收藏喜+1!值得使用的100个Python小技巧

目前Python可以说是非常流行,在目前的编程语言中,Python的抽象程度是最高的,是最接近自然语言的,很容易上手。
你可以用它来完成很多任务,比如数据科学、机器学习、Web开发、脚本编写、自动化等。
下面,给大家分享100个Python小技巧,帮助大家更好的了解和学习Python。
▍1、for循环中的else条件
这是一个for-else方法,循环遍历列表时使用else语句。
下面举个例子,比如我们想检查一个列表中是否包含奇数。
那么可以通过for循环,遍历查找。
numbers = [2, 4, 6, 8, 1]for number in numbers:if number % 2 == 1:print(number)break
else:print("No odd numbers")
如果找到了奇数,就会打印该数值,并且执行break语句,跳过else语句。
没有的话,就不会执行break语句,而是执行else语句。
▍2、从列表中获取元素,定义多个变量
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
one, two, three, four, five = my_list
▍3、使用heapq模块,获取列表中n个最大或最小的元素
import heapqscores = [51, 33, 64, 87, 91, 75, 15, 49, 33, 82]print(heapq.nlargest(3, scores)) # [91, 87, 82]
print(heapq.nsmallest(5, scores)) # [15, 33, 33, 49, 51]
▍4、将列表中的所有元素作为参数传递给函数
我们可以使用 * 号,提取列表中所有的元素
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4]print(my_list) # [1, 2, 3, 4]
print(*my_list) # 1 2 3 4如此便可以将列表中的所有元素,作为参数传递给函数
def sum_of_elements(*arg):total = 0for i in arg:total += ireturn totalresult = sum_of_elements(*[1, 2, 3, 4])
print(result) # 10▍5、获取列表的所有中间元素
_, *elements_in_the_middle, _ = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
print(elements_in_the_middle) # [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
▍6、使用一行代码赋值多个变量
one, two, three, four = 1, 2, 3, 4
▍7、列表推导式
只用一行代码,便可完成对数组的迭代以及运算。
比如,将列表中的每个数字提高一倍。
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared_numbers = [num * num for num in numbers]print(squared_numbers) # [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]推导式不仅列表能用,字典、集合、生成器也能使用。
下面看一下,使用字典推导式,将字典的值提高一倍。
dictionary = {'a': 4, 'b': 5}
squared_dictionary = {key: num * num for (key, num) in dictionary.items()}print(squared_dictionary) # {'a': 16, 'b': 25}
▍8、通过Enum枚举同一标签或一系列常量的集合
枚举是绑定到唯一的常量值的一组符号名称(成员)。
在枚举中,成员可以通过身份进行比较,枚举本身可以迭代。
from enum import Enumclass Status(Enum):NO_STATUS = -1NOT_STARTED = 0IN_PROGRESS = 1COMPLETED = 2print(Status.IN_PROGRESS.name) # IN_PROGRESS
print(Status.COMPLETED.value) # 2
▍9、重复字符串
name = "Banana"
print(name * 4) # BananaBananaBananaBanana
▍10、比较3个数字的大小
如果想比较一个值和其他两个值的大小情况,你可以使用简单的数学表达式。
1 < x < 10这个是最简单的代数表达式,在Python中也是可以使用的。
x = 3print(1 < x < 10) # True
print(1 < x and x < 10) # True
▍11、使用1行代码合并字典
first_dictionary = {'name': 'Fan', 'location': 'Guangzhou'}
second_dictionary = {'name': 'Fan', 'surname': 'Xiao', 'location': 'Guangdong, Guangzhou'}result = first_dictionary | second_dictionaryprint(result)
# {'name': 'Fan', 'location': 'Guangdong, Guangzhou', 'surname': 'Xiao'}
▍12、查找元组中元素的索引
books = ('Atomic habits', 'Ego is the enemy', 'Outliers', 'Mastery')print(books.index('Mastery')) # 3▍13、将字符串转换为字符串列表
假设你在函数中获得输出,原本应该是一个列表,但实际上却是一个字符串。
input = "[1,2,3]"
你可能第一时间会想到使用索引或者正则表达式。
