c_str());return -1;}if (mat.cols * mat.rows != image_size || mat.channels() != 1) {fprintf(stderr, "image size fail: width: %d, height: %d, channels: %d\n", mat.cols, mat.rows, mat.channels());return -1;}mat.convertTo(mat, CV_32F);float probability = lr2.predict((float*)mat.data, image_size);int label = prefix == "0_" ? 0 : 1;if ((probability > 0.5 && label == 1) || (probability < 0.5 && label == 0)) ++count;}}float correct_rate = count / (test_single_class_num * 2.);fprintf(stdout, "correct rate: %f\n", correct_rate);return 0;
}执行结果如下:训练时,MBGD成本函数error值并不向BGD一样逐渐减少,偶尔会波动,但是总体上还是逐渐减少;设置相同的error,MBGD比SGD训练时间少好多;预测准确率为99.83%
GitHub: https://github.com/fengbingchun/NN_Test
相关文章:
华科提出目标检测新方法:基于IoU-aware的定位改进,简单又有效
作者 | 周强来源 | 我爱计算机视觉(ID:aicvml)【导语】近日,华中科技大学发表了一篇新论文《IoU-aware Single-stage Object Detector for Accurate Localization》,在此论文中作者提出了一种非常简单的目标检测定位改…

js init : function ()
这个init外面应该还有一层,比如 var a { init: function () {...}, exit: function () {...} } 这样的话,可以用a.init()来调用这个函数, <script type"text/javascript">var obj{init:function(str){alert("init调用&…
Google提出移动端新SOTA模型MixNets:用混合深度卷积核提升精度
作者 | Google译者 | 刘畅编辑 | Jane出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100) 【导语】目前,深度卷积(Depthwise convolution)在追求高性能的卷积网络中的应用变得越来越流行,但很多研究忽略了其内核…

桌面窗口的一些发现
最近因业务需要,玩了一下全屏问题。后来,对windows xp sp2的桌面窗口产生了兴趣。写了段代码,玩了一下。同时结合网上的一些知识,发现了以下一些现象。(转载请指明出处) 首先窗口名有#32769、Progman、Shel…

三说输入法[转]
如果我愿意,我会不停地说下去,直到烦死你们,谁让我用的输入法快呢。 我说了几句搜狗或股沟输入法的坏话,引来一些人的争论,大大在我预料之中,这年头,当你想说一些知名度较高的人或物的坏话时&am…

回忆之城市搜索
直接看效果点这里 HTML <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head lang"zh-CN"><meta charset"utf-8"><title> 城市搜索 </title><link rel"stylesheet" href"ui-departure.css"> </head> <b…

ATL::CStringA和std::string之间转换的一些误区
对于刚做windows下VC的开发同学,类型转换应该是一个令其很苦恼的问题。我刚写工作的时候,也为这类问题不停的在网上搜索转换方法。最近工作中遇到一个“神奇”的bug(一般“神奇”的问题往往是低级错误导致的),最后跟踪…

Windows XP鲜为人知的70招
一、Windows XP优化恢复Windows经典界面很多人安装了Windows XP后的第一感觉就是Windows变得漂亮极了。只是可惜美丽的代价要耗掉我们本就不富裕的内存和显存。要想恢复到和经典Windows类似的界面和使用习惯,请在桌面上单击鼠标右键,选择“属性”命令即可…
Github开源趋势榜Top 1:英伟达升级发布二代StyleGAN,效果更完美
整理 | Jane出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)2018 年底,英伟达借鉴风格迁移的思路,提出当时最先进的无条件生成模型—— StyleGAN ,吸引了大家广泛关注。随后,代码开源,一位 Uber …

百度地图 ip查询 service
官方文档:http://developer.baidu.com/map/wiki/index.php?titlewebapi/ip-api 请求 一个例子: http://api.map.baidu.com/location/ip?ak3GFi2F04wXaVuwmGu8fN49kL1234567890&ip180.161.128.181 返回 {"address": "CN|\u6cb3\u535…

python3编写简易统计服务器
打点这个功能总是美其名曰“帮助提升用户体验”,其实说白了就是记录用户做了哪些操作。目前国内很多通用软件都做了相关功能,像360、QQ等这样的以用户体验出众的软件,其打点的面自然也很广很细。当然这种“侵犯”用户隐私的事情在业内各个公司…
作价20亿美元!英特尔收购以色列AI芯片公司Habana Labs
出品 | AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai1000)12月16日,英特尔宣布以约 20 亿美元收购以色列公司Habana Labs,这成为英特尔在以色列仅次于 Mobileye(153 亿美元) 的第二大收购案。Habana Labs 成立于 2016 年&#x…

这就是奇客文化?简直太有才了!
这就是奇客文化?简直太有才了……

java中的char类型
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 一:char的初始化 char是Java中的保留字,与别的语言不同的是,char在Java中是16位的,因为Java用的是Unicode。不过8位的ASCII码包含在Unicode中,是从0~127的。 Ja…
[原创] 如何追踪每一笔记录的来龙去脉:一个完整的Audit Logging解决方案—Part I...
一、提出问题 在开发一个企业级 应用的时候,尤其在一个涉及到敏感数据的应用,比如财务系统、物流系统,我们往往有这样的需求:对于数据库中每一笔数据的添加、修改和删除,都需要有一个明确的日志,以便我们可…