实际上,使用ast模块的literal_eval方法就能搞定。
import astdef string_to_list(string):return ast.literal_eval(string)string = "[1, 2, 3]"
my_list = string_to_list(string)
print(my_list) # [1, 2, 3]string = "[[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]]"
my_list = string_to_list(string)
print(my_list) # [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
▍14、计算两数差值
计算出2个数字之间的差值。
def subtract(a, b):return a - bprint((subtract(1, 3))) # -2
print((subtract(3, 1))) # 2上面的这个方法,需要考虑数值的先后顺序。
def subtract(a, b):return a - bprint((subtract(a=1, b=3))) # -2
print((subtract(b=3, a=1))) # -2使用命名参数,安排顺序,这样就不会出错了。
▍15、用一个print()语句打印多个元素
print(1, 2, 3, "a", "z", "this is here", "here is something else")
▍16、在同一行打印多个元素
print("Hello", end="")
print("World") # HelloWorldprint("Hello", end=" ")
print("World") # Hello Worldprint('words', 'with', 'commas', 'in', 'between', sep=', ')
# words, with, commas, in, between
▍17、打印多个值,在每个值之间使用自定义分隔符
print("29", "01", "2022", sep="/") # 29/01/2022print("name", "domain.com", sep="@") # name@domain.com
▍18、不能在变量名的开头使用数字
four_letters = "abcd" # this works4_letters = "abcd" # this doesn’t work这是Python的变量命名规则。
▍19、不能在变量名的开头使用运算符
+variable = "abcd" # this doesn’t work
▍20、数字的第一位不能是0
number = 0110 # this doesn't work这个确实挺神奇的。
▍21、在变量名的任何地方使用下划线
a______b = "abcd" # this works
_a_b_c_d = "abcd" # this also works这并不意味着,你可以无限使用,为了代码的易读性,还是需要合理使用。
▍22、使用下划线分割数值较大的数字
print(1_000_000_000) # 1000000000
print(1_234_567) # 1234567如此,看到一大堆数字时,也能轻松阅读。
▍23、反转列表
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']my_list.reverse()print(my_list) # ['d', 'c', 'b', 'a']
▍24、使用步进函数对字符串切片
my_string = "This is just a sentence"
print(my_string[0:5]) # This# Take three steps forward
print(my_string[0:10:3]) # Tsse
▍25、反向切片
my_string = "This is just a sentence"
print(my_string[10:0:-1]) # suj si sih# Take two steps forward
print(my_string[10:0:-2]) # sjs i
▍26、使用开始或结束索引进行切片
my_string = "This is just a sentence"
print(my_string[4:]) # is just a sentenceprint(my_string[:3]) # Thi
▍27、/和//的区别
print(3/2) # 1.5
print(3//2) # 1
▍28、==和is的区别
is:检查两个变量是否指向同一对象内存中
==:比较两个对象的值
first_list = [1, 2, 3]
second_list = [1, 2, 3]# 比较两个值
print(first_list == second_list) # True# 是否指向同一内存
print(first_list is second_list)
# Falsethird_list = first_listprint(third_list is first_list)
# True
▍29、合并字典
dictionary_one = {"a": 1, "b": 2}
dictionary_two = {"c": 3, "d": 4}merged = {**dictionary_one, **dictionary_two}print(merged) # {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3, 'd': 4}
▍30、检查字符串是否大于另一字符串
first = "abc"
second = "def"print(first < second) # Truesecond = "ab"
print(first < second) # False
▍31、检查字符串是否以特定字符开头(不使用索引)
my_string = "abcdef"
print(my_string.startswith("b")) # False
▍32、使用id()查找变量的唯一id
print(id(1)) # 4325776624
print(id(2)) # 4325776656
print(id("string")) # 4327978288
▍33、整数、浮点数、字符串、布尔值和元组都是不可变的
当变量被赋值为整数、浮点数、字符串、布尔值、元组这些不可变类型后,该变量就会指向一个内存对象。
如果重新给变量再赋值,它的内存对象就会发生改变。
number = 1
print(id(number)) # 4325215472
print(id(1)) # 4325215472number = 3
print(id(number)) # 4325215536
print(id(1)) # 4325215472
▍34、字符串和元组也是不可变的
此处再说明一次。
name = "Fatos"
print(id(name)) # 4422282544name = "fatos"
print(id(name)) # 4422346608
▍35、列表、集合和字典都是可变的
这意味着发生更改时,不会改变其内存对象。
cities = ["Beijing", "Guangzhou", "chengdu"]
print(id(cities)) # 4482699712cities.append("Beijing")
print(id(cities)) # 4482699712下面是字典。
my_set = {1, 2, 3, 4}
print(id(my_set)) # 4352726176my_set.add(5)
print(id(my_set)) # 4352726176
▍36、把一个列表变成不可变的列表
my_set = frozenset(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])my_set.add("a")使用frozenset()后,你就无法更改了。
▍37、if-elif块可以在没有else块的情况下存在
但是elif不能在没有if语句之前独立存在。
def check_number(number):if number > 0:return "Positive"elif number == 0:return "Zero"return "Negative"print(check_number(1)) # Positive
▍38、使用sorted()检查2个字符串是否为相同
def check_if_anagram(first_word, second_word):first_word = first_word.lower()second_word = second_word.lower()return sorted(first_word) == sorted(second_word)print(check_if_anagram("testinG", "Testing")) # True
print(check_if_anagram("Here", "Rehe")) # True
print(check_if_anagram("Know", "Now")) # False
▍39、获取字符的Unicode值
print(ord("A")) # 65
print(ord("B")) # 66
print(ord("C")) # 66
print(ord("a")) # 97
▍40、获取字典的键
dictionary = {"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}keys = dictionary.keys()
print(list(keys)) # ['a', 'b', 'c']
▍41、获取字典的值
dictionary = {"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}values = dictionary.values()
print(list(values)) # [1, 2, 3]
▍42、交换字典的键、值位置
dictionary = {"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}reversed_dictionary = {j: i for i, j in dictionary.items()}
print(reversed) # {1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c'}
▍43、将布尔值转换为数字
print(int(False)) # 0
print(float(True)) # 1.0▍44、在算术运算中使用布尔值
x = 10
y = 12result = (x - False)/(y * True)
print(result) # 0.8333333333333334▍45、将任何数据类型转换为布尔值
print(bool(.0)) # False
print(bool(3)) # True
print(bool("-")) # True
print(bool("string")) # True
print(bool(" ")) # True▍46、将值转换为复数
print(complex(10, 2)) # (10+2j)也可以将数字转换为十六进制数。
print(hex(11)) # 0xb▍47、在列表的第一个位置添加一个值
如果使用append(),将从列表的最后一个位置插入新值。
可以通过使用insert(),来指定插入新元素的索引和数值。
那么列表的第一个位置为0,即下标为0。
my_list = [3, 4, 5]my_list.append(6)
my_list.insert(0, 2)
print(my_list) # [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
▍48、Lambda函数只能在一行代码中
无法通过多行代码,来使用lambda函数。
comparison = lambda x: if x > 3:print("x > 3")else:print("x is not greater than 3")报错。