进程间通信:同步双工管道
因为工作需要,需要设计出一个双工的IPC。(转载请指明出处)在一番比较后,我发现管道是比较符合我们的需求的。但是我们需求要求管道的对方是可信任的,而在vista以下系统是没有GetNamedPipeClientProcessId、GetNamedPip…
就因为一个笔记本,运营和产品吵得不可开交......
上班最讨厌的一件事情,莫过于开会,因为每次开会感觉就要吵架,这个今天开会又吵架了,吵架竟然是因为产品小姐姐的笔记本。产品小姐姐用了一本可擦笔记本记录会议内容,运营小姐姐竟然说这个本子有什么用,不就…

Ka的递归编程练习 Part4|Hanoi汉诺塔,双色汉诺塔的也有
1 #include <stdio.h>2 void hanoi(int s,char a,char b,char c) //a是出发盘,b是中途盘,c是结束盘 3 {4 if(s0) return;5 hanoi(s-1,a,c,b); //把最底下的从a借助c移动到b6 printf("%d from %c move to %c\n",s,a,c);7 …

一种精确从文本中提取URL的思路及实现
在今年三四月份,我接受了一个需求:从文本中提取URL。这样的需求,可能算是非常小众的需求了。大概只有QQ、飞信、阿里旺旺等之类的即时通讯软件存在这样的需求。在研究这个之前,我测试了这些软件这块功能,发现它们这块的…
解读 | 2019年10篇计算机视觉精选论文(上)
作者 | 神经小兮来源 | HyperAI超神经(ID:HyperAI)2019 年转眼已经接近尾声,我们看到,这一年计算机视觉(CV)领域又诞生了大量出色的论文,提出了许多新颖的架构和方法,进一步提高了视…

不错的工具:Reflector for .NET
下载地址: http://www.aisto.com/roeder/dotnet/ 注意:下载时要输一些注册信息,输入用户名时,中间要加一个空格。

Possible MySQL server UUID duplication for server
在mysql enterprise monitor监控过程中出现这样的event事件,Topic: Possible MySQL server UUID duplication for server 事件,从该提示的描述来看貌似是存在重复的uuid,而实际上主从关系并不存在重复的uuid。主从关…
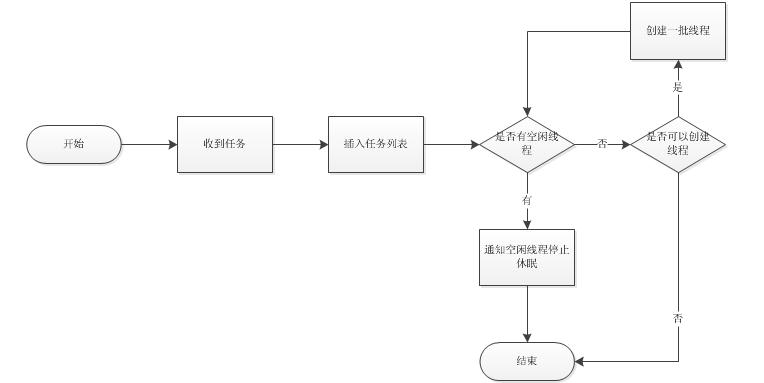
使用VC实现一个“智能”自增减线程池
工作中接手了一款产品的改造。因为该产品可能使用很多线程,所以产品中使用了线程池。(转载请指明来自BreakSoftware的CSDN博客) 线程池的一个优点是降低线程创建和销毁的频率;缺点是可能在比较闲的时候还存在一定数量的空闲线程。…

国内外财务软件科目结构的比较
科目结构是整个会计核算的基础。国内外财务软件都是任意定义科目的分段及科目编码长度,一般都能支持六段到九段。但科目结构在不同的国家有不同的规范,因而在不同的财务软件中也就有不同的控制。在科目分类上,国内外有明显的区别。国外财务软…
朋友圈装死,微博蹦迪,Python教你如何掌握女神情绪变化 | CSDN博文精选
作者 | A字头来源 | 数据札记倌很多人都是在朋友圈装死,微博上蹦迪。微信朋友圈已经不是一个可以随意发表心情的地方了,微博才是!所以你不要傻傻盯着女神的朋友圈发呆啦!本文教你如何用Python自动通知女神微博情绪变化,…

java异常笔记
Throwable是所有Java程序中错误处理的父类,有两种资类:Error和Exception。Error:表示由JVM所侦测到的无法预期的错误,由于这是属于JVM层次的严重错误,导致JVM无法继续执行,因此,这是不可捕捉到的…
2019最新进展 | Transformer在深度推荐系统中的应用
作者 | Alex-zhai来源 | 深度传送门(ID:deep_deliver)【导读】最近基于Transformer的一些NLP模型很火(比如BERT,GPT-2等),因此将Transformer模型引入到推荐算法中是近期的一个潮流。Transformer比起传统的L…

自己架设windows升级服务器
大部分对计算机比较熟悉的朋友都知道,通常安装好Windows 操作系统后要做的第一件事就是上Windows Update网站去给Windows 安装补丁程序,否则各种漏洞对系统就是一个很大的威胁。不过遗憾的是很多人还没有这样的意识,疏忽了给系统打补丁。这也…

内嵌IE网页窗口中消除IE默认脚本设置影响的方法
随着人们对客户端软件界面要求的不断提高,软件开发商面临着一个问题:如何快速廉价开发出各种丰富效果的UI界面。设计出一套丰富控件的界面库是不容易的,且产品经理丰富的想法和UED对效果的追求,往往会使程序员疲于编写这些“效果控件”。目前市面上使用的很多界面库是基于X…

win7 64位操作系统中 Oracle 11g 安装教程(图解)
1.下载Oracle 11g R2 for Windows版本,下载地址如下 官方网站: http://download.oracle.com/otn/nt/oracle11g/112010/win32_11gR2_database_1of2.zip http://download.oracle.com/otn/nt/oracle11g/112010/win32_11gR2_database_2of2.zip 2.解压两…