▍49、Lambda中的条件语句应始终包含else语句
comparison = lambda x: "x > 3" if x > 3运行上面的代码,报错。
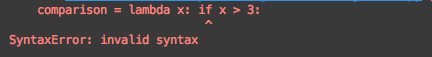
这是由于条件表达式的特性,而不是lambda的导致的。
▍50、使用filter(),获得一个新对象
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4]odd = filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 1, my_list)print(list(odd)) # [1, 3]
print(my_list) # [1, 2, 3, 4]▍51、map()返回一个新对象
map()函数将给定函数应用于可迭代对象(列表、元组等),然后返回结果(map对象)。
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4]squared = map(lambda x: x ** 2, my_list)print(list(squared)) # [1, 4, 9, 16]
print(my_list) # [1, 2, 3, 4]▍52、range()的step参数
for number in range(1, 10, 3):print(number, end=" ")
# 1 4 7
▍53、range()默认从0开始
def range_with_zero(number):for i in range(0, number):print(i, end=' ')def range_with_no_zero(number):for i in range(number):print(i, end=' ')range_with_zero(3) # 0 1 2
range_with_no_zero(3) # 0 1 2
▍54、不需要和0比较长度
如果长度大于0,则默认为True。
def get_element_with_comparison(my_list):if len(my_list) > 0:return my_list[0]def get_first_element(my_list):if len(my_list):return my_list[0]elements = [1, 2, 3, 4]
first_result = get_element_with_comparison(elements)
second_result = get_element_with_comparison(elements)print(first_result == second_result) # True
▍55、可以在同一个作用域内多次定义一个方法
但是,只有最后一个会被调用,覆盖以前。
def get_address():return "First address"def get_address():return "Second address"def get_address():return "Third address"print(get_address()) # Third address▍56、在外部直接访问私有属性
在定义属性或方法时,在属性名或者方法名前增加两个下划线,定义的就是私有属性或方法。
如果想要在外部访问,那么只需要在名称前面加上 '_类名' 变成 '_类名__名称'。
class Engineer:def __init__(self, name):self.name = nameself.__starting_salary = 62000dain = Engineer('Dain')
print(dain._Engineer__starting_salary) # 62000
▍57、检查对象的内存使用情况
import sysprint(sys.getsizeof("bitcoin")) # 56
▍58、定义一个方法,可以调用任意个参数
def get_sum(*arguments):result = 0for i in arguments:result += ireturn resultprint(get_sum(1, 2, 3)) # 6
print(get_sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)) # 15
print(get_sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)) # 28▍59、使用super()或父类的名称调用父类的初始化
使用super函数调用父类的初始化方法。
class Parent:def __init__(self, city, address):self.city = cityself.address = addressclass Child(Parent):def __init__(self, city, address, university):super().__init__(city, address)self.university = universitychild = Child('Peking University', 'Fudan University', 'Tsinghua University')
print(child.university) # Tsinghua University使用父类的名称调用父类。
class Parent:def __init__(self, city, address):self.city = cityself.address = addressclass Child(Parent):def __init__(self, city, address, university):Parent.__init__(self, city, address)self.university = universitychild = Child('Peking University', 'Fudan University', 'Tsinghua University')
print(child.university) # Tsinghua University▍60、在类中使用 + 操作符
在两个int数据类型之间使用 + 运算符时,将得到它们的和。
而在两个字符串数据类型之间使用它时,会将其合并。
print(10 + 1) # 两数相加
print('first' + 'second') # 字符串相加
这个就是操作符重载,你还可以在类中使用(__add__)。
class Expenses:def __init__(self, rent, groceries):self.rent = rentself.groceries = groceriesdef __add__(self, other):return Expenses(self.rent + other.rent,self.groceries + other.groceries)april_expenses = Expenses(1000, 200)
may_expenses = Expenses(1000, 300)total_expenses = april_expenses + may_expenses
print(total_expenses.rent) # 2000
print(total_expenses.groceries) # 500▍61、在类中使用 < 和 == 操作符
下面定义一个操作重载示例( < 操作符),使用__lt__方法。
class Game:def __init__(self, score):self.score = scoredef __lt__(self, other):return self.score < other.scorefirst = Game(1)
second = Game(2)print(first < second) # True同样的,== 操作符使用__eq__方法。
class Journey:def __init__(self, location, destination, duration):self.location = locationself.destination = destinationself.duration = durationdef __eq__(self, other):return ((self.location == other.location) and(self.destination == other.destination) and(self.duration == other.duration))first = Journey('Location A', 'Destination A', '30min')
second = Journey('Location B', 'Destination B', '30min')print(first == second)还有一些其他的定义。
__sub__() for -
__mul__() for *
__truediv__() for /
__ne__() for !=
__ge__() for >=
__gt__() for >
▍62、为类的对象定义自定义的可打印版本
class Rectangle:def __init__(self, a, b):self.a = aself.b = bdef __repr__(self):return repr('Rectangle with area=' + str(self.a * self.b))print(Rectangle(3, 4)) # 'Rectangle with area=12'
▍63、交换字符串中字符的大小写
string = "This is just a sentence."
result = string.swapcase()print(result) # tHIS IS JUST A SENTENCE.
▍64、检查字符串是否都是空格
string = " "
result = string.isspace()print(result) # True▍65、检查字符串是否都是字母或数字
name = "Password"
print(name.isalnum()) # Truename = "Secure Password "
print(name.isalnum()) # Falsename = "S3cur3P4ssw0rd"
print(name.isalnum()) # Truename = "133"
print(name.isalnum()) # True
▍66、检查字符串是否都是字母
string = "Name"
print(string.isalpha()) # Truestring = "Firstname Lastname"
print(string.isalpha()) # Falsestring = "P4ssw0rd"
print(string.isalpha()) # False
▍67、根据参数删除字符
从右侧开始。
string = "This is a sentence with "
print(string.rstrip()) # "This is a sentence with"string = "this here is a sentence…..,,,,aaaaasd"
print(string.rstrip(".,dsa")) # "this here is a sentence"同样的,左侧也能操作。
string = "ffffffffFirst"
print(string.lstrip("f")) # First
▍68、检查字符串是否为数字
string = "seven"
print(string.isdigit()) # Falsestring = "1337"
print(string.isdigit()) # Truestring = "5a"
print(string.isdigit()) # Falsestring = "2**5"
print(string.isdigit()) # False
▍69、检查字符串是否为中文数字
# 42673
string = "四二六七三"print(string.isdigit()) # False
print(string.isnumeric()) # True▍70、检查字符串是否所有单词都是大写开头
string = "This is a sentence"
print(string.istitle()) # Falsestring = "10 Python Tips"
print(string.istitle()) # Truestring = "How to Print A String in Python"
# False
print(string.istitle())string = "PYTHON"
print(string.istitle()) # False
▍71、在元组中使用负索引
numbers = (1, 2, 3, 4)print(numbers[-1]) # 4
print(numbers[-4]) # 1
▍72、在元组中嵌套列表和元组
mixed_tuple = (("a"*10, 3, 4), ['first', 'second', 'third'])print(mixed_tuple[1]) # ['first', 'second', 'third']
print(mixed_tuple[0]) # ('aaaaaaaaaa', 3, 4)
▍73、快速统计元素在列表中出现的次数
names = ["Besim", "Albert", "Besim", "Fisnik", "Meriton"]print(names.count("Besim")) # 2
▍74、使用slice()获取元素
使用slice()获取最后n个元素。
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
slicing = slice(-4, None)
print(my_list[slicing]) # [4, 5, 6]print(my_list[-3]) # 4使用slice()做切片任务。
string = "Data Science"slice_object = slice(5, None)
print(string[slice_object]) # Science▍75、计算元素在元组中出现的次数
my_tuple = ('a', 1, 'f', 'a', 5, 'a')print(my_tuple.count('a')) # 3
▍76、获取元组中元素的索引
my_tuple = ('a', 1, 'f', 'a', 5, 'a')print(my_tuple.index('f')) # 2
▍77、步进获得元组
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)print(my_tuple[::3]) # (1, 4, 7, 10)
▍78、通过索引获取子元组
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)print(my_tuple[3:]) # (4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
▍79、将列表、集合、字典中所有元素删除
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4]
my_list.clear()
print(my_list) # []my_set = {1, 2, 3}
my_set.clear()
print(my_set) # set()my_dict = {"a": 1, "b": 2}
my_dict.clear()
print(my_dict) # {}
▍80、合并集合
使用union()方法,返回一个新集合。
first_set = {4, 5, 6}
second_set = {1, 2, 3}print(first_set.union(second_set)) # {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}还可以使用update()方法,将第二个集合的元素插入到第一个集合中去。
first_set = {4, 5, 6}
second_set = {1, 2, 3}first_set.update(second_set)print(first_set) # {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
▍81、在函数里输出结果
def is_positive(number):print("Positive" if number > 0 else "Negative") # Positiveis_positive(-3)
▍82、if语句中的多个条件
math_points = 51
biology_points = 78
physics_points = 56
history_points = 72my_conditions = [math_points > 50, biology_points > 50,physics_points > 50, history_points > 50]if all(my_conditions):print("Congratulations! You have passed all of the exams.")
else:print("I am sorry, but it seems that you have to repeat at least one exam.")
# Congratulations! You have passed all of the exams.
▍83、在一个if语句中,至少满足多个条件中的一个
math_points = 40
biology_points = 78
physics_points = 56
history_points = 72my_conditions = [math_points > 50, biology_points > 50,physics_points > 50, history_points > 50]if any(my_conditions):print("Congratulations! You have passed all of the exams.")
else:print("I am sorry, but it seems that you have to repeat at least one exam.")
# Congratulations! You have passed all of the exams.▍84、任何非空字符串都为True
print(bool("Non empty")) # True
print(bool("")) # False
▍85、任何非空列表、元组、字典都为True
print(bool([])) # False
print(bool(set([]))) # Falseprint(bool({})) # False
print(bool({"a": 1})) # True
▍86、None、False、0都为False
print(bool(False)) # False
print(bool(None)) # False
print(bool(0)) # False
▍87、在函数中使用全局变量
在函数无法直接修改全局变量的值。
string = "string"def do_nothing():string = "inside a method"do_nothing()print(string) # string可通过修饰符global,修改全局变量的值。
string = "string"def do_nothing():global stringstring = "inside a method"do_nothing()print(string) # inside a method▍88、计算字符串或列表中元素的数量
使用collections中的Counter计算字符串或列表中元素的数量。
from collections import Counterresult = Counter("Banana")
print(result) # Counter({'a': 3, 'n': 2, 'B': 1})result = Counter([1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 1, 6])
print(result) # Counter({1: 5, 2: 1, 3: 1, 4: 1, 5: 1, 6: 1})
▍89、检查2个字符串是否为相同
可以使用Counter()方法。
from collections import Counterdef check_if_anagram(first_string, second_string):first_string = first_string.lower()second_string = second_string.lower()return Counter(first_string) == Counter(second_string)print(check_if_anagram('testinG', 'Testing')) # True
print(check_if_anagram('Here', 'Rehe')) # True
print(check_if_anagram('Know', 'Now')) # False可以使用sorted()方法。
def check_if_anagram(first_word, second_word):first_word = first_word.lower()second_word = second_word.lower()return sorted(first_word) == sorted(second_word)print(check_if_anagram("testinG", "Testing")) # True
print(check_if_anagram("Here", "Rehe")) # True
print(check_if_anagram("Know", "Now")) # False
▍90、使用itertools中的count计算元素的数量
from itertools import countmy_vowels = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u', 'A', 'E', 'I', 'O', 'U']current_counter = count()string = "This is just a sentence."for i in string:if i in my_vowels:print(f"Current vowel: {i}")print(f"Number of vowels found so far: {next(current_counter)}")输出如下。
Current vowel: i
Number of vowels found so far: 0
Current vowel: i
Number of vowels found so far: 1
Current vowel: u
Number of vowels found so far: 2
Current vowel: a
Number of vowels found so far: 3
Current vowel: e
Number of vowels found so far: 4
Current vowel: e
Number of vowels found so far: 5
Current vowel: e
Number of vowels found so far: 6
▍91、对字符串或列表的元素进行次数排序
collections模块的Counter(),默认情况下是不会根据元素的频率对它们进行排序的。
from collections import Counterresult = Counter([1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 2, 2])
print(result) # Counter({2: 5, 1: 1, 3: 1})
print(result.most_common()) # [(2, 5), (1, 1), (3, 1)]map()函数将给定函数应用于可迭代对象(列表、元组等),然后返回结果(map对象)。
▍92、查找列表中出现频率最高的元素
my_list = ['1', 1, 0, 'a', 'b', 2, 'a', 'c', 'a']print(max(set(my_list), key=my_list.count)) # a
▍93、copy()和deepcopy()的区别
浅拷贝: 拷贝父对象,但是不会拷贝对象的内部的子对象。
深拷贝: 拷贝父对象. 以及其内部的子对象。
下面是一个copy()的例子。
first_list = [[1, 2, 3], ['a', 'b', 'c']]second_list = first_list.copy()first_list[0][2] = 831print(first_list) # [[1, 2, 831], ['a', 'b', 'c']]
print(second_list) # [[1, 2, 831], ['a', 'b', 'c']]这里是一个deepcopy()的例子。
import copyfirst_list = [[1, 2, 3], ['a', 'b', 'c']]second_list = copy.deepcopy(first_list)first_list[0][2] = 831print(first_list) # [[1, 2, 831], ['a', 'b', 'c']]
print(second_list) # [[1, 2, 3], ['a', 'b', 'c']]
▍94、访问字典中不存在的键时,避免报错
如果你想访问字典一个不存在的键,代码会报错。
my_dictonary = {"name": "Name", "surname": "Surname"}
print(my_dictonary["age"]) 错误如下。
KeyError: 'age'可以通过使用defaultdict(),代码将不会报错。
from collections import defaultdictmy_dictonary = defaultdict(str)
my_dictonary['name'] = "Name"
my_dictonary['surname'] = "Surname"print(my_dictonary["age"])
▍95、构建迭代器
class OddNumbers:def __iter__(self):self.a = 1return selfdef __next__(self):x = self.aself.a += 2return xodd_numbers_object = OddNumbers()
iterator = iter(odd_numbers_object)print(next(iterator)) # 1
print(next(iterator)) # 3
print(next(iterator)) # 5
▍96、删除列表的重复项
my_set = set([1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(list(my_set)) # [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
▍97、打印模块的安装位置
import pandasprint(pandas) # <module 'torch' from '/Users/...'
▍98、使用not in检查一个值是否在列表中
odd_numbers = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
even_numbers = []for i in range(9):if i not in odd_numbers:even_numbers.append(i)print(even_numbers) # [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
▍99、sort()和sorted()的区别
sort():对原始列表进行排序
sorted():返回一个新的排序列表
groceries = ['milk', 'bread', 'tea']new_groceries = sorted(groceries)
# new_groceries = ['bread', 'milk', 'tea']print(new_groceries)# groceries = ['milk', 'bread', 'tea']
print(groceries)groceries.sort()# groceries = ['bread', 'milk', 'tea']
print(groceries)
▍100、使用uuid模块生成唯一ID
UUID代表唯一标识符。
import uuid# 根据主机ID、序列号和当前时间生成UUID
print(uuid.uuid1()) # 308490b6-afe4-11eb-95f7-0c4de9a0c5af# 生成一个随机UUID
print(uuid.uuid4()) # 93bc700b-253e-4081-a358-24b60591076a

相关文章:

一款基jquery超炫的动画导航菜单
今天给大家分享一款基jquery超炫的动画导航菜单。这款导航菜单,初始时页面中间一个按钮,单击按钮,菜单从左侧飞入页中。再次单击按钮,导航飞入左侧消息。动画效果很非常炫。一起看下效果图: 在线预览 源码下载 实现的…

如何用C#动态编译、执行代码
在开始之前,先熟悉几个类及部分属性、方法:CSharpCodeProvider、ICodeCompiler、CompilerParameters、CompilerResults、Assembly。 一、CSharpCodeProvider 提供对C#代码生成器和代码编译器的实例的访问。如果要动态生成VB代码,可…

【解决】MySql 5.6 运行崩溃错误
【解决】MySql 5.6 运行崩溃错误 最近弄了一台云主机,配置是20G磁盘空间,1G运行内存的Linux服务器。在上面安装了LAMP(RHEL7.2Apache2.4MySql5.6PHP5.6),然后搭建wordpress网站,可是网站运行没多久…

制作安全网站的checklist
原作者charlee、原始链接 http://tech.idv2.com/2008/04/19/secure-website-checklist/ fcicq最近在IPA上看到一篇安全相关的文章,它的最末尾有个checklist,于是催我把它翻译了。前几天比较忙,周末没什么事儿了,就翻译一下吧。 原…

百变冰冰!手把手教你实现CVPR2021最新妆容迁移算法
作者:小潘师兄来源:AI算法与图像处理简介在本文中,我们从不同的角度将妆容迁移问题分解为两步提取-分配过程。为此,我们提出了一种基于风格的可控GAN模型,该模型由三个部分组成,每个部分分别对应于目标风格…

Vlan 4096的限制原因
为什么80%的码农都做不了架构师?>>> VLAN配置的最大可能值为4094,它的由来如下所述: IEEE802.1q协议也就是“Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks”(虚拟桥接局域网,简称虚拟局域网)协议&#…

Hive 数据模型
Hive 数据模型 Hive 数据表有五种类型:内部表,外部表,分区表,桶表,视图表,默认以 tab 分隔 * MySQL (Oracle) 表默认以逗号分隔,因此,要想导入 MySQL(Oracle) 数据,需要设…

完整中英文世界国家级联下拉列表插件【前端版】
为什么80%的码农都做不了架构师?>>> 这个小东西是之前小项目上临时增加功能的产物,那时候在网上找了很久都没有能用的插件,要么是数据残缺少得可怜,还有就是实现手段非常低效不可维护那种,各种奇拔问题&am…

何时使用margin和padding?
margin和padding的意义相信大家都很清楚,可是在具体应用中,到底应该使用哪一个,就比较难于判断了。 这篇文章 说得挺清楚的,在这里翻译一下,供参考。 何时应当使用margin 需要在border外侧添加空白时。 空白处不需要…

10年IT老兵给新人程序员的几点建议
【CSDN 编者按】对于很多计算机专业的同学而言,“进大厂”已经成为毕业后职业道路的首选。但是面试官最喜欢什么样的应届生你知道吗?在校期间应该为找工作做哪些准备?除了技术好,在职场中还有哪些必备软实力?今天&…

asp.net文件上传下载的简单实现
使用FileUpload上传: protected void btnUpload_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (FileUpload1.HasFile) { /*通过文件扩展名判断文件类型*/ string fileExt System.IO.Path.Ge…

JAVA数组的定义及用法
数组是有序数据的集合,数组中的每一个元素具有同样的数组名和下标来唯一地确定数组中的元素。 1. 一维数组 1.1 一维数组的定义 type arrayName[]; type[] arrayName; 当中类型(type)能够为Java中随意的数据类型,包含简单类型组合类型,数组名…

英特尔公布新技术路线图,将为 AWS、高通代工芯片
编译|刘春霖出品|AI科技大本营(ID:rgznai100)图源|IC photo今天英特尔宣布其旗下的工厂将开始制造高通芯片,并公布了公司有史以来最详细的制程工艺和封装技术路线图,希望在 2025 年前赶上台积电、三星电子。除了公布其近十多年来首个全新晶体管架构 Ribb…

epoll相关资料整理
http://www.cppblog.com/converse/archive/2008/10/13/63928.htmlepoll相关资料整理 学习epoll有一段时间了,最近终于有一个服务器采用了epoll模型,从中积累了一些epoll的资料.个人感觉目前可以找到的epoll相关的资料太少了,因为epoll仅被linux 2.6以上版本内核所支持,它的应用…

18.绝对路径和相对路径
什么是绝对路径(Absolute Pathname)? 1.绝对路径必定由“/”开头 2.绝对路径是为档案/文件的所在位置做指向 3.在任何时候,都可以用绝对路径来找到我们想要的文件 PS:绝对路径只对当前所在目录有效。 什么是相对路径&a…

IE的box模型显示bug
原作者charlee、原始链接http://tech.idv2.com/2007/01/02/ie-box-model-bug/以及本声明。 box模型即由<div>等块元素的 margin、padding、border、width、height 等属性构成的显示模型,它是CSS布局的基础。通过设置<div>的各种属性,可以得到…

AI 能匹敌程序员了吗?OpenAI 新研究展示 NLP 大模型的局限性
作者:Ben Dickson来源:数据实战派Codex在一篇新论文中,OpenAI 的研究人员展示了 Codex 的详细信息,它是一种生成软件源代码的深度学习模型。Codex 可以为 OpenAI 和 GitHub 联合开发的 “AI 配对程序员” 工具 Copilot 提供支持。…

MSLicensing中断远程桌面连接
---------------------------中断远程桌面连接---------------------------客户端无法建立跟远程计算机的连接。导致这个错误的可能的原因是:1) 远程计算机上的远程连接可能没有启用。2) 已超出远程计算机上的连接最大数。3) 建立连接时出现了一个网络错误。------------------…

如何恢复,迁移,添加, 删除 Voting Disks
如何恢复,迁移,添加, 删除 Voting Disks 恢复流程 在11gR2 之前,我们可以直接直接使用dd命令对voting disk进行备份。 DD示例 备份votedisk盘: [rootraw1 bin]# dd if/dev/raw/raw2 of/home/oracle/voting_disk.bak 恢复votedisk盘…

跨站脚本攻击(XSS)FAQ
原作者charlee、原始链接http://tech.idv2.com/2006/08/30/xss-faq/以及本声明。 该文章简单地介绍了XSS的基础知识及其危害和预防方法。Web开发人员的必读。译自 http://www.cgisecurity.com/articles/xss-faq.shtml。 简介 现在的网站包含大量的动态内容以提高用户体验&…

linux中的for命令
bash shell提供了for命令,用于创建通过一系列值重复的循环。每次重复使用系列中的一个值执行一个定义的命令集。for命令基本格式为:for var in listdo commandsdone1.读取列表中的值 #!/bin/bash #basic for command for test in a b c d e f doecho The…
终于有人把计算机视觉讲明白了 。。。
机器学习是目前比较热门的技术,包含深度学习、强化学习、对抗学习、对偶学习、迁移学习、分布式学习、以及元学习等内容。得益于大数据、大模型、大计算的发展,深度学习在计算机视觉、语音处理、自然语言方面相继取得了突破,达到甚至超过了人…
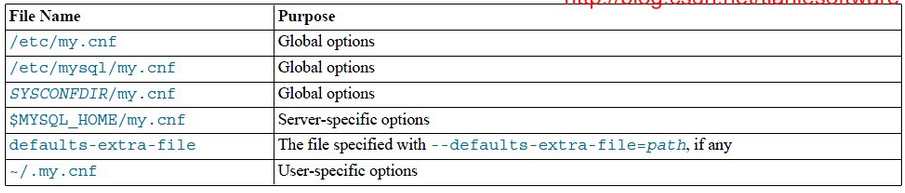
mysql启动与关闭(手动与自动)
手动管理mysql的启动与关闭 [rootmysql ~]# service mysql start --手动启动mysql Starting MySQL. SUCCESS! [rootmysql ~]# service mysql stop --手动关闭mysql Shutting down MySQL.. SUCCESS! [rootmysql ~]# mysqld --verbose --help --查看MySQL的默认参数的具体值 如果…

C#中抽象类和接口的区别
一、抽象类:抽象类是特殊的类,只是不能被实例化;除此以外,具有类的其他特性;重要的是抽象类可以包括抽象方法,这是普通类所不能的。抽象方法只能声明于抽象类中,且不包含任何实现,派…

echo向文件中写入
echo命令向一个文件写入内容的方法详解,感兴趣的朋友可以参考下。 覆盖型写法 (文件里原来的内容被覆盖)echo "aaa" > a.txtecho aaa > a.txt 添加型写法 (新内容添加在原来内容的后面)echo "aaa" >> a.txtecho aaa >…

火山引擎向企业客户开放上万款抖音同款特效
你喜爱的抖音特效,在其他平台上也能使用了。 7月28日,抖音联合火山引擎举办特效技术开放日,首次披露抖音特效的生产流程和技术原理。活动中,火山引擎宣布已向企业客户开放了上万款抖音同款特效,包括猴哥、漫画惊讶脸…

5.1 python的缩进
python 并不像其他语言一样要求以大括号来分辨逻辑,仅仅使用 tab 键(默认的四个空格)来区分代码。比如 ainput(Please input a num: ) b0 if int(a)>b: print(a>0) else: print(a<0) 返回结果:当输入小于0时,…

centOS 自动安装php
centos下安装php#yum install -y php这个只安装PHP建议安装运行库及MySQL的支持#yum install -y php php-devel php-mysql如果你的系统是CentOS 5.6那么上面这条命令安装的是PHP 5.1,要安装 PHP 5.3则执行下面的命令:#yum install -y php53 php53-devel php53-mysql自动安装启动…

strcpy_s与strcpy的比較
strcpy_s和strcpy()函数的功能差点儿是一样的。strcpy函数,就象gets函数一样,它没有方法来保证有效的缓冲区尺寸,所以它仅仅能假定缓冲足够大来容纳要拷贝的字符串。在程序执行时,这将导致不可预料的行为。用strcpy_s就能够避免这…
抖音发布特效数据报告:每五个投稿有一个使用特效
7月28日,抖音与火山引擎联合举办特效技术开放日,首次发布了《抖音特效数据报告》。报告显示,2021上半年 ,抖音平台平均每天上线超过100个新款特效;平均每五个投稿里,就有一个使用特效,特效已经成…
